20-F: Annual and transition report of foreign private issuers pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d)
Published on June 29, 2017
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 20-F
(Mark One)
|
o |
REGISTRATION STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OR (g) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
|
|
|
OR | |
|
|
|
|
x |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
|
|
|
OR | |
|
|
|
|
o |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
|
|
|
OR | |
|
|
|
|
o |
SHELL COMPANY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Date of event requiring this shell company report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 001-33910
|
ATA Inc. |
|
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter) |
|
|
|
Not applicable |
|
(Translation of Registrants name into English) |
|
|
|
Cayman Islands |
|
(Jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
|
|
|
1/F East Gate, Building No. 2, Jian Wai Soho, No. 39 Dong San Huan Zhong Road, Chao Yang District, Beijing 100022, China |
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
|
|
Amy Tung Chief Financial Officer ATA Inc. 1/F East Gate, Building No. 2, Jian Wai Soho, No. 39 Dong San Huan Zhong Road, Chao Yang District, Beijing 100022, China Telephone: 8610-6518-1122 Facsimile: 8610-5869-8106 |
|
(Name, Telephone E-mail and/or Facsimile Number and Address of Company Contact Person) |
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act.
|
Title of each class |
|
Name of each exchange on which |
|
American Depositary Shares, each representing two common shares, par value $0.01 per share |
|
NASDAQ Global Market |
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act. None
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act. None
Indicate the number of outstanding shares of each of the issuers classes of capital or common stock as of the close of the period covered by the annual report:
|
|
|
|
|
48,482,724 common shares. |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
o Yes x No
If this report is an annual or transaction report, indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
o Yes x No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
x Yes o No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
x Yes o No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of large accelerated filer, accelerated filer, and emerging growth company in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer o |
Accelerated filer o |
|
Non-accelerated filer x |
Emerging growth company o |
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
The term new or revised financial accounting standard refers to any update issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board to its Accounting Standards Codification after April 5, 2012.
Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
|
U.S. GAAP x |
|
International Financial Reporting Standards as issued |
|
Other o |
If Other has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow:
o Item 17 o Item 18
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
o Yes x No
|
|
Page |
|
1 | |
|
2 | |
|
3 | |
|
Item 1. Identity of Directors, Senior Management and Advisors |
3 |
|
3 | |
|
3 | |
|
37 | |
|
69 | |
|
70 | |
|
97 | |
|
110 | |
|
114 | |
|
115 | |
|
116 | |
|
Item 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
126 |
|
Item 12. Description of Securities Other Than Equity Securities |
128 |
|
131 | |
|
131 | |
|
Item 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds |
131 |
|
131 | |
|
134 | |
|
134 | |
|
134 | |
|
134 | |
|
Item 16D. Exemptions From the Listing Standards for Audit Committees |
135 |
|
Item 16E. Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers |
135 |
|
136 | |
|
136 | |
|
137 | |
|
138 | |
|
138 | |
|
138 | |
|
138 | |
|
S-1 |
Except where the context otherwise requires and for purposes of this annual report only:
· All references to years are to the calendar year from January 1 to December 31 and references to our fiscal year or years are to the fiscal year or years ended March 31. On June 1, 2017, our company declared a change in our fiscal year end from March 31 to December 31. We will file a transition report on Form 20-F after December 31, 2017 to account for the transition period from April 1, 2017 to December 31, 2017 to reflect this change. Going forward, all references to our fiscal year or years are to the fiscal year or years ended December 31;
· we, us, our company, our, and ATA refer to ATA Inc. and its subsidiaries as the context requires;
· China, Chinese and PRC refers to the Peoples Republic of China, excluding, for purposes of this annual report only, Taiwan and the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macau;
· all references to Renminbi or RMB are to the legal currency of China, and all references to U.S. dollars, dollars, $ or US$ are to the legal currency of the United States;
· U.S. GAAP refers to generally accepted accounting principles in the United States; and
· PRC GAAP refers to generally accepted accounting principles in the Peoples Republic of China.
This annual report on Form 20-F includes our audited consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 and audited consolidated balance sheets as of March 31, 2016 and 2017. Each of our ADSs represents two common shares. Our ADSs are listed on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol ATAI.
This annual report on Form 20-F contains forward-looking statements that are based on our current expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections about us and our industry. All statements other than statements of historical fact in this annual report are forward-looking statements. In some cases, these forward-looking statements can be identified by words and phrases such as may, should, intend, predict, potential, continue, will, expect, anticipate, estimate, plan, believe, is /are likely to or the negative form of these words and phrases or other comparable expressions. The forward-looking statements included in this annual report relate to, among others:
· our goals and strategies;
· our future prospects and market acceptance of our technologies, products and services;
· our future business development and results of operations;
· projected revenues, profits, earnings and other estimated financial information;
· our plans to expand and enhance our products and services;
· competition in the computer-based testing, educational services and online education markets; and
· Chinese laws, regulations and policies, including those applicable to the education industry, Internet content providers, Internet content and foreign exchange.
These forward-looking statements involve various risks, assumptions and uncertainties. Although we believe that our expectations expressed in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations may turn out to be incorrect. Our actual results could be materially different from our expectations. Important risks and factors that could cause our actual results to be materially different from our expectations are generally set forth in Item 3.D. of this annual report, Key information Risk Factors and elsewhere in this annual report.
The forward-looking statements made in this annual report relate only to events or information as of the date on which the statements are made in this annual report. All forward-looking statements included herein attributable to us or other parties or any person acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained or referred to in this section. Except to the extent required by applicable laws and regulations, we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which the statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
ITEM 1. IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISERS
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE
Not applicable.
A. Selected Financial Data
Selected Consolidated Financial Data
The following selected consolidated statement of comprehensive income (loss) data for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 (other than ADS data) and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of March 31, 2016 and 2017 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report and should be read in conjunction with such consolidated financial statements and related notes. Our selected consolidated statement of comprehensive income data for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2013 and 2014 (other than ADS data) and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of March 31, 2013, 2014 and 2015 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this annual report. The following information should also be read in conjunction with Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects. Our audited consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
2014 |
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
(In thousands, except for share and ADS data) |
| ||||||||||
|
Selected Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income (Loss) Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Testing services |
|
335,791 |
|
358,837 |
|
319,055 |
|
384,800 |
|
430,057 |
|
62,479 |
|
|
Online education services |
|
11,343 |
|
5,949 |
|
5,711 |
|
4,897 |
|
7,462 |
|
1,084 |
|
|
Other |
|
19,541 |
|
19,882 |
|
25,392 |
|
27,443 |
|
34,867 |
|
5,066 |
|
|
Total net revenues |
|
366,675 |
|
384,668 |
|
350,158 |
|
417,140 |
|
472,386 |
|
68,629 |
|
|
Gross profit |
|
177,844 |
|
196,188 |
|
177,619 |
|
209,123 |
|
232,533 |
|
33,783 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
150,830 |
|
154,809 |
|
147,938 |
|
157,388 |
|
161,026 |
|
23,394 |
|
|
Income from operations |
|
27,013 |
|
41,379 |
|
31,758 |
|
51,735 |
|
71,507 |
|
10,389 |
|
|
Share of losses of equity method investments |
|
|
|
|
|
(2,197 |
) |
(8,829 |
) |
(16,121 |
) |
(2,342 |
) |
|
Impairment loss of long-term investments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(32,199 |
) |
(4,678 |
) |
|
Income tax expense |
|
(7,005 |
) |
(19,895 |
) |
(9,575 |
) |
(18,922 |
) |
(38,597 |
) |
(5,607 |
) |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
23,208 |
|
27,276 |
|
23,056 |
|
26,051 |
|
(9,969 |
) |
(1,448 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(253 |
) |
(36 |
) |
|
Net income (loss) attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
23,208 |
|
27,276 |
|
23,056 |
|
26,051 |
|
(9,716 |
) |
(1,412 |
) |
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
2014 |
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) per common share |
|
0.50 |
|
0.59 |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
(0.03 |
) |
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
|
0.50 |
|
0.59 |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
(0.03 |
) |
|
Basic earnings (loss) per ADS (1) |
|
1.00 |
|
1.18 |
|
0.98 |
|
1.14 |
|
(0.42 |
) |
(0.06 |
) |
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per ADS (1) |
|
1.00 |
|
1.18 |
|
0.98 |
|
1.14 |
|
(0.42 |
) |
(0.06 |
) |
|
Dividends declared per common share |
|
0.554 |
|
|
|
1.260 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
44,967,823 |
|
45,227,159 |
|
45,597,580 |
|
45,635,186 |
|
45,772,916 |
|
|
|
|
Diluted |
|
45,115,617 |
|
45,231,555 |
|
45,597,580 |
|
45,635,186 |
|
45,772,916 |
|
|
|
(1) Each ADS represents two common shares.
|
|
|
As of March 31, |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
2014 |
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
| ||||||||||
|
Selected Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
290,030 |
|
311,947 |
|
240,295 |
|
247,668 |
|
222,448 |
|
32,318 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
51,115 |
|
68,353 |
|
48,150 |
|
50,552 |
|
56,161 |
|
8,159 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
354,770 |
|
398,093 |
|
312,951 |
|
316,488 |
|
295,945 |
|
42,995 |
|
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
4,358 |
|
|
Long term investments |
|
|
|
|
|
35,730 |
|
50,686 |
|
88,892 |
|
12,914 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
457,818 |
|
491,237 |
|
455,244 |
|
470,461 |
|
519,840 |
|
75,523 |
|
|
Deferred revenues, current |
|
7,377 |
|
8,383 |
|
21,743 |
|
16,612 |
|
10,222 |
|
1,485 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
79,568 |
|
77,149 |
|
76,158 |
|
74,352 |
|
103,030 |
|
14,968 |
|
|
Deferred income tax liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22,621 |
|
3,286 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
82,271 |
|
79,345 |
|
77,922 |
|
76,231 |
|
127,383 |
|
18,506 |
|
|
Common shares |
|
3,461 |
|
3,475 |
|
3,514 |
|
3,531 |
|
3,534 |
|
513 |
|
|
Retained earnings (accumulated deficit) |
|
(28,649 |
) |
(1,372 |
) |
21,684 |
|
47,735 |
|
38,019 |
|
5,523 |
|
|
Total shareholders equity attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
375,548 |
|
411,892 |
|
377,322 |
|
394,231 |
|
391,377 |
|
56,860 |
|
|
Non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,080 |
|
157 |
|
|
Total shareholders equity |
|
375,548 |
|
411,892 |
|
377,322 |
|
394,231 |
|
392,457 |
|
57,017 |
|
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
2014 |
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
Key Operating Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of tests delivered(1) |
|
9,266,581 |
|
9,688,210 |
|
8,821,781 |
|
10,380,175 |
|
12,213,205 |
|
(1) Includes free tests delivered for business development purpose. The number of tests delivered excluding free tests in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017 was 8,744,859, 9,411,226, 8,767,389, 10,258,866 and 12,127,203, respectively.
Exchange Rate Information
We conduct our business primarily in China and a substantial majority of our revenues and expenses are denominated in Renminbi. The conversion of Renminbi into U.S. dollars in this annual report is based on the noon buying rate in The City of New York for cable transfers of Renminbi per U.S. dollar certified for customs purposes by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, as set forth in the H.10 weekly statistical release of Federal Reserve Board. Unless otherwise noted, all translations from Renminbi to U.S. dollars in this annual report were made at a rate of RMB 6.8832 to US$1.00, which was the noon buying rate in effect as of March 31, 2017. The noon buying rate on June 22, 2017 was RMB 6.8275 to US$1.00. We make no representation that any Renminbi or U.S. dollar amounts could have been, or could be, converted into U.S. dollars or Renminbi, as the case may be, at any particular rate, the rates stated below, or at all. The Chinese government restricts or prohibits the conversion of Renminbi into foreign currency and foreign currency into Renminbi for certain types of transactions.
The following table sets forth information concerning exchange rates between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar for the periods indicated. These rates are provided solely for your convenience and are not necessarily the exchange rates that we used in this annual report.
|
|
|
Renminbi per U.S. Dollar Noon Buying Rate |
| ||||||
|
|
|
Average (1) |
|
High |
|
Low |
|
Period-end |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2013 |
|
6.2783 |
|
6.2105 |
|
6.3879 |
|
6.2108 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2014 |
|
6.1220 |
|
6.0402 |
|
6.2273 |
|
6.2164 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2015 |
|
6.1952 |
|
6.1107 |
|
6.2741 |
|
6.1990 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 |
|
6.3584 |
|
6.1927 |
|
6.5932 |
|
6.4480 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 |
|
6.7425 |
|
6.4571 |
|
6.9580 |
|
6.8832 |
|
|
Most recent six months: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 2016 |
|
6.9198 |
|
6.8771 |
|
6.9580 |
|
6.9430 |
|
|
January 2017 |
|
6.8907 |
|
6.8360 |
|
6.9575 |
|
6.8768 |
|
|
February 2017 |
|
6.8694 |
|
6.8517 |
|
6.8821 |
|
6.8665 |
|
|
March 2017 |
|
6.8940 |
|
6.8687 |
|
6.9132 |
|
6.8832 |
|
|
April 2017 |
|
6.8876 |
|
6.8778 |
|
6.8988 |
|
6.8900 |
|
|
May 2017 |
|
6.8843 |
|
6.8098 |
|
6.9060 |
|
6.8098 |
|
|
June 2017 (period through June 22, 2017) |
|
6.8063 |
|
6.7888 |
|
6.8285 |
|
6.8275 |
|
Source: H.10 weekly statistical release of the Federal Reserve Board
(1) Annual averages are calculated using the exchange rates for the last day of each month during the relevant year. Monthly averages are calculated using daily exchange rates during the relevant month.
B. Capitalization and Indebtedness
Not applicable.
C. Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds
Not applicable.
D. Risk Factors
Risks Relating to Our Business
A limited number of our clients have accounted for and are expected to continue to account for a high percentage of our revenues. The loss of or significant reduction in orders from any of these clients could significantly reduce our revenues and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our three largest clients in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, the Chinese Institute of Certified Public Accountants, or the CICPA, the Asset Management Association of China, or the AMAC, and the China Banking Association, or CBA, accounted for 19.1%, 18.6% and 11.8%, respectively, of our net revenues in that period. We provide both computer-based testing and test administration services to our three largest clients. We generated RMB 233.6 million ($33.9 million) from our services to CICPA, AMAC and CBA in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
As of March 31, 2017, our gross accounts receivable from CICPA, AMAC and CBA were RMB 0.5 million ($0.1 million), RMB 10.8 million ($1.6 million) and RMB 2.1 million ($0.3 million), respectively.
Due to our dependence on a limited number of clients, any one of the following events, among others, could cause material fluctuations or declines in our revenues and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations:
· a reduction, delay or cancellation of contracts or product or service orders from one or more of our major clients;
· a delay in paying or failure to pay outstanding accounts receivable;
· a decision by one or more of our major clients to award contracts or orders to one of our competitors; and
· a decision by one or more of our major clients to significantly reduce the price they are willing to pay for our services or products.
Any of these events could occur due to causes outside of our control, such as macro-economic conditions, changes in a clients management or the personnel with whom we interact, changes in technology, the actions of our competitors, changes in governmental regulations and policies and changes in a clients budgeting or financial prospects.
Our financial results are subject to fluctuations and seasonality related to the revenue cycles for our products and services. Our relatively long and unpredictable sales cycle and other factors beyond our control may decrease our revenues in a particular period. As a result, it is difficult for us to predict our results of operations and you should not rely on our historical operating results as an indication of our future financial performance.
Our results of operations have varied in the past from period to period, and are likely to vary in the future, due to the fact that a substantial portion of our sources of revenues are seasonal. We have experienced seasonality and expect in the future to continue to experience seasonality in net revenues and accounts receivable related to our test delivery services, with the quarters ending June 30 and December 31 typically having higher net revenues from testing services and the quarters ending September 30 and March 31 typically having lower net revenues from testing services. This is primarily because the tests from which we derive substantial revenues are mostly delivered in the quarters ending June 30 and December 31. Test timing can be a major contributing factor to quarterly fluctuations of financial results. For example, we generated revenues of RMB 273.5 million in the quarter ended December 31, 2016 as compared to RMB 65.1 million in the quarter ended September 30, 2016, primarily because one of our major test sponsors, CICPA, held tests during the third quarter of fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
In addition, our sales cycles are generally long and unpredictable. A clients decision to purchase our products and services often involves a lengthy evaluation process. Throughout the sales cycle, we often spend considerable time educating and providing information to prospective clients regarding the use and benefits of our products and services. Moreover, budget constraints and the need for multiple approvals within large enterprises, governmental agencies and educational institutions may also delay purchasing decisions. As a result, the sales cycle for our services may last a year or longer. Such a lengthy sales cycle, and any future increases in our sales cycle, could lead to higher sales and marketing expenses and adversely affect our cash flow from operations. In addition, the lengthy sales cycle has made, and may continue to make, our financial results prone to fluctuations or decrease our revenues in a particular period.
If our revenues for a particular quarter are lower than we expect, we may be unable to reduce our operating expenses for that quarter by a corresponding amount, which could negatively affect our operating results for that quarter. As a result, you should not rely on our quarter-to-quarter comparisons of our operating results as indicators of likely future performance. Our operating results may be below the expectations of public market analysts and investors in one or more future quarters. If that occurs, the market price of our ADSs could decline and you could lose part or all of your investment. Fluctuations of our quarterly financial results may also lead to increased volatility in the market price of our ADSs.
The market for our services in China is still emerging and evolving rapidly. If market acceptance of our services declines or fails to grow, our revenue growth may slow or we may experience a decrease in revenues.
As the market for our services in China is still emerging and evolving rapidly, our success will depend to a large extent on our ability to convince our clients that our technologies and services are valuable and that it is more cost-effective for them to utilize our services than for them to develop similar services in-house.
We must address the following concerns, among others, with our clients as they decide to implement our computer-based testing services to use our technologies and services:
· concern over the commitment of time, personnel and funding necessary to implement our computer-based testing services;
· ability of clients to develop their own computer-based testing services;
· possible perceived security and academic integrity risks associated with computer-based testing services and third-party curriculum providers; and
· reluctance of the academic community to adopt computer-based learning materials and computer-based tests.
A decline in the demand for computer-based testing services by test sponsors could negatively affect demand for our computer-based testing services and technologies. Even if demand for computer-based testing services continues to grow, this demand may not grow as quickly as we anticipate. If market acceptance of our services declines or fails to grow, our revenue growth may slow or we may experience a decrease in revenues.
The markets for our new service offerings are still new and unpredictable. If we cannot succeed in adapting to client needs in the new markets or effectively addressing risks associated with this expansion, our revenue growth may slow and our reputation may be negatively affected.
We have allocated, and intend to continue to allocate, time, effort and capital to expand our service offerings, and test-delivery systems, such as our proprietary mobile test administration platform called the Mobile Testing Service, or MTS, which we launched in 2013, and our new patented online testing platform, EzTest, which we launched in 2015. In November 2013, we completed our acquisition of Xing Wei Institute (Hong Kong) Limited, or Xing Wei, a private education technology company that provides training solutions as well as online and mobile training platforms for corporations in China, to expand our service offering with respect to training and consulting for corporations. In August 2014, we and the New Oriental Education & Technology Group formed a joint venture to provide online and mobile education solutions to growing base of professionals in China. In December 2014, we made a strategic investment in Master Mind Education Company, or Master Mind, which marks our expansion into Chinas K-12 education market. In January 2015, we made a strategic investment in Beijing Satech Internet Educational Technology Ltd., or Satech, which marks our expansion into SAT exam-related training market. With the aim of continuing to expand in the overseas education market, we subsequently increased our investment in Satech in April 2016. In September 2015, we made another strategic investment in Brilent Inc., or Brilent, which we expect to offer our clients with services that improve the effectiveness of selecting the most suitable individual for their job openings. To diversify our service offerings and explore further growth opportunities, we continued to make a number of strategic investments in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017. In April 2016, we made a strategic investment in Beijing Empower Education Online, Co., Ltd., or EEO, an online education company that operates web-based virtual classroom platforms in China, to further increase our business efforts in online learning and the K-12 education market. In May 2016, we made a strategic investment in Medicine (Beijing) Education Technology Ltd., a China-based online education technology company focused on providing training and exam preparation services in the specialty niche sectors of medicine, pharmacy and healthcare. In June 2016, we made a strategic investment in ApplySquare Education & Technology Co., Ltd., which signals our entry into the Chinese higher education market. In July 2016, we made a strategic investment in Beijing GlobalWisdom Information Technology Co., Ltd., through which we expect to explore growth opportunities in Chinas online language education market. In September 2016, we made a strategic investment in Beijing Puhua Huitong Education Technology Co., Limited to further increase our penetration into the adult continuing education market. In February 2017, we entered into a partnership with Nantong MOOC-CN Investment Center (Limited Partnership), or MOOC-CN Investment, pursuant to which MOOC-CN Investment agreed to make a strategic investment to help us expand into the K-12 education assessment market, with particular focus on the development of K-12 education assessment tools and content. In May 2017, we made an additional investment of RMB 5.5 million ($0.8 million) in EEO, while our equity interest in EEO remained unchanged. As the markets for these offerings are relatively new for us, we cannot assure you that we will succeed in adapting to client needs in these markets or effectively addressing risks associated with this expansion. In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, we recorded impairment loss of RMB 32.2 million ($4.7 million) related to these investments in certain companies providing K-12 related online education services, which failed to meet the expected milestones and operation forecasts and encountered shortage of working capital resulted from continuous negative operating cash flows.
It may be difficult for us to accurately predict demand for these and other new service offerings we develop. Furthermore, the PRC government may enact unforeseen regulations and policies that could limit our ability to provide or expand certain services, such as prohibitions on foreign-invested entities engaging in certain businesses. Additional risks that we face expanding in these markets include the following:
· we may underestimate the amount of capital, personnel and other resources required to carry out our expansion plans, which may affect the success of our expansion and/or negatively impact the quality of our other product and service offerings;
· if we are unsuccessful in the relevant new market, it may negatively affect our reputation and the status of our brand in other markets;
· we may fail to develop sufficient payment collection, technical support and other administrative capabilities necessary to successfully develop and manage our new service offerings on an increasingly large scale; and
· we have recorded impairment loss relating to certain strategic investments and may continue to incur additional impairment loss associated with our future investments which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
If we fail to maintain our relationship with major test sponsors, our revenue growth may slow or we may experience a decrease in revenues.
The success of our service offerings depends on our ability to gain and maintain relevant business relationships, such as our relationship with major test sponsors for computer-based tests in China, our relationship with the licensor of certain test titles, and our relationship with Saville Assessment in relation to psychometric tests for our HR Select employee assessment solution. Factors that are beyond our control may cause our relationship with relevant parties to change. For example, our exclusive Test of English for International Communication, or TOEIC distributor contract ended on February 28, 2014 due to ETS decision to change its distribution model. Although we are still a distributor and administrator of TOEIC exams in China and signed a non-exclusive distributor contract with ETS on June 23, 2014 (which was subsequently extended on January 20, 2017) to continue delivery of certain TOEIC exams to our existing institutional clients until December 31, 2019, we had lost a majority of the revenues generated from administering TOEIC exams due to contractual limitations on the scope of TOEIC exam services to selected market segments in China. If we fail to maintain our relationship with major test sponsors, our revenue growth may slow or we may experience a decrease in revenues.
Failure to comply with the regulations relating to information security and privacy protection, such as breaches or perceived breaches of our security measures relating to test collection, scoring and storage, unauthorized disclosure or misuse of personal data through breach of our computer systems or otherwise, could result in negative publicity and clients loss, expose us to protracted and costly litigation, and harm our business and results of operations.
The internet industry is facing significant challenges regarding information security and privacy protection, particularly with regard to the collection, storage, transmission and sharing of confidential information, among others. As part of our service offerings, we collect, process, transmit and store highly confidential information, including personal information and test questions, answers and scores. We are required under PRC law to maintain the security and confidentiality of the information we handle as part of our testing services, which is also essential to protecting the integrity and accuracy of the test taking process and retaining our client base. In December 2012, the Standing Committee of the PRC National Peoples Congress promulgated the Decision on Strengthening Network Information Protection, or the Network Information Protection Decision, to enhance the legal protection of information security and privacy on the internet. The Network Information Protection Decision specifically requires internet operators to take security measures to ensure confidentiality of information of users. We have adopted various security measures pertaining to the collection, processing, transmission or storage of user information. Any breach or perceived breach in our security measures as a result of third-party action, employee error, and malfeasance or otherwise, or any instances or claims of cheating on tests that we administer could result in liability claims and have a negative impact on our reputation.
The PRC regulatory and enforcement regime with regard to data security and data protection has also been evolving rapidly in recent years. On July 1, 2015, the National Peoples Congress Standing Committee promulgated the National Security Law, or the New National Security Law, which took effect on the same date and replaced the former National Security Law promulgated in 1993. Under the New National Security Law, we are obligated to safeguard national security by, for example, providing evidence related to activities endangering national security, providing convenience and assistance for national security work, and providing necessary support and assistance for national security institutions, public security institutions as well as military institutions. As such, we may have to provide data to the PRC government authorities and military institutions to ensure compliance with the New National Security Law. Complying with such regulations could cause us to incur substantial costs, require us to change our data practices in a manner adverse to our business, or even subject us to negative publicity which could harm our reputation with users and negatively affect our business operations and the trading price of our ADSs. In addition, in November 2016, the National Peoples Congress Standing Committee promulgated the Cyber Security Law, which took effect on June 1, 2017, to protect cyberspace security and order. The Cyber Security Law tightens control of cyber security and sets forth various security protection obligations for network operators. According to the Cyber Security Law, network operators shall, among others, take security measures to protect the network from unauthorized interference, damage and unauthorized access and prevent data from being divulged, stolen or tampered with. In case of any misuses of information collected from our clients or students or any unauthorized interference, damage, or unauthorized or inappropriate disclosure of such information due to our failure to protect it, we could be subject to negative publicity, liability claims or regulatory penalties. Any such negative publicity, liability claims or regulatory penalties could cause us to lose clients, expose us to costly litigation and have a material adverse impact on our business and results of operations.
If certain tests are not allowed to be administered in China due to cheating fears, our revenue growth may slow or we may experience a decrease in revenues.
We administered a number of international tests in China, such as TOEIC. In recent years, academic cheating has been frequently reported to occur in the international tests. These tests may be canceled by their owners due to cheating fears. If certain tests that we are administering are not allowed to be taken in China, our revenue growth may slow or we may experience a decrease in revenues.
Reductions in public funding available to our clients that are governmental agencies could adversely impact demand by these agencies and institutions for our products and services.
We derive a significant portion of our total net revenues from licensing and service fees from Chinese governmental agencies. Demand and ability to pay for our products and services by these agencies are affected by government budgetary cycles, funding availability and government policies. Funding reductions, reallocations or delays could adversely impact demand for our products and services by our clients or reduce the fees these clients are willing to pay for our products and services.
A significant portion of our revenues are dependent on market acceptance of our E-testing platform and other computer-based testing technologies, and if we are unable to anticipate and meet our clients technological needs and challenges from new technologies and industry standards, our products and services may lose market acceptance or become obsolete, and our margins and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Our advanced technologies for the creation and delivery of computer-based tests, including our E-testing platform and our performance-based testing technologies, are a key factor in growing and maintaining our relationships with test sponsors, educational institution clients and educational program content providers. Our future success depends on our ability to upgrade our systems, develop new technologies and anticipate and meet the technical needs of our clients on a regular basis. The emergence in the market of new test creation and delivery technologies or substitute products and services could reduce our competitiveness or render our current technologies and services obsolete. Moreover, if other companies develop similar technologies offering functionality comparable to that of our technologies, pricing pressure may increase and our margins and results of operations may be adversely affected. Additionally, industry standards such as standard interfaces and data exchange protocols may be developed for testing technologies, and if these industry standards are incompatible with our technologies, demand for our technologies, products and services may decline significantly. To the extent we are unable to maintain our market leadership position in key testing technologies or anticipate and respond to technological developments and changes in industry standards in a timely and cost-effective manner, our products and services may lose market acceptance or become obsolete.
Technical errors or failures in relation to computer-based tests delivered through our test delivery platform could result in negative publicity, loss of clients, liability claims and costly and disruptive litigation.
Due to the complexity of the technologies we use to create and deliver computer-based tests for our clients, technical errors or failures may occur in relation to these services. These may include errors, failures or bugs in our software applications and test security technologies, breakdowns or failures of our servers and computer networks, and connectivity failures between our networks. While we have not experienced major problems to date due to errors, breakdowns, failures, bugs or defects, we cannot assure you that we will not experience such problems in the future. If such a problem were to occur, it could disrupt or compromise the integrity of the test taking process or of test content and results, which could lead to negative publicity and loss of clients and may subject us to liability claims. Although we have established a formal crisis management system to respond to technical problems, it has never been tested in a real crisis situation. Any litigation or negative publicity resulting from an error or failure, with or without merit, could result in substantial costs and divert managements attention and resources from our business and operations.
If we fail to maintain a strong brand, our business may not grow and our financial results may be adversely impacted.
We believe that maintaining and enhancing the value of the ATA brand is important to attracting clients. Our success in maintaining brand awareness will depend on our ability to consistently provide high quality, value-adding, user-friendly and secure products and services. As we expand our product and service offerings, we are increasing our efforts to establish a wider recognition of the ATA brand. To establish a wider recognition of our ATA brand among test takers, test sponsors and companies, we may need to spend significant resources on advertising. As we have limited experience with advertising and other activities required to establish a widely recognized brand, we cannot assure you that we will effectively allocate our resources for these activities or succeed in maintaining and broadening our brand recognition and appeal. If we fail to maintain a strong brand, our business may not grow and our financial results may be adversely impacted.
Actions by our authorized test centers could lead to damage to our brand and reputation, which could cause us to incur substantial costs and strain our relationships with our clients.
As of March 31, 2017, we had contractual relationships with 3,147 authorized test centers. We do not own these centers and their employees are not our employees. Under our contracts with these test centers, we require them to provide sufficient facilities to properly administer computer-based tests and to follow prescribed guidelines for facility maintenance and test administration. We also conduct regular reviews of their facilities and operations and provide consulting services on test administration. However, our contractual arrangements with the test centers provide us with only limited ability to oversee their activities, and most test centers engage in other activities, such as serving as classrooms, when not administering tests. If a test center were to engage in unauthorized or unlawful conduct, whether related to administering computer-based tests or otherwise, our clients, prospective clients and the general public may associate this conduct with our brand, and negative publicity associated with this conduct could harm our reputation and lessen overall demand for computer-based testing services. Furthermore, our business may also be adversely affected if our authorized test centers do not maintain their premises, administer our computer-based tests, or hire qualified personnel and train them properly in a manner consistent with our standards and requirements. In addition, a liability claim against an ATA authorized test center or any center personnel may result in unfavorable publicity for us, our products and services and our other test centers, and could damage our brand and reputation, whether or not the claim is successful. While we may terminate our contracts and relationships with our authorized test centers if any of these events were to occur, we may not be able to identify problems or take action quickly enough to prevent harm to our reputation.
We depend on our key personnel and our business may be severely disrupted if we lose their services and are unable to replace them.
Our future success is dependent upon the continued services of our key executives, as we rely on their industry experience and expertise in our business operations. In particular, we rely heavily on Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, our chairman and chief executive officer for his business vision, management skills, technical expertise, experience in the testing, IT and education industries and working relationships with many of our clients, shareholders and other participants in the testing, IT and education industries. If Mr. Ma is unable or unwilling to continue in his present positions, or if he joined a competitor or formed a competing company in violation of his employment agreement, we may not be able to replace him easily and our business may be severely disrupted.
We may face increasing competition from international and domestic competitors. If we fail to successfully compete, our revenues and market share may decrease, and our results of operations may be adversely affected.
As our business and markets continue to expand, we will face increasing competition, including competition from new entrants, both domestic and international, who will try to gain market share from us. Competitors may introduce new technologies, products and services that have better performance, offer lower prices and gain broader acceptance than our technologies, products and services. Such new products may reduce the overall market for our products and services.
In the computer-based testing services market, we compete primarily on the basis of technology, price, management experience, established infrastructure, reputation and brand. In the future, as more companies enter this market, we believe pricing may become increasingly competitive as well. For our HR Select employee assessment solution, while there are other companies providing services to corporate human resources departments, we are differentiated by our focus on offering more professional testing services with proprietary testing technologies. Traditional Chinese test preparation material providers, such as publishing companies, indirectly compete with our online education services. Increased competition could cause us to lose clients or make it necessary for us to reduce our prices in order to retain our clients, which may negatively affect our revenues and results of operations.
We may not be able to attract and retain the highly skilled employees we need to support our planned growth.
Due to intense market competition for highly skilled workers, we have faced difficulties locating experienced and skilled personnel in certain areas, such as administration, marketing, product development, sales, finance and accounting. In particular, we have had difficulty finding personnel with experience in the computer-based testing services market. We cannot assure you that we will be able to attract or retain the key personnel that we will need to achieve our business objectives. Even if we can identify qualified candidates, they may be subject to non-competition agreements with their prior employers that prevent us from hiring them. In addition, we cannot assure you that we will be able to retain our current skilled personnel. According to our contracts with our employees, all of our employees are prohibited from engaging in any activities that compete with our business during the period of their employment and for two years after termination of their employment with us. Furthermore, all employees are prohibited, for a period of two years following termination, from soliciting other employees to leave us and, for a period of five years following termination, from soliciting our existing clients. However, we may have difficulty enforcing these non-competition and non-solicitation provisions in China because the Chinese legal system, especially with respect to the enforcement of such provisions, is still developing.
Many of our contracts with governmental agencies and public educational institutions take the form of framework agreements and offer little contractual or legal protections, and it may be impractical for us to pursue or obtain legal remedies against these clients.
Many governmental agencies and other public sector entities in China require the use of simple framework agreements for the procurement of products and services from us that lack many of the detailed aspects of our business arrangement. For example, the terms of service may lack the clarity we would normally have in our contracts with commercial enterprises, or contract terms protecting our intellectual property may not be as clear and detailed as we would normally have in our contracts with commercial enterprises. Moreover, it may not be feasible or practicable for us to take legal action against our government and public sector clients to enforce our contractual rights. As a result, we may lack the same contractual or legal protections, or ability to enforce such protections, that we would normally have under the contracts we typically enter into with our other clients.
Unauthorized use of our intellectual property by third parties, including infringement of our ATA brand, and the expenses incurred in protecting our intellectual property rights, may adversely affect our business.
Our copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, patents and other intellectual property are important to our success. In particular, we believe that our ATA brand name represents a valuable asset as we have sought to gain a reputation for high quality and secure testing services and advanced testing technologies within our markets. Unauthorized use of any of our intellectual property may adversely affect our business and reputation. We rely on trademark, patent, and copyright law, trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements with our employees, clients, business partners and others to protect our intellectual property rights. Nevertheless, it may be possible for third parties to obtain and use our intellectual property without authorization. The unauthorized use of intellectual property is common and widespread in China and enforcement of intellectual property rights by Chinese regulatory agencies is inconsistent. Moreover, litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce our intellectual property rights. Future litigation could result in substantial costs and diversion of our managements attention and resources, and could disrupt our business, as well as have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Given the relative unpredictability of Chinas legal system and potential difficulties enforcing a court judgment in China, there is no guarantee that we would be able to halt the unauthorized use of our intellectual property through litigation.
We may be subject to intellectual property infringement claims, which may force us to incur substantial legal expenses and, if determined adversely against us, may materially disrupt our business.
We cannot assure you that our business operations, in particular, our software, trademarks, know-how and other technologies do not or will not infringe upon patents, valid copyrights or other intellectual property rights held by third parties. We may become subject to legal proceedings and claims from time to time relating to the intellectual property of others in the ordinary course of our business. For example, we have been unable to register our ATA trademark with the China Trademark Office due to similarity with other marks. Although we have not received notice of trademark infringement claims since we began using the mark in 1999 and believe that the risk of litigation is remote, we may be subject to such claims in the future. If we are found to have violated the intellectual property rights of others, we may be enjoined from using such intellectual property, and we may incur licensing fees or be forced to develop alternatives. In addition, we may incur substantial expenses, and may be forced to divert management and other resources from our business operations, to defend against these third-party infringement claims, regardless of their merit. Successful infringement or licensing claims against us may result in substantial monetary liabilities or may materially disrupt the conduct of our business by restricting or prohibiting our use of the intellectual property in question.
Because there is limited business insurance coverage in China, any business disruption or litigation we experience might result in our incurring substantial costs and diverting significant resources to handle such disruption or litigation.
The insurance industry in China is not fully developed. Insurance companies in China offer limited business insurance products. While business disruption insurance may be available to a limited extent in China, we have determined that the risks of disruption and the difficulties and costs associated with acquiring such insurance render it commercially impractical for us to have such insurance. As a result, we do not have any business liability, disruption or litigation insurance coverage for our operations in China. Any business disruption or litigation might result in our incurring substantial costs and the diversion of resources.
We may face challenges and risks in connection with possible investments and acquisitions as well as forming joint ventures, including identifying suitable opportunities and integrating acquired or new businesses and assets with our existing operations, which could interrupt our business operations or adversely affect our results of operations.
As part of our business strategy, we may seek to broaden our service offerings, obtain additional clients and strengthen our service quality by acquiring other companies or businesses or making strategic investments. However, our ability to implement our acquisition or investment strategy will depend on a number of factors, including the availability of suitable acquisition candidates at an acceptable cost or at all, our ability to compete effectively to attract and reach agreement with acquisition or investment candidates or joint venture partners on commercially reasonable terms, and the availability of financing to complete acquisitions or investment or joint ventures as well as our ability to obtain any required government approvals or licenses. As such, the identification of suitable acquisition or investment targets or joint venture candidates and the consummation of proposed acquisition or investment or joint venture transactions could be difficult, time consuming and costly, and we may not be able to successfully capitalize on identified opportunities. In addition, we cannot assure you that any particular acquisition or investment or joint venture transaction will produce the intended benefits or synergies. For example, we recorded impairment loss of RMB 32.2 million (US$4.7 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 related to our investment in certain companies providing online education and K-12 related services. In addition, we may not be successful in integrating acquisitions with our existing operations and personnel. Moreover, the acquisitions or investment we pursue may require us to expend significant management and other resources, which may result in interruption to our business operations.
There are other risks associated with acquisitions, including:
· unforeseen or hidden liabilities, including exposure to legal proceedings, associated with newly acquired companies;
· failure to generate sufficient revenues to offset the costs and expenses of acquisitions;
· integration of the management of the acquired business into our own;
· potential impairment losses or amortization expenses relating to goodwill and intangible assets arising from any of such acquisitions, which may materially reduce our net income or result in a net loss;
· potential conflicts with our existing employees as a result of our integration of newly acquired companies; and
· possible contravention of Chinese regulations applicable to such acquisitions.
Furthermore, raising capital to finance acquisitions or investments could cause earnings or ownership dilution to your shareholding interests, which in turn could result in losses to you. Any one or a combination of the above risks could interrupt our business operations and adversely affect our results of operations.
The listing of the shares of our wholly-owned subsidiary ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd. or ATA Online, on stock exchanges in China may not provide the benefits we anticipate, and the listing could negatively impact holders of our ADSs.
To provide ATA Online with the ability and flexibility to raise funds from the PRC capital markets for business expansion, we restructured our testing services business and online education services into our wholly-owned subsidiary ATA Online and listed its shares on the National Equities Exchange and Quotations, an emerging over-the-counter market in China (the New Third Board) in December 2015.
The listing of the shares of ATA Online on the New Third Board may not realize the anticipated benefits of such listing, and ATA Onlines operation as a listed company may result in distraction of ATA management. Although ATA Online remains our consolidated subsidiary after the listing, the ownership interest of our ADS holders in the earnings of ATA Onlines operations could be diluted, depending on the amount of funds raised, the returns on that funds and the manner in which that funds is raised (debt or equity). In addition, volatility in the trading price of our ADSs may increase due to events more specifically impacting ATA Onlines share trading price and operations. Our influence over the election of ATA Onlines board of directors will be decreased if ATA Onlines shareholders appoint directors who are independent of ATA.
We may need additional capital and any failure by us to raise additional capital on terms favorable to us, or at all, could limit our ability to grow our business and develop or enhance our product and service offerings to respond to market demand or competitive challenges.
Capital requirements are difficult to plan in our rapidly changing industry. We believe that our current cash and expected future cash flows from operations will be sufficient to meet our anticipated working capital and capital expenditures for the next 12 months and the foreseeable future beyond that point. We may, however, require additional cash resources due to changed business conditions or other future developments, including any investments or acquisitions we may decide to pursue. If our sources of liquidity are insufficient to satisfy our cash requirements, we may seek to sell additional equity or debt securities or obtain a credit facility. The sale of additional equity securities could result in dilution to our shareholders. The incurrence of indebtedness would result in increased debt service obligations and could require us to agree to operating and financing covenants that would restrict our operations. Our ability to obtain additional capital on acceptable terms is subject to a variety of uncertainties, including:
· investors perception of, and demand for, securities of computer-based testing and education companies;
· conditions of the U.S., PRC and other capital markets in which we may seek to raise funds;
· our future results of operations and financial condition;
· Chinese government regulation of foreign investment in China;
· economic, political and other conditions in China; and
· Chinese government policies relating to the borrowing and remittance of foreign currency outside China.
We cannot assure you that financing will be available in amounts or on terms acceptable to us, if at all. Any failure by us to raise additional funds on terms favorable to us, or at all, could limit our ability to grow our business and develop or enhance our product and service offerings to respond to market demand or competitive challenges.
We may be unable to maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting, and as a result we may be unable to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud.
We are subject to provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires that we include a report from management on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting in our annual reports on Form 20-F. Our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting is effective as of March 31, 2017, and our independent registered public accounting firm reported on our internal controls over financial reporting. However, if we fail to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting in the future, our management and our independent registered public accounting firm may not be able to conclude that we have effective internal control over financial reporting at a reasonable assurance level. Our failure to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting could result in a loss of investor confidence in the reliability of our reporting processes, which could materially and adversely affect the trading price of our ADSs.
Our reporting obligations as a public company will continue to place a significant strain on our management, operational and financial resources and systems for the foreseeable future. Our failure to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting could result in the loss of investor confidence in the reliability of our financial reporting processes, which in turn could harm our business and negatively impact the trading price of our ADSs.
Our independent registered public accounting firms audit documentation related to their audit reports included in this annual report may include audit documentation located in China. The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board currently cannot inspect audit documentation located in China and, as such, you may be deprived of the benefits of such inspection.
Our independent registered public accounting firm that issues the audit reports included in our annual reports filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, as auditors of companies that are traded publicly in the United States and a firm registered with the U.S. Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), or the PCAOB, is required by the laws of the United States to undergo regular inspections by the PCAOB to assess its compliance with the laws of the United States and professional standards. However, audit documentations located in China are not currently inspected by the PCAOB because the PCAOB is currently unable to conduct inspections without the approval of the PRC authorities.
Inspections conducted by the PCAOB outside of China have identified deficiencies in those firms audit procedures and quality control procedures, which may be addressed as part of the inspection process to improve future audit quality. The lack of PCAOB inspections in China prevents the PCAOB from regularly evaluating audit documentation located in China and its related quality control procedures. As a result, investors may be deprived of the benefits of PCAOB inspections.
The inability of the PCAOB to conduct inspections in China makes it more difficult to evaluate the effectiveness of our auditors audit procedures or quality control procedures as compared to audits outside of China that are subject to PCAOB inspections. Investors may lose confidence in our reported financial information and procedures and the quality of our financial statements.
Our independent registered public accounting firm may be temporarily suspended from practicing before the SEC if unable to continue to satisfy the SEC investigation requests in the future. If a delay in completion of our audit process occurs as a result, we could be unable to timely file certain reports with the SEC, which may lead to the delisting of our stock.
On January 22, 2014, Judge Cameron Elliot, an SEC administrative law judge, issued an initial decision suspending the Chinese member firms of the Big Four accounting firms, including our independent registered public accounting firm, from practicing before the SEC for six months. In February 2014, the initial decision was appealed. While under appeal and in February 2015, the Chinese member firms of the Big Four accounting firms reached a settlement with the SEC. As part of the settlement, each of the Chinese member firms of Big Four accounting firms agreed to settlement terms that include a censure, undertakings to make a payment to the SEC, procedures and undertakings as to future requests for documents by the SEC, and possible additional proceedings and remedies should those undertakings not be adhered to.
If the settlement terms are not adhered to, our independent registered public accounting firm may be suspended from practicing before the SEC which could in turn delay the timely filing of our financial statements with the SEC. In addition, it could be difficult for us to timely identify and engage another qualified independent registered public accounting firm to replace our current one. A delinquency in our filings with the SEC may result in NASDAQ initiating investigation procedures, which could adversely harm our reputation and have other material adverse effects on our overall growth and prospects.
We may be classified as a passive foreign investment company, which could result in adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. holders of our ADSs or common shares.
We believe that we were not a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes for our taxable year ended March 31, 2017, and we do not expect to be a PFIC in any future taxable year. However, PFIC status is tested each year and depends on the composition of our assets and income and the value of our assets from time to time. Since we currently hold, and expect to continue to hold, a substantial amount of cash and other passive assets and, since the value of our assets is to be determined in large part by reference to the market prices of our ADSs and common shares, which is likely to fluctuate over time, there can be no assurance that we will not be a PFIC for any future taxable year. If we are a PFIC for any taxable year during which a U.S. investor held our ADSs or common shares, certain adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences would apply to the U.S. investor. See Item 10. Additional Information E. Taxation United States Federal Income Taxation Passive Foreign Investment Company.
Risks Relating to Regulation of Our Business
If the China Securities Regulatory Commission, or CSRC, or another PRC regulatory agency determines that CSRC approval was required in connection with our initial public offering, we may become subject to penalties.
On August 8, 2006, six PRC regulatory agencies, including the CSRC, promulgated the Provisions Regarding Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors, or the M&A Rule, which became effective on September 8, 2006. The M&A Rule, among other things, requires that an offshore company controlled by PRC companies or individuals that has acquired a PRC domestic company for the purpose of listing the PRC domestic companys equity interest on an overseas stock exchange must obtain the approval of the CSRC prior to the listing and trading of such offshore companys securities on an overseas stock exchange. On September 21, 2006 the CSRC, pursuant to the M&A Rule, published on its official web site procedures specifying documents and materials required to be submitted to it by offshore companies seeking CSRC approval of their overseas listings.
Our PRC counsel, Jincheng Tongda & Neal Law Firm, advised us that CSRC approval was not required for our initial public offering in February 2008 because the CSRC approval required under the M&A Rule only applies to an offshore company that has acquired a domestic PRC company for the purpose of listing the domestic PRC companys equity interest on an overseas stock exchange, while (i) we obtained our equity interest in each of our PRC subsidiaries by means of direct investment other than by acquisition of the equity or assets of a PRC domestic company in 2008, (ii) our former contractual arrangements with ATA Online (please see Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party TransactionsB. Related Party Transactions. for more details) do not constitute the acquisition of ATA Online, (iii) the M&A Rule does not apply to the acquisition by ATA Learning, a wholly foreign owned enterprise, and (iv) although Article 11 of the M&A Rule prohibits the circumvention of the M&A Rule through establishing FIEs, ATA Learning was established in 2003 before the M&A Rule was promulgated, which makes this acquisition not a circumvention of the M&A Rule. However, if it is determined that CSRC approval was required, we may face regulatory actions or other sanctions from the CSRC or other PRC regulatory agencies. These regulatory agencies may impose fines and penalties on our operations in China, limit our operating privileges in China, or take other actions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, reputation and prospects, as well as the trading price of our ADSs.
Because we may rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our current and future Chinese subsidiaries for our cash requirements, restrictions under Chinese law on their ability to make such payments could materially and adversely affect our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could benefit our business, pay dividends to you, and otherwise fund and conduct our businesses.
We have adopted a holding company structure, and our holding companies may rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our current and future Chinese subsidiaries for their cash requirements, including the funds necessary to service any debt we may incur or financing we may need for operations other than through our Chinese subsidiaries. Chinese legal restrictions permit payments of dividends by our Chinese subsidiaries only out of their accumulated after-tax profits, if any, determined in accordance with PRC GAAP. Our Chinese subsidiaries are also required under Chinese laws and regulations to allocate at least 10% of their after-tax profits determined in accordance with PRC GAAP to statutory reserves until such reserves reach 50% of the companys registered capital. Allocations to these statutory reserves and funds can only be used for specific purposes and are not transferable to us in the form of loans, advances or cash dividends. As of March 31, 2017, our Chinese subsidiaries allocated RMB 55.2 million ($8.0 million) to the general reserve fund, which is restricted for distribution to the Company. We are in full compliance with PRC laws and regulations relating to such allocations. Any limitations on the ability of our Chinese subsidiaries to transfer funds to us could materially and adversely limit our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could be beneficial to our business, pay dividends and otherwise fund and conduct our business.
The discontinuation of any of the preferential tax treatments currently enjoyed by our subsidiaries in the PRC could materially increase our tax obligations.
Effective from January 1, 2008, the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, or EIT Law, imposes a tax rate of 25% on all enterprises, including foreign-invested enterprises, and terminates many of the tax exemptions, reductions and preferential treatments available under previous tax laws. However, enterprises that were established before March 16, 2007 and already enjoyed preferential tax treatments may continue to enjoy them (i) in the case of certain preferential tax rates that are specified by tax legislations for a transition period of five years from January 1, 2008 or (ii) in the case of tax exemption or reduction for a specified term, until the expiration of such term.
Under the EIT Law, qualified high-and-new technology enterprises eligible for key support from the State (HNTE) are entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15%, subject to an annual review during the valid period of their HNTE certificates. In December 2008, ATA Testing Authority (Beijing) Limited, or ATA Testing, was recognized as a HNTE and obtained its HNTE certificate, which entitled ATA Testing to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2008 to 2010. In October 2011, ATA Testing successfully renewed its HNTE certificate for another three years from 2011 and therefore it is entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2011 to 2013. In October 2014, ATA Testing successfully renewed its HNTE certificate for another three years from 2014 and therefore it is entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2014 to 2016. ATA Testing is currently in the process of re-applying for its HNTE certificate for another three years. Upon successful re-application, ATA Testing should be entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% retroactively from January 1, 2017. In December 2009, each of ATA Learning, ATA Online, and ATA Learning Data & Technology (Beijing) Limited (ATA Data, formerly known as Beijing Jindixin Software Technology Limited, or Beijing JDX), received an approval from the tax authority that it qualified as an HNTE for three years, entitling them to a preferential income tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2009 to 2011. From May 2012 to July 2012, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data successfully renewed their HNTE certificates, respectively, for another three years from 2012 and therefore are entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2012 to 2014. In November 2015, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data successfully renewed their HNTE certificates, for another three years from 2015 and therefore are entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2015 to 2017. We cannot assure you that ATA Testing, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data will continue to qualify as an HNTE after the expiration of their HNTE certificates, or that the local tax authorities will not, in the future, change their position and revoke any of our past preferential tax treatments.
The discontinuation of any of our preferential tax treatments could materially increase our tax obligations and adversely affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
Under the EIT Law, we may be classified as a resident enterprise of China. Such classification will likely result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and U.S. holders of our ADSs or common shares.
Under the EIT Law, an enterprise established outside of China with its de facto management body in China is considered a resident enterprise, meaning that it can be treated the same as a Chinese enterprise for enterprise income tax purposes. In addition, a tax circular, or Circular 82, issued by the State Administration of Taxation, or the SAT on April 22, 2009 regarding the standards used to classify certain Chinese controlled enterprises established outside of China as resident enterprises clarified that dividends and other income paid by such resident enterprises will be considered to be PRC source income, subject to PRC withholding tax currently at a rate of 10%, when paid to non-PRC enterprise shareholders. Circular 82 also subjects such resident enterprises to various reporting requirements with the PRC tax authorities. Under the Implementation Rules to the EIT Law, a de facto management body is defined as a body that exercises substantial and overall management and control over the manufacturing and business operations, personnel, and human resources, finances and properties of an enterprise. In addition, Circular 82 details that certain Chinese-controlled enterprises will be classified as resident enterprises if the following are located or resident in China: senior management personnel and departments that are responsible for daily production, operation and management; financial and personnel decision making bodies; key properties, accounting books, company seal, and minutes of board meetings and shareholders meetings; and half or more of the senior management or directors having voting rights.
Currently, a substantial majority of the members of our management team as well as the management team of some of our offshore holding companies are located in China. However, Circular 82 only applies to offshore enterprises controlled by PRC enterprises or PRC enterprise groups, not those controlled by PRC individuals or foreign entities like us. In the absence of detailed implementing regulations or other guidance determining that offshore companies controlled by PRC individuals or foreign entities like us are PRC resident enterprises, we do not currently consider our Company or any of our overseas subsidiaries to be a PRC resident enterprise.
However, the SAT may take the view that the determining criteria set forth in Circular 82 reflects the general position on how the de facto management body test should be applied in determining the tax resident status of all offshore enterprises. Or additional implementing regulations or guidance may be issued determining that our Cayman Islands holding company is a resident enterprise for PRC enterprise income tax purposes. If the PRC tax authorities determine that our Cayman Islands holding company is a resident enterprise for PRC enterprise income tax purposes, a number of unfavorable PRC tax consequences could follow. First, we will be subject to enterprise income tax at a rate of 25% on our worldwide income as well as PRC enterprise income tax reporting obligations. This would mean that income such as interest on offering proceeds and other non-China source income would be subject to PRC enterprise income tax at a rate of 25%, in comparison to no taxation in the Cayman Islands. Second, although under the EIT Law and its implementing rules dividends paid to us by our PRC subsidiaries would qualify as tax-exempt income, we cannot guarantee that such dividends will not be subject to a 10% withholding tax, as the PRC foreign exchange control authorities, which enforce the withholding tax, have not yet issued guidance with respect to the processing of outbound remittances to entities that are treated as resident enterprises for PRC enterprise income tax purposes. Finally, a 10% withholding tax will be imposed on dividends we pay to our non-PRC enterprise shareholders, and future guidance may extend the withholding tax to dividends we pay to our non-PRC individual shareholders and gains derived by our non-PRC shareholders from transferring our ADSs or common shares. Similar results would follow if our BVI holding company is considered a PRC resident enterprise. In addition to the uncertainty in how the new resident enterprise classification could apply, it is also possible that the rules may change in the future, possibly with retroactive effect. We are closely monitoring the development of this area of rules and are evaluating appropriate arrangements of our management activity to avoid being classified as a PRC resident enterprise.
Chinas regulation of loans and direct investments by offshore holding companies to their Chinese subsidiaries may restrict our ability to execute our business strategy.
In order to execute our business strategy, we must invest the funds in our Chinese subsidiaries through loans or capital contributions. Under applicable Chinese laws, any loan made by us to ATA Testing or ATA Learning, both of which are foreign-invested enterprises, cannot exceed statutory limits tied to each companys registered capital and total investment as approved by the Ministry of Commerce or its local counterpart, and all such loans must be registered with Chinas State Administration of Foreign Exchange, or SAFE, or its local counterpart. Loans by us to ATA Online, as a domestic PRC enterprise, must be approved by the relevant government authority and must also be registered with SAFE. We may also decide to finance ATA Learning and ATA Testing by increasing their registered capital through capital contributions. Any capital contributions to ATA Learning and ATA Testing must be filed with the Ministry of Commerce or its local counterpart. SAFE promulgated the Circular of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Reforming the Management Approach regarding the Settlement of Foreign Exchange Capital of Foreign-invested Enterprises, or SAFE Circular 19, on March 30, 2015. According to the SAFE Circular 19, a foreign-invested enterprise will be able to convert foreign exchange in its capital account into RMB at any time. In order to use the converted RMB, the foreign-invested enterprise still needs to provide supporting documents and go through the review process with the banks. A failure by us to obtain the necessary government approvals or complete any required registrations or other procedures for a capital contribution, an increase in approved total investment or a loan on a timely basis, may restrict our ability to execute our business strategy.
In June 2016, SAFE promulgated the Notice of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Reforming and Standardizing the Administrative Provisions on Capital Account Foreign Exchange Settlement, or SAFE Circular No. 16, which removed certain restrictions previously provided under several SAFE circulars, including the Notice of the General Affairs Department of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on the Relevant Operating Issues concerning the Improvement of the Administration of Payment and Settlement of Foreign Currency Capital of Foreign-invested Enterprises, or SAFE Circular No. 142, in respect of conversion by a foreign-invested enterprise of foreign currency registered capital into RMB and use of such RMB capital. However, SAFE Circular No. 16 continues to prohibit foreign-invested enterprises from, among other things, using RMB fund converted from its foreign exchange capitals for expenditure beyond its business scope, and providing loans to non-affiliated enterprises except as permitted in the business scope.
A failure by our shareholders who are Chinese citizens or residents in China to comply with regulations issued by SAFE could restrict our ability to distribute profits, restrict our overseas and cross-border investment activities or subject us to liability under Chinese laws, which could adversely affect our business and prospects.
SAFE promulgated the Circular on Relevant Issues Concerning Foreign Exchange Control on Domestic Residents Offshore Investment and Financing and Roundtrip Investment through Special Purpose Vehicles, or SAFE Circular 37, on July 4, 2014. SAFE Circular 37 requires PRC residents to register with local branches of SAFE in connection with their direct establishment or indirect control of an offshore entity, for the purpose of overseas investment and financing, with such PRC residents legally owned assets or equity interests in domestic enterprises or offshore assets or interests, referred to in SAFE Circular 37 as a special purpose vehicle. SAFE Circular 37 further requires amendment to the registration in the event of any significant changes with respect to the special purpose vehicle, such as increase or decrease of capital contributed by PRC individuals, share transfer or exchange, merger, division or other material event. In the event that a PRC shareholder holding interests in a special purpose vehicle fails to fulfill the required SAFE registration, the PRC subsidiaries of that special purpose vehicle may be prohibited from making profit distributions to the offshore parent and from carrying out subsequent cross-border foreign exchange activities, and the special purpose vehicle may be restricted in its ability to contribute additional capital into its PRC subsidiary. Moreover, failure to comply with the various SAFE registration requirements described above could result in liability under PRC law for evasion of foreign exchange controls.
Our significant shareholder, Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, has completed his registration with SAFE, and we have urged our other Chinese resident shareholders to register under SAFE Circular 37 and they are currently in the application process. However, we cannot assure you that their applications will be accepted by SAFE. Failure by such shareholders to comply with SAFE Circular 37 could subject us to fines or legal sanctions, restrict our overseas or cross-border investment activities, limit our subsidiaries ability to make distributions or pay dividends or affect our ownership structure, which could adversely affect our business and prospects. See Item 3.D. Key Information Risk Factors Risks Relating to Regulation of Our Business Because we may rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our current and future Chinese subsidiaries for our cash requirements, restrictions under Chinese law on their ability to make such payments could materially and adversely affect our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could benefit our business, pay dividends to you, and otherwise fund and conduct our businesses.
Furthermore, as there is uncertainty concerning the reconciliation of these SAFE regulations with other approval requirements, it is unclear how these regulations, and any future regulation concerning offshore or cross-border transactions, will be interpreted, amended and implemented by the relevant government authorities. We cannot predict how these regulations will affect our business operations or future strategy. For example, we may be subject to a more stringent review and approval process with respect to our foreign exchange activities, such as remittance of dividends and foreign currency-denominated borrowings, which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. In addition, if we decide to acquire a PRC domestic company, we cannot assure you that we or the owners of such company, as the case may be, will be able to obtain the necessary approvals or complete the necessary filings and registrations required by the foreign exchange regulations. This may restrict our ability to implement our acquisition strategy and could adversely affect our business and prospects.
We may be subject to fines and legal sanctions imposed by SAFE or other Chinese government authorities if we or our Chinese employees fail to comply with Chinese regulations relating to employee share options granted by offshore listed companies to Chinese citizens.
Under applicable PRC regulations, Chinese citizens who are granted share options by an offshore listed company are required, through a Chinese agent, which can be a Chinese branch or representative of the offshore listed company, a Chinese institution which has controlling relationship or actual control relationship with the offshore listed company or a Chinese institution qualified for asset custody business, to register with the SAFE and complete certain other procedures, including applications for foreign exchange payment quotas and opening special bank accounts. We and our Chinese employees who have been granted share options are subject to such PRC regulations. If we or our Chinese employees fail to comply with these regulations, we or our Chinese employees may be subject to fines and legal sanctions imposed by the SAFE or other Chinese government authorities, which may prevent us from further granting options under our share incentive plans to our employees. Such events could adversely affect our business operations. See Item 4.B. Information on the Company Business overview Regulations SAFE Regulations on Employee Share Options.
Risks Relating to Doing Business in the Peoples Republic of China
Chinas economic, political and social conditions, as well as changes in any government policies, laws and regulations, could adversely affect the overall economy in China or the prospects of the industries in which we operate, which in turn could reduce our net revenues.
Substantially all of our operations are conducted in China. Accordingly, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects are subject, to a significant extent, to economic, political and social developments in China.
The Chinese economy differs from the economies of most developed countries in many respects, including the amount of government involvement, level of development, growth rate, control of foreign exchange and allocation of resources. Although the Chinese economy has been transitioning from a planned economy to a more market-oriented economy since the late 1970s, the Chinese government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. The Chinese government also exercises significant control over Chinas economic growth through the allocation of resources, controlling the incurrence and payment of foreign currency-denominated obligations, setting monetary policy and providing preferential treatment to particular industries or companies. Changes in any of these policies, laws and regulations could adversely affect the overall economy in China or the prospects of the industries in which we operate, which could harm our business.
Chinas social and political conditions are also not as stable as those of the United States and other developed countries. Any sudden changes to Chinas political system or the occurrence of widespread social unrest could have negative effects on our business and results of operations. In addition, China has contentious relations with some of its neighbors, most notably Taiwan. A significant further deterioration in such relations could have negative effects on the Chinese economy and lead to changes in governmental policies that would be adverse to our business interests.
The Chinese legal system has inherent uncertainties that could limit the legal protections available to you and us.
Unlike common law systems, the Chinese legal system is based on written statutes and decided legal cases have little precedential value. Since 1979, the Chinese government has promulgated a comprehensive system of laws and regulations governing economic matters in general. The overall effect of legislation since then has been to significantly enhance the protections afforded to various forms of foreign investment in China. Our Chinese operating subsidiaries, ATA Learning and ATA Testing, are wholly foreign-owned enterprises, which are enterprises incorporated in China and wholly-owned by foreign investors, and are subject to laws and regulations applicable to foreign investment in China in general and laws and regulations applicable to wholly foreign-owned enterprises in particular. Our Chinese operating subsidiary, ATA Online, is subject to laws and regulations governing the formation and conduct of domestic PRC companies. Relevant Chinese laws, regulations and legal requirements may change frequently, and their interpretation and enforcement involve uncertainties. In addition, we may have to resort to administrative and court proceedings to enforce the legal protection that we enjoy either by law or contract. However, since Chinese administrative and court authorities have significant discretion in interpreting and implementing statutory and contractual terms, it may be more difficult to evaluate the outcome of administrative and court proceedings and the level of legal protection we enjoy than in more developed legal systems. Such uncertainties, including the inability to enforce our contracts and intellectual property rights, could materially and adversely affect our business and operations. Accordingly, we cannot predict the effect of future developments in the Chinese legal system, particularly with regard to the computer-based testing services sectors, including the promulgation of new laws, changes to existing laws or the interpretation or enforcement thereof, or the preemption of local regulations by national laws. These uncertainties could limit the legal protections available to us and other foreign investors, including you.
Restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to utilize our revenues effectively and the ability of our Chinese subsidiaries to obtain financing.
A substantial majority of our revenues and operating expenses are denominated in Renminbi. Restrictions on currency exchange imposed by the Chinese government may limit our ability to utilize revenues generated in Renminbi to fund our business activities outside China, if any, or expenditures denominated in foreign currencies. Under current Chinese regulations, Renminbi may be freely converted into foreign currency for payments relating to current account transactions, which include among other things dividend payments and payments for the import of goods and services, by complying with certain procedural requirements. Revenues generated in the PRC can be converted into foreign currency to pay salaries of employees located outside of the PRC upon the employee completing registration procedures. Revenues generated in the PRC can also be used to pay off debt generated outside of the PRC, provided that the Company completes relevant foreign debt registration or approval requirements. Although the Renminbi has been fully convertible for current account transactions since 1996, we cannot assure you that the relevant Chinese government authorities will not limit or eliminate our ability to purchase and retain foreign currencies for current account transactions in the future.
Conversion of Renminbi into foreign currencies and of foreign currencies into Renminbi for payments relating to capital account transactions, which include among other things investments, loans and acquisitions of land and other fixed assets overseas, generally requires the approval of SAFE and other relevant Chinese governmental authorities. Restrictions on the convertibility of the Renminbi for capital account transactions could affect the ability of our Chinese subsidiaries to make investments overseas or to obtain foreign exchange through debt or equity financing, including by means of loans or capital contributions from us.
Fluctuations in exchange rates could result in foreign currency exchange losses.
Because substantially all of our revenues and expenditures are denominated in Renminbi, fluctuations in the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and Renminbi will affect our balance sheet and earnings per share in U.S. dollars. In addition, appreciation or depreciation in the value of the Renminbi relative to the U.S. dollar would affect our financial results reported in U.S. dollar terms without giving effect to any underlying change in our business or results of operations. Fluctuations in the exchange rate will also affect the relative value of any dividend we issue that will be exchanged into U.S. dollars and earnings from and the value of any U.S. dollar-denominated investments we make in the future.
The value of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar and other currencies is affected by, among other things, changes in Chinas political and economic conditions and Chinas foreign exchange policies. The Peoples Bank of China regularly intervenes in the foreign exchange market to limit fluctuations in Renminbi exchange rates and achieve policy goals. Very limited hedging transactions are available in China to reduce our exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. To date, we have not entered into any hedging transactions in an effort to reduce our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. While we may decide to enter into hedging transactions in the future, the availability and effectiveness of these hedging transactions may be limited and we may not be able to successfully hedge our exposure at all. In addition, our currency exchange losses may be magnified by Chinese exchange control regulations that restrict our ability to convert Renminbi into foreign currency.
Any future outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome or avian flu in China, or similar adverse public health developments, may disrupt our business and operations.
Our business and operations could be materially and adversely affected by the outbreak of avian influenza, severe acute respiratory syndrome, or SARS, or other similar adverse public health developments. In recent years, there have been reports on the occurrences of avian influenza in various parts of China and neighboring countries, including confirmed human cases. Any prolonged adverse public health development may result in health or other government authorities requiring the closure of our offices or the offices of our clients, or the cancellation of exams or classes to avoid students and others from congregating in closed spaces. Such occurrences would disrupt our business operations and adversely affect our results of operations. We have not adopted any written preventive measures or contingency plans to combat any future outbreak of avian flu, SARS or any other epidemic.
Risks Relating to Our ADSs
Our ADS price and the ADS or stock prices of other technology companies with business operations primarily in China, have fluctuated widely in recent years, which could result in substantial losses to investors.
The trading prices of our ADSs are volatile, and this volatility may continue. For instance, between April 1, 2016 and June 5, 2017, our ADS price as reported on Nasdaq ranged between a low of $2.96 and a high of $6.91. Numerous factors that are beyond our control may cause the market price of our ADSs to fluctuate significantly. In particular, the performance and fluctuation of the market prices of other technology companies with business operations mainly in China that have listed their securities in the United States may affect the volatility in the price of and trading volumes for our ADSs. The trading performances of these Chinese companies securities at the time of or after their offerings may affect the overall investor sentiment towards Chinese companies listed in the United States and consequently may impact the trading performance of our ADSs. These broad market and industry factors may significantly affect the market price and volatility of our ADSs, regardless of our actual operating performance.
In addition to market and industry factors, the price and trading volume for our ADSs may be highly volatile for specific business reasons. Factors such as variations in our revenues, earnings and cash flow, announcements of new investments, cooperation arrangements or acquisitions, and fluctuations in market prices for our services could cause the market price for our ADSs to change substantially. Any of these factors may result in large and sudden changes in the volume and price at which our ADSs will trade. We cannot give any assurance that these factors will not occur in the future.
Although publicly traded, the trading market in our ADSs has been substantially less liquid than the ADSs or stock of many companies quoted on the Nasdaq Global Market, and this low trading volume may adversely affect the price of our ADSs.
Although our ADSs are traded on the Nasdaq Global Market, the trading volume of our ADSs has generally been very low. Reported average daily trading volume of our ADSs for the three-month period ended May 31, 2017 was approximately 17,176 ADSs. Limited trading volume will subject our ADSs to greater price volatility and may make it difficult for our shareholders to sell their ADSs at a price that is attractive to them, if at all.
The sale or availability for sale of substantial amounts of our ADSs could adversely affect their market price.
Sales of substantial amounts of our ADSs in the public market or the perception that these sales could occur, could adversely affect the market price of our ADSs and could materially impair our future ability to raise capital through offerings of our ADSs.
As of June 22, 2017, there were 48,436,886 common shares outstanding. In addition, there were outstanding options to purchase an aggregate of 2,451,067 common shares, including options to purchase an aggregate of 916,337 common shares immediately exercisable as of June 22, 2017. All of the ADSs sold in our initial public offering are freely tradable without restriction or further registration under the U.S. Securities Act of 1933, or the Securities Act, unless held by our affiliates as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act. Subject to applicable restrictions and limitations under Rule 144 of the Securities Act of 1933, all of our shares outstanding as of the date of this annual report are eligible for sale in the public market. In addition, the common shares subject to options for the purchase of our common shares will become eligible for sale in the public market to the extent permitted by the provisions of various vesting agreements, and Rules 144 and 701 under the Securities Act of 1933. If these additional shares are sold, or if it is perceived that they will be sold in the public market, the trading price of our common shares could decline.
A significant percentage of our outstanding common shares are held by a small number of our existing shareholders, and these shareholders may have significantly greater influence on us and our corporate actions by nature of the size of their shareholdings relative to our public shareholders.
One of our existing shareholders, Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, beneficially owns approximately 50.0% of our outstanding common shares as of June 22, 2017. Accordingly, Mr. Ma has had, and may continue to have, significant influence in determining the outcome of any corporate transaction or other matter submitted to the shareholders for approval, including mergers, consolidations and the sale of all or substantially all of our assets, election of directors and other significant corporate actions. In addition, without the consent of Mr. Ma, we could be prevented from entering into transactions that could be beneficial to us.
Anti-takeover provisions in our organizational documents may discourage our acquisition by a third party, which could limit your opportunity to sell your shares at a premium.
Our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association include provisions that could limit the ability of others to acquire control of us, modify our structure or cause us to engage in change of control transactions, including, among other things, the following:
· provisions that provide for a staggered board which operates to prevent a third party from obtaining control of our board in a relatively short period of time because at least two annual shareholders meetings, instead of one, would generally be required to effect a change in majority of the board.
· provisions that restrict the ability of our shareholders to call meetings and to propose special matters for consideration at shareholder meetings; and
· provisions that authorize our board of directors, without action by our shareholders, to issue preferred shares and to issue additional common shares, including common shares represented by ADSs.
These provisions could have the effect of depriving you of an opportunity to sell your ADSs at a premium over prevailing market prices by discouraging third parties from seeking to acquire control of us in a tender offer or similar transactions.
The voting rights of holders of ADSs must be exercised in accordance with the terms of the deposit agreement, the ADRs, and the procedures established by the depositary. The process of voting through the depositary may involve delays that limit the time available to you to consider proposed shareholders actions and also may restrict your ability to subsequently revise your voting instructions.
A holder of ADSs may exercise its voting rights with respect to the underlying common shares only in accordance with the provisions of the deposit agreement and the ADRs. We do not recognize holders of ADSs representing our common shares as our shareholders, and instead we recognize the ADS depositary as our shareholder.
When the depositary receives from us notice of any shareholders meeting, it will distribute the information in the meeting notice and any proxy solicitation materials to you. The depositary will determine the record date for distributing these materials, and only ADS holders registered with the depositary on that record date will, subject to applicable laws, be entitled to instruct the depositary to vote the underlying common shares. The depositary will also determine and inform you of the manner for you to give your voting instructions, including instructions to give discretionary proxies to a person designated by us. Upon receipt of voting instructions of a holder of ADSs, the depositary will endeavor to vote the underlying common shares in accordance with these instructions. You may not receive sufficient notice of a shareholders meeting for you to withdraw your common shares and cast your vote with respect to any proposed resolution, as a holder of our common shares. In addition, the depositary and its agents may not be able to send materials relating to the meeting and voting instruction forms to you, or to carry out your voting instructions, in a timely manner. We cannot assure you that you will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that you can instruct the depositary to vote your shares. The additional time required for the depositary to receive from us and distribute to you meeting notices and materials, and for you to give voting instructions to the depositary with respect to the underlying common shares, will result in your having less time to consider meeting notices and materials than holders of common shares who receive such notices and materials directly from us and who vote their common shares directly. If you have given your voting instructions to the depositary and subsequently decide to change those instructions, you may not be able to do so in time for the depositary to vote in accordance with your revised instructions. The depositary and its agents will not be responsible for any failure to carry out any instructions to vote, for the manner in which any vote is cast or for the effect of any such vote.
Except in limited circumstances, the depositary for our ADSs will give us a discretionary proxy to vote our common shares underlying your ADSs if you do not vote at shareholders meetings, which could adversely affect your interests.
Under the deposit agreement for the ADSs, the depositary will give us a discretionary proxy to vote our common shares underlying your ADSs at shareholders meetings if you do not vote, unless we notify the depositary that:
· we do not wish to receive a discretionary proxy;
· we think there is substantial shareholder opposition to the particular question; or
· we think the subject of the particular question would have a material adverse impact on our shareholders.
The effect of this discretionary proxy is that, absent the situations described above, you cannot prevent our common shares underlying your ADSs from being voted and it may make it more difficult for shareholders to influence the management of our company. Holders of our common shares are not subject to this discretionary proxy.
You may not receive distributions on our common shares or any value for them if such distribution is illegal or if any required government approval cannot be obtained in order to make such distribution available to you.
The depositary of our ADSs has agreed to pay to you the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian for our ADSs receives on our common shares or other deposited securities after deducting its fees and expenses. You will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of our common shares your ADSs represent. However, the depositary is not responsible to make a distribution available to any holders of ADSs if it decides that it is unlawful to make such distribution. For example, it would be unlawful to make a distribution to a holder of ADSs if it consisted of securities that required registration under the Securities Act but that were not properly registered or distributed pursuant to an applicable exemption from registration. The depositary is not responsible for making a distribution available to any holders of ADSs if any government approval or registration required for such distribution cannot be obtained after reasonable efforts made by the depositary. We have no obligation to take any other action to permit the distribution of our ADSs, common shares, rights or anything else to holders of our ADSs. This means that you may not receive the distributions we make on our common shares or any value for them if it is unlawful or unreasonable from a regulatory perspective for us to make them available to you. These restrictions may have a material adverse effect on the value of your ADSs.
You may be subject to limitations on transfer of your ADSs.
Your ADSs represented by ADRs are transferable on the books of the depositary. However, the depositary may close its books at any time or from time to time when it deems expedient in connection with the performance of its duties. The depositary may close its books from time to time for a number of reasons, including in connection with corporate events such as a rights offering, during which time the depositary needs to maintain an exact number of ADS holders on its books for a specified period. The depositary may also close its books in emergencies, and on weekends and public holidays. The depositary may refuse to deliver, transfer or register transfers of our ADSs generally when the books of the depositary are closed, or at any time if we or the depositary thinks it is advisable to do so because of any requirement of law or any government or government body, or under any provision of the deposit agreement, or for any other reason.
We are a Cayman Islands company and, because judicial precedent regarding the rights of shareholders is more limited under Cayman Islands law than under U.S. federal or state laws, you may have less protection of your shareholder rights than you would under U.S. federal or state laws.
Our corporate affairs are governed by our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association, the Cayman Islands Companies Law and the common law of the Cayman Islands. The rights of shareholders to take action against the directors, actions by minority shareholders and the fiduciary responsibilities of our directors to us under Cayman Islands law are to a large extent governed by the common law of the Cayman Islands. The common law of the Cayman Islands is derived in part from comparatively limited judicial precedent in the Cayman Islands as well as from English common law, which has persuasive, but not binding, authority on a court in the Cayman Islands. The rights of our shareholders and the fiduciary responsibilities of our directors under Cayman Islands law are not as clearly established as they would be under statutes or judicial precedent in some jurisdictions in the United States. In particular, the Cayman Islands has a less developed body of securities laws than the United States. In addition, some jurisdictions, such as Delaware, have more fully developed and judicially interpreted bodies of corporate law than the Cayman Islands. As a result of all of the above, public shareholders may have more difficulty in protecting their interests in the face of actions taken by management, members of the board of directors or controlling shareholders than they would as public shareholders of a U.S. company.
Certain judgments obtained against us by our shareholders may not be enforceable.
We are a Cayman Islands company and substantially all of our assets are located outside of the United States. Nearly all of our current operations are conducted in China. In addition, most of our directors and officers are nationals and residents of countries other than the United States. A substantial portion of the assets of these persons are located outside the United States. As a result, it may be difficult for you to effect service of process within the United States upon these persons. It may also be difficult for you to enforce in U.S. court judgments obtained in U.S. courts based on the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws against us and our officers and directors, none of whom is resident in the United States and the substantial majority of whose assets is located outside of the United States. In addition, there is uncertainty as to whether the courts of the Cayman Islands or China would recognize or enforce judgments of U.S. courts against us or such persons predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state. In addition, there is uncertainty as to whether such Cayman Islands or Chinese courts would be competent to hear original actions brought in the Cayman Islands or China against us or such persons predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state.
Your right to participate in any future rights offerings may be limited, which may cause dilution to your holdings.
We may from time to time distribute rights to our shareholders, including rights to acquire our securities. However, we cannot make rights available to you in the United States unless we register the rights and the securities to which the rights relate under the Securities Act or an exemption from the registration requirements is available. We are under no obligation to file a registration statement with respect to any such rights or securities or to endeavor to cause such a registration statement to be declared effective. Moreover, we may not be able to establish an exemption from registration under the Securities Act. Accordingly, you may be unable to participate in our rights offerings and may experience dilution in your holdings.
ITEM 4. INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY
A. History and Development of the Company
Our predecessor company, American Testing Authority, Inc., a New York company, began operations in 1999, and in the same year established ATA Testing Authority (Beijing) Limited, or ATA Testing, as a wholly-owned subsidiary in China. In November 2001, our founders established ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited, or ATA BVI, in the British Virgin Islands. In the following year, American Testing Authority, Inc. merged into ATA BVI and ATA BVI became our holding company.
In June 2003, we established a Chinese joint venture company, ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., or ATA Learning, with Yinchuan Economic and Technological Development Zone Investment Holding Co. Ltd., or Yinchuan Holding. Initially, we held a 40% equity interest in ATA Learning. In May 2005, we acquired Yinchuan Holdings 60% equity interest and converted ATA Learning into a wholly-owned subsidiary of ATA BVI.
We incorporated ATA Inc. in the Cayman Islands in September 2006 as our listing vehicle. ATA Inc. became our ultimate holding company in November 2006 when it issued shares to the existing shareholders of ATA BVI in exchange for all of the outstanding shares of ATA BVI.
In February 2009, we completed the acquisition of the entire equity of Beijing JDX, and JDX Holdings Limited, or JDX BVI, which are related companies incorporated in China and the British Virgin Islands, respectively, engaged in the development and marketing of software for computer-based tests. JDX BVI was dissolved in October 2009.
In November 2013, we completed the acquisition of the entire equity interest of Xing Wei Institute (Hong Kong) Limited, or Xing Wei, a private education technology company that provides training solutions as well as online and mobile training platforms for corporations in China.
In connection with the listing of our testing service business on the New Third Board, we acquired the entire equity interest of ATA Online through ATA Learning and Zhongxiao Zhixing in May 2015, with ATA Learning owning 90% and Zhongxiao Zhixing owning 10% of ATA Onlines share equity. In connection therewith, we terminated a series of contractual arrangements with ATA Online and its nominee shareholders, which provided us control over ATA Online. As a result, ATA Online became our wholly-owned subsidiary which hosted our testing services business and online education services. See Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party TransactionsB. Related Party Transactions. In addition, we transferred the non-testing services business from ATA Online to ATA Learning, and as a result, ATA Online transferred to ATA Learning 20% and 33% equity investments in Satech and Master Mind, respectively, in May 2015.
In May 2016, ATA Testing acquired from ATA Inc. the entire equity interest of Beijing JDX, which changed its company name to ATA Learning Data & Technology (Beijing) Limited, or ATA Data, in August 2016. In June 2017, MOOC-CN Investment and an individual shareholder acquired a total of 20% equity interest in ATA Data. Such investment aimed to help us expand into the K-12 education assessment market, with particular focus on the development of K-12 education assessment tools and contents. ATA Data changed its company name to Muhua Shangce Learning Data & Technology (Beijing) Limited, or Muhua Shangce, in connection with such investment. After the investment, ATA Testing, MOOC-CN Investment and the individual shareholder each holds 56%, 18% and 2% equity interests in Muhua Shangce respectively, with the remaining 24% being reserved as an employee stock option pool for future incentive issuance to Muhua Shangces employees.
In September 2016, we completed the acquisition of 60% equity interest in Beijing Puhua Huitong Education Technology Co., Limited., or Puhua Technology, by injection of RMB 2.0 million ($0.3 million) in cash. Puhua Technology is a continuing education service provider focused on delivery of both degree and non-degree granting continuing education programs for adults.
The following diagram illustrates our current corporate structure. Except for ATA BVI and Xing Wei, which are incorporated in the British Virgin Islands and Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the PRC, respectively, all of our subsidiaries are incorporated in Mainland China.
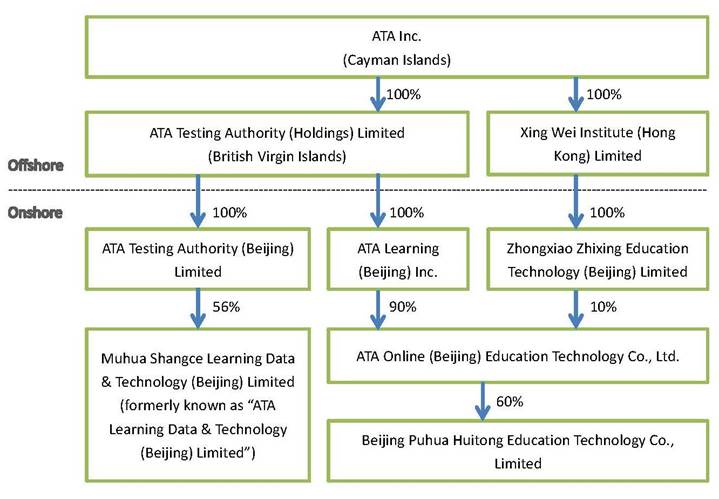
Our principal executive offices are located at 1/F East Gate, Building No. 2, Jian Wai Soho, No. 39 Dong San Huan Zhong Road, Chao Yang District, Beijing, China, and our telephone number is (86-10) 6518-1122. Our web site address is http://www.atai.net.cn. The information on our web site does not form a part of this annual report. On February 1, 2008, we completed our initial public offering, which involved the sale by us of 4,874,012 of our ADSs, representing 9,748,024 of our common shares. Our agent for service of process in the United States is CT Corporation System, located at 111 Eight Avenue, New York, New York 10011.
B. Business overview
Overview
We believe that we are the leading provider of computer-based testing services in China, based on test delivery capacity and geographic coverage. We offer comprehensive services for the creation and delivery of computer-based tests utilizing our nation-wide test delivery platform, proprietary testing technologies and extensive experience providing testing services in China. Our computer-based testing services are used for professional licensure and certification tests in various industries, including IT services, banking, teaching and insurance. Our computer-based testing services clients principally include professional associations, such as CICPA and AMAC, Chinese governmental agencies, including the PRC Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, and large state-owned enterprises, such as Sinopec and China Mobile.
Our test center network, which we believe is the largest test center network of any commercial testing service provider in China, comprised 3,147 authorized test centers located throughout China as of March 31, 2017. Combined with our test delivery technologies, this network allows our clients to administer large-scale nationwide computer-based and paper-based tests in a consistent, secure and cost-effective manner. From our inception in 1999 through March 31, 2017, we have delivered approximately 100.3 million tests, including approximately 11.9 million free tests for business development purposes. Over the course of two days on October 15 and October 16, 2016, we delivered tests for the fifth consecutive year to more than 2.3 million tests for the CPA, demonstrating our ability to administer computer-based tests across the country on a massive scale through our nationwide test delivery platform. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, approximately 12.2 million tests were delivered using our computer-based testing technologies and services.
Our proprietary computer-based testing technologies include our E-testing platform for delivering computer-based tests, our patented mobile testing platform called the Mobile Testing Service, or MTS, our cloud-based online testing platform called EzTest, and our content creation and management technologies. Our E-testing platform is composed of a set of self-developed tools and applications for facilitating the computer-based testing process, and is capable of handling large-scale tests and quickly and securely transmitting, processing and storing large amounts of data. Our self-developed MTS, launched in 2013 and EzTest, launched in 2015, are applications compatible for Windows, iOS and Android systems that function as exam testing systems which were developed on the basis of cloud technology. Test takers can take tests through MTS and EzTest on their mobile devices, and test administrators can host, manage and administer the tests through MTS anywhere. Both MTS and EzTest platforms enhance the mobility, security, efficiency and cost-effectiveness of test administration by utilizing state-of-the-art cloud technology to transmit test data through portable mobile devices. Our computer-based testing technologies, including E-testing platform, MTS and EzTest, provide diversified solutions to test sponsors and clients in various circumstances. Our self-developed test content creation and management technologies include our Dynamic Simulation Technology, an advanced performance-based testing technology which leading IT certification sponsors have adopted for their computer-simulated tests delivered around the world. We have also developed content creation technologies for the conversion of paper-based tests into computer-based formats to make test administration easier and cheaper.
We have received a number of awards and commendations in recognition of the quality of our services and our achievements in the development of computer-based testing technologies. For example, we recently received the 2016 Asian Education Contribution Award from the Asian Education Beijing Forum Organizing Committee and China Distance Education Magazine in November 2016. In June 2016, we were recognized as one of the Top 10 China Online Education Service Providers by the Top 100 China Online Education Selection Committee. In May 2016, we won the Industry Leader Award and Future Unicorn Enterprise Award at the 2016 China Internet Education Selection Ceremony, which was organized by the 2016 China Internet Education Selection Ceremony Organizing Committee.
Leveraging our testing platform, technologies and expertise, we administer an ever expanding portfolio of test titles in China and have expanded our service offerings beyond our core computer-based testing services to include other test-focused services. ATA launched online training services in 2006 to help candidates across China attain continuing educational requirement after their professional licensure and certification tests, which are delivered through our E-learning platform, which is an online training platform providing technology support and services to individual end-users for online distance education. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, we expanded our online education services by offering an online continued education training platform for professionals who have already acquired the CBA exam certificates. We plan to continue to expand our service offerings to include online education technologies, career-oriented training and soft skills development for test takers.
Our total net revenues increased to RMB 472.4 million ($68.6 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 417.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 and RMB 350.2 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, respectively. We had net income of RMB 23.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, RMB 26.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 and net loss of RMB 10.0 million ($1.4 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
Our Test Delivery Platform and Technologies
We offer our clients a comprehensive platform and suite of technologies for the development and delivery of computer-based tests. Our E-testing platform integrates all aspects of the test delivery process for computer-based tests, from test form compilation to test scoring and results analysis. Our test delivery services are further enhanced by our nation-wide network of test centers, which allows us to deliver both computer-based and paper-based tests on a large scale in a consistent, secure and cost-effective manner. We also offer our clients advanced technologies and software applications for the creation of sophisticated computer-based tests, including advanced performance-based tests. While we still offer a choice between paper-based testing and computer-based testing for our institutional clients, currently all of our national public exams are delivered using computer-based testing, and we expect the trend towards computer-based exams to continue. For example, we have been helping the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, or MOHURD, to transfer its Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Field Professionals Qualification Exam held in Ningxia, Gansu and Qinghai from paper-based testing to computer-based testing in 2016. By combining our advanced test content creation technologies with our test delivery platform and network of test centers, we can offer our clients a comprehensive and integrated solution to enhance the effectiveness of the entire testing process, as shown in the following diagram.
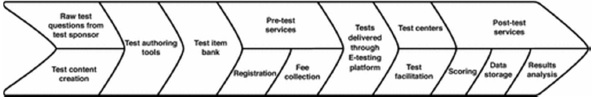
Our E-Testing Platform
Our E-testing platform incorporates a number of technologies and protocols designed to ensure the stable, cost-effective, secure, accurate, fast and easy-to-manage delivery of computer-based tests on a large scale. It is flexible and easily customized for many types of test content and the specific requirements of the test sponsor. Tests delivered through our E-testing platform may be conducted at our ATA authorized test centers or at other locations at the test sponsors discretion. Our E-testing platform is composed of a set of tools and applications for facilitating the computer-based testing process, including a network sub-system for managing and transferring test content, test taker information and test results data in a secure and efficient manner. Our E-testing platform software applications are pre-installed on designated personal computers at the testing site prior to the test date and are designed to handle large-scale testing environments and are capable of transmitting, receiving, processing and storing large amounts of information in a short time span. We currently have the capability to deliver more than 1,200,000 tests per day using our 150 servers, which can be increased to enlarge capacity. We periodically upgrade our equipment and software applications to handle increasing testing volume as required.
Our Mobile Testing Service
Our proprietary mobile test administration platform MTS significantly enhances the mobility, security, efficiency and cost-effectiveness of test administration. MTS obviates the need to pre-install software on designated personal computers at the testing site prior to the test date and allows us to monitor the status and process of an entire exam through a safe, non-public LAN, thus reducing the cost of test administration and improving test administration efficiency. Through MTS, test packets can be downloaded to personal electronic devices prior to the exam, and candidate responses can be synced with the test server during the exam. MTS consists of three main components: (i) a small MTS Box that is placed in the testing center and operated by onsite proctors to wirelessly connect between the MTS Cloud Server and the test takers own electronic device, such as a personal computer or tablet; (ii) an MTS Cloud Server that processes the exchange of data, such as the upload or download of test data, between the MTS Box and our servers; and (iii) MTS Test Client, an app that supports multiple operating systems and enables secure data transmission between the MTS Box and test takers personal electronic devices during live exams. MTS has already been deployed for use in our administration of the Cambridge English Junior Exam in 22 countries or regions and we expect it to garner widespread use in the future.
Our SAAS Mode Online Testing Platform
EzTest is our new online testing platform launched in 2015. It provides comprehensive functions required by most test delivery organizations and individuals, including item banking, test form composition, test delivery, online proctoring and test result analysis. EzTest functions on all computer system browsers and most mobile system browsers without the need to install additional software or plug-ins. This enables its users to create their own content and deliver test at any time, any place and on any device. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, our EzTest online testing platform was successfully used by leading PRC blue chip companies, such as China National Chemical Corporation and China UnionPay.
Our ATA Authorized Test Center Network
To help our clients reach a broad base of test takers, we have established a large network of authorized test centers across Mainland China and in Macau, which we refer to as our ATA authorized test centers. As of March 31, 2017, we had contractual relationships with 3,147 ATA authorized test centers. Our network of ATA authorized test centers provides the means for delivering and administering tests nationally both simultaneously and on a regularly scheduled basis under consistent and secure testing conditions.
The following map shows the geographic distribution of our ATA authorized test centers as of March 31, 2017:
Extensive Network of Test Centers
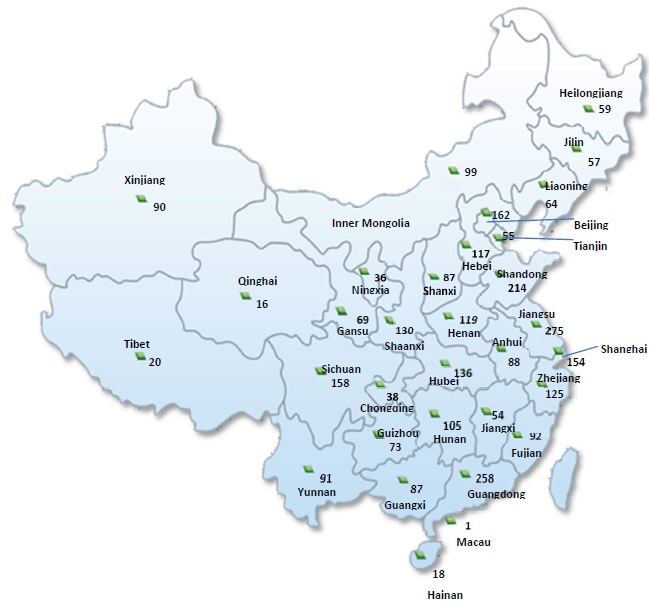
We do not own any of our ATA authorized test centers but instead enter into a standard form of contract with qualified independent operators to act as ATA authorized test centers. Most of our ATA authorized test centers are owned by Chinese vocational schools, which we believe enhances the quality and reliability of the centers. Under our contracts with the test centers, we license our E-testing platform technology and provide ongoing technical support and training during the contract period. We require each test center to provide sufficient facilities to properly administer computer-based tests and to follow prescribed guidelines for facility maintenance and test administration. We also conduct regular reviews of their facilities and operations. We assist our clients in liaising and coordinating testing arrangements with our ATA authorized test centers.
Our ATA authorized test centers are divided into general test centers, which offer a wide range of tests and have the right to use our ATA brand name and logo, and special test centers with which we enter into contracts to carry out specific tests for specific test sponsor clients. We receive license fees from our general test center operators in the form of either a single initial license fee or a combination of initial license fee and continuing annual license fees. Under either fee arrangement, we and our licensees can extend the licensing agreement indefinitely.
Our Test Content Creation and Management Technologies
We offer our clients advanced technologies and software applications for the creation of sophisticated computer-based tests, including advanced performance-based tests.
Our Dynamic Simulation Technology is a performance-based testing technology that creates, illustrates, runs and scores tests in a virtual computer environment that accurately and realistically simulates the operating environment and functions of the software applications being tested without requiring the installation or use of those applications. Our Dynamic Simulation Technology is designed to provide maximum interactivity and allow the test taker to perform tasks in the simulated environment and operate through multi-level testing paths. The current version of Dynamic Simulation Technology, version 5.0 is an interpreter-based simulation technology, which represents our fifth generation of simulation testing technologies.
Interpreter-based simulation offers high flexibility, adaptability to most applications, low disk space usage and short lead times for developing new tests once the system is in place. Based on feedback from our clients, we believe that we are the only company in the world that has developed and marketed interpreter-based simulation technology for testing and educational use. For this reason, we believe that our Dynamic Simulation Technology is the worlds leading technology for the creation and illustration of performance-based tests through simulation. Currently content in over eight languages has been delivered through this technology around the world.
We also have two non-simulation testing technologies: Real Environment Technology and ATA Markup Language. Our Real Environment Technology is used for creating and running performance-based tests and learning exercises that track and score within the actual operating system or software application being tested. Our ATA Markup Language is used for the creation and illustration of knowledge-based test items that require the test taker to respond to specific questions in a traditional question-and-answer format. While less sophisticated than our performance-based testing technologies, ATA Markup Language remains a key technology for our large base of clients who contract with us for the conversion of paper-based tests to computer-based tests. In addition, many performance-based tests also include traditional multiple-choice questions created and run by our ATA Markup Language and related software applications.
We have developed test item authoring tool applications for our Dynamic Simulation Technology, Real Environment Technology and ATA Markup Language. We have also developed other authoring tools, such as user interface cloning and translation software, for increasing the efficiency of the test content creation and revision process. To meet individual client needs, we have developed test engine applications for integrating tests using our testing technologies on multiple testing platforms.
In addition to incorporating our technologies into our test service offerings, we also directly generate revenue from our Dynamic Simulation Technology and related simulation authoring tools by licensing them to international IT certification sponsors, such as Citrix and CompTIA, for the creation of test items and test preparation course exercise items delivered to students and test takers all over the world.
Our Service Offerings
Testing Development and Delivery Services
Computer-based test authoring, delivery and result analysis services. Our test delivery platform and technologies allow us to offer our clients a comprehensive set of services for the authoring, test delivery and result analysis of computer-based tests as well as administrative services such as test registration, scheduling, fee collection and certification fulfillment. We assist our clients with creating and delivering a wide range of computer-based tests, including governmental agencies with licensure tests required for job positions within various governmental agencies, industry associations with tests that test the competence of individuals who practice in certain industries that require technical expertise and which carry professional titles, as well as Chinese universities with admission tests that test the knowledge and skills of high school graduates who apply to such universities, such as:
· the National Unified Certified Public Accountants Exam, sponsored and regulated by CICPA;
· the Fund Practitioners Certification Exam, sponsored and regulated by the AMAC, under CSRCs supervision;
· the Certification of China Banking Professionals Exam, sponsored and regulated by CBA under the supervision of the China Banking Regulatory Commission, or CBRC;
· the National Tax Adviser Occupational Qualification Exam, sponsored and regulated by China Certified Tax Agents Association, or CCTAA;
· the National Tour Guide Qualification Exam, sponsored and regulated by the China National Tourism Administration;
· the Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Field Professionals Qualification Exam, sponsored and regulated by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the Peoples Republic of China;
· the National Security Guard Exam, sponsored and regulated by the Ministry of Public Security of the Peoples Republic of China;
· the self-developed admission tests administered by various reputable Chinese universities; and
· corporate assessment services for large scale/day-to-day recruitment exercise and internal for talent management assessment purposes.
Utilizing our comprehensive and advanced item authoring system and rendering technologies, we assist our clients in developing sophisticated computer-based tests, including performance-based items. Creation of effective and reliable computer-based tests involves a multi-step process:
· Test design. Our content development consultants work together with the client to determine the test scope, target audience, test objectives and required competency level to formulate an overall test blueprint. We then arrange for the client to work with our internal subject matter experts, or engage outside subject matter experts with specific experience in the subject area, to work with us on the scope of knowledge covered by the test and to design and author specific testing items for required knowledge points.
· Test item authoring. Based on the test blueprint and using our advanced test engine technologies, we work together with subject matter experts to create individual test items designed to determine a test takers proficiency and effectiveness in solving both practical and conceptual problems. The test items are designed to support immediate test scoring and results processing. Test items generally fall into two types: standardized items and constructed responses items. Once all of the test items have been created, our content development consultants and subject matter experts commence a review process to ensure the validity of each test item, clarity of language and overall quality. All of the test items are then deposited in a master test item pool.
· Test form and item bank construction. Once the test items are ready, we tag attributes to test items for building up test item banks, which enable test forms to be formulated based on the blueprint of a test. Test forms with the same level of difficulty are generated from the test item bank to ensure fairness across test forms.
· Final user acceptance test. Before publication, the test undergoes a final user acceptance test during which selected test takers take the test and provide feedback. Based on the test results from the beta test, we evaluate the efficacy of the test, eliminate problematic test items and otherwise fine tune the test items to ensure quality.
· Continuous upgrades through result analysis and user feedback. As we deliver tests in real-world environments, we monitor and analyze the quality and adequacy of the test content and update test items as we develop or adopt new technologies and techniques. We also communicate with test users and collect feedback from the test sponsors and test takers to ensure that test items are up-to-date.
Our services are modularized, and depending on the clients needs, we perform some or all of the above services to individual client. For example, in some cases, clients may have already created all of the test items and may only require us to build the test using our E-testing platform. Computer-based tests can also be scheduled on an on-demand basis, or as regularly scheduled tests, which are prescheduled and taken by test takers at a designated time.
Our computer-based testing delivery services generally include the following, subject to the test sponsors specific needs:
· installing our E-testing platform on the computer system of our authorized test centers to enable centralized administrative tasks to be implemented for the test or, in the case of repeated clients, updating the platform as necessary, for new tests;
· providing technical support throughout the test administration process;
· updating test session information and performing test rehearsals and final test environment inspection;
· administering the test sessions and collecting responses from candidates; and
· processing test scores, summarizing and analyzing test scores and generating results.
We also offer a number of logistical support services relating to test administration that we incorporate into the testing fee for our test delivery platform based on clients customized needs. These support services include:
· managing test taker registration and scheduling;
· managing test fee collection;
· preparing and conducting pre-test training of personnel at each ATA authorized test center;
· providing test data management, such as test score publishing and inquiry; and
· printing and delivering certificates for test takers who have satisfied the test sponsor certification requirements.
We usually offer test content creation services and test delivery services as an integrated solution and collect a fixed fee per test per test taker. The fee we charge depends on the length and complexity of the test, the amount of effort it takes to transform the testing content into computer-based test format and other factors in the test development and administration process, such as security levels and the amount of logistical services provided.
Administration of TOEIC exams in China. We have been a long-time distributor and test administrator of TOEIC exams in China, which are products of ETS, the worlds largest educational research and assessment organization. Originally designed in 1979 by ETS for governmental agencies and corporations, TOEIC measures the ability of non-native speakers of English to communicate in English in the workplace. According to ETS, the TOEIC exam is being used by over 14,000 companies, government agencies and English language learning programs in 150 countries, with around eight million TOEIC exams administered around the world in 2016. TOEIC has become the top professional English language assessment tool in the world, according to ETS.
TOEIC tests include large-scale, fixed-date testing open to the general public for a set fee as well as on-demand testing given for specific enterprises or organizations. We administered our first TOEIC exam in three cities in China in March 2009. We collect a per-test taker fee for each test delivered. TOEIC exams in China used to be only available in a paper-based format, but since August 2011, we began also delivering computer-based TOEIC exams through our delivery system at our authorized test centers.
On February 28, 2014, our exclusive TOEIC distributor contract with ETS ended and we no longer exclusively administer TOEIC exams in China due to ETS decision to change its distribution model; however, we are still a distributor and administrator of TOEIC exams in China and signed a non-exclusive distributor contract with ETS on June 23, 2014 to continue delivery of certain TOEIC exams to our existing institutional clients from April 1, 2014 through December 31, 2016. On January 20, 2017, we renewed such non-exclusive distributor contract with ETS to extend its term for another three years from January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2019.
Distribution and administration of Cambridge tests. We entered into an exclusive ten-year Master Distribution and Services Agreement in March 2013 with The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge (Cambridge), an affiliate of the University of Cambridge which has the largest dedicated research department of any UK-based language assessment organization. Under this agreement, we will host, support, market and deliver platform services to certain Cambridge tests and collect a per-test taker fee for each test delivered. As of March 31, 2017, we have enabled the delivery of 10,139 Cambridge English Junior Exam in 22 countries or regions through our MTS and expect to expand delivery of this and other Cambridge test titles to other jurisdictions in the future.
Administration and delivery of ACT exams in China. In October 2016, we successfully provided test delivery services for the American College Test (ACT) in China. ACT is a paper-based college entrance exam administered by ACT, Inc. We are currently in the process of assisting ACT, Inc. with the conversion of the ACT exams from paper-based to computer-based testing, which we expect to be completed and launched in the second half of 2018. We also signed an exclusive five-year agreement with ACT on April 21, 2017 to provide Chinese candidates with a comprehensive journey of preparation towards the ACT exams.
Administration and delivery of the Vocational Qualification Test for National Land Registration Agents. In June 2016, we provided a range of testing services, including test center monitoring and test administration and delivery, for the Vocational Qualification Test for National Land Registration Agents, which is a paper-based test sponsored and regulated by China Real Estate Valuers and Agents Association (CREVA) under the supervision of the Ministry of Land and Resources and the PRC Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, or MOHRSS. This was the first time that we delivered and supported the Vocational Qualification Test for National Land Registration Agents, in which a total of 17,075 test takers participated over the course of two days on June 18 and June 19, 2016.
HR Select Employee Assessment Solution
In March 2009, we launched our self-developed HR Select employee assessment solution. HR Select is a service that enables corporate human resources departments to test, benchmark and analyze job applicants based on general, industry-specific and job-specific profiles and individual skill-sets, making it an invaluable tool for campus recruitment, lateral hiring and internal promotions. Employers using HR Select can choose to adopt any of a multitude of evaluation parameters, including:
· General work skills, including among others foreign language skills, software application skills, management skills, reading comprehension ability and data processing skills;
· Position-specific skills, including customized tests for IT, finance, management, customer service, administrative and sales positions; and
· Compatibility traits, which look at non-skills elements that indicate a candidates likelihood of success, such as personal values, self-image, motivation and other personality traits.
HR Select leverages our computer-based testing technologies and expertise to allow employers to evaluate candidates on each of these properties and to analyze and categorize the results to make effective recruitment decisions. Candidates are tested using our E-testing platform at our authorized test centers or online at a place of their choosing. We have also leveraged our particular expertise in certain industries where we have been delivering computer-based tests and educational services, including the IT and finance industries, to provide targeted services to employer clients. For example, Saville Wave, which is a career personality test, is available via the HR Select service to assess a candidates behavioral based personality and predict his workplace performance. Employers may adopt ready-made tests available in our system, or use their own self-developed tests. If they use their own tests, they can choose to keep the test confidential or permit other HR Select clients to view the tests. By allowing test content to be shared, we believe HR Select can facilitate the standardization of recruitment criteria within industries. HR Select incorporates our computer-based testing technologies to allow clients to deliver the evaluation tests online in a secure, accurate and easy-to-manage manner. HR Select can be administered at ATA authorized test centers or via our customized online platform.
Our current HR Select clients principally include large domestic and foreign-invested companies in professional industries such as insurance and banking. Since the end of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2011, the four largest Chinese state-owned banks have all become customers of our computer-based testing services that incorporate our HR Select solution. To complement our HR Select offerings, we signed an exclusive ten-year partnership agreement with Saville Assessment, a global human resources assessment firm whose products are available in over 80 countries, in August 2011 to deliver Savilles unique and proprietary psychometric measurement instruments and specialized personality instrument through our testing platform. Savilles psychometric assessment has enhanced our HR Select product portfolio and moved us one step closer to our goal of being a premium provider of international, brand name test content.
Online Education Services
We offer online education services to candidates aiming to fulfill their post qualification continuing educational requirement. Our online education services integrate our testing and assessment technologies with online education content targeted at professional licensure and certification tests in China.
Online education platform for the futures industries. Leveraging the scale of ATA-delivered futures certification test, ATA launched an online education web site to provide a flexible and scalable platform aimed at helping candidates across China to fulfill their Continuous Professional Development (CPD) requirement after passing their professional licensure and certification tests delivered through our testing platform for the China Futures Association. Online education customers gain access to Internet web sites that contain the latest training materials provided by the test sponsors and streaming video of teaching sessions and practice tests developed by ATA.
Online continued education training platform for banking professionals. In May 2014, we were authorized by the CBA on an exclusive basis to develop an online continued education training platform for professionals who had acquired the Vocational Qualification Certificate for China Banking Professionals. This online training platform aims to provide such banking professionals with continuing vocational training to fulfill the minimum continuing education requirements after obtaining their qualification certificates. After more than two years of development and testing, we successfully launched this online training platform in July 2016, and the registrants have been growing steadily to approximately 130,000 as of March 31, 2017. Under our agreement with the CBA, we were granted the exclusive right to provide online education services for CBA for five years and were entitled to charge service fees based on the total number of activated online training sessions delivered by the platform each month.
Data Storage and Security
One of the most important aspects of our computer-based testing services is ensuring the integrity and security of the test-taking process. To accomplish this, we use multiple technologies and methods to ensure the security of test content, test results and other sensitive data used or obtained in relation to our services.
We have developed and implemented the following technologies and measures to protect security throughout all stages of test development and delivery:
Preparation and Storage of Test Items
To reduce the risks associated with potential unauthorized disclosure or misuse of test questions by ATA personnel during the process of creating test item banks, we divide test item authoring and management tasks among multiple persons and limit each persons access to the test item content through the use of access permissions. Each test item author is only responsible for creating a limited amount of test item content and is permitted access only to that content for which that person is responsible. As a result, no one has full access to the contents beyond his or her scope of work. Test item bank managers receive limited permissions and are not given access to the content of individual test items. Moreover, our test item authoring and test item bank management tools record and track all access and modifications to test items or the test item pool to detect any breaches to the security protocols. Once the test item banks are created, the content is encrypted and stored on our secure central servers or the clients servers. Our servers are located in a central machine room operated by one of the most well-established server hosting service providers in China. These servers are protected by firewalls and stored using NetApp TM equipment, which permits real-time back-up. We encrypt all test item banks using our self-developed encryption algorithm, which strive to prevent decryption or reverse engineering through the use of electronic fingerprinting, anti-tracking and trapping technologies.
Creation of Test Forms and Transmission of Test Materials to the Test Site
Our software applications automatically compile individual test forms from the test item bank according to the test blueprint and pre-arranged parameters. During this process, no access of the content of individual test items is permitted and all steps in the process are digitally recorded. The encrypted test forms are delivered to the test sites server either on hard disc or through a secure network, generally one day before the day of the test. The relevant information on each test taker is separately transferred in encrypted format to the test site via the Internet. A hardware dongle containing an encrypted time stamp is used to ensure that the test begins and ends on time. A hardware dongle is a hardware device that must be inserted into the USB port of the test sites central computer to decrypt and operate the test content. We design our own hardware dongles, which incorporate ATA-owned integrated circuit technology, and outsource its production to multiple factories in China. A decryption algorithm used along with the hardware dongle to complete decryption of test materials and commence the test.
Conduct of the Test
We train all test center personnel on protocols and supervision techniques to be used during test time. Test center administrators confirm test takers identities through photographs, fingerprints and other biometric data. We also issue to each test taker upon registration a password that must be inputted on the test day to start the test. Once the test session has begun, software installed as part of each test tracks all actions and operations taken during the test and records them on the test site central server in real time. The testing software is designed to prevent test takers from accessing any network during test time. When a test taker opens up a question, it is decrypted and displayed. To protect against cheating, we have invested in surveillance equipment and the order in which test answer choices appear is randomly generated with each answer choice encoded as a unique number and letter chain. Immediately upon the test takers completion of each test item, the recorded data is re-encoded and re-encrypted.
Transmission, Reading and Storage of Test Results
In most instances, tests are scored on the test site server immediately following conclusion of the test and subsequently uploaded to our central servers. All transferred data is encrypted and data code integrity is verified using the latest technologies, including MD5 and Hash. Following scoring, we store all test content and results on our firewall-protected central servers.
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property protections, including copyrights, trademarks, patents, and trade secrets are important to our success. We rely on copyright, trademark and patent law, trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements with our employees, clients, business partners and others to protect our intellectual property rights. All of our senior management and engineering employees are required to sign agreements acknowledging that all inventions, trade secrets, works of authorship, innovations and other processes generated by them that relate to our business are our property, and to assign to us any ownership rights in those works. Despite our efforts, it may be possible for third parties to obtain and use our intellectual property without authorization.
As of March 31, 2017, we have registered 212 software copyrights relevant to our product and service offerings with the National Copyright Administration of the Peoples Republic of China, or NCA, including 26 software copyrights which were newly registered in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
As of March 31, 2017, we have also registered 265 domain names relating to our web sites, including www.atai.net.cn, the primary URL for our web site, with the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers and the China Internet Network Information Center, a domain name registration service provider in China.
We have also sought patent protection relating to our testing technology. On February 22, 2013, we submitted applications to Chinas State Intellectual Property Office seeking necessary invention patent and utility model protection for our testing transmission technology. Our application for utility model protection was granted on August 28, 2013, which gives us a protection period of 10 years starting from the date of application. In addition, our testing technologies also enjoy protection in China as trade secrets under Chinas Anti-Unfair Competition Law.
Clients
The quality and flexibility of our product and service offerings has attracted a broad base of clients. Our clients principally include Chinese governmental agencies, professional associations, well-known IT vendors as well as individual online education services consumers. CICPA, AMAC and CBA accounted for 19.1%, 18.6% and 11.8%, respectively, of our total net revenues for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017. No other client accounted for more than 10% of our total net revenues for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
As of March 31, 2017, we had 365 contracts with test sponsors for our computer-based testing services. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, our five largest computer-based testing services clients based on revenue were:
· CICPA, which has been designated by Ministry of Finance of the Peoples Republic of China as the sole administrator of CPA qualification tests in China;
· AMAC, which has been designated by CSRC as the sole administrator of Fund Practitioners Certification tests in China;
· CBA, which has been designated by the MOHRSS and CBRC as the sole administrator of banking industry qualification tests in China;
· the Professional Skills Qualification Center of the PRC Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security; and
· CCTAA, which has been designated by the State Administration of Taxation as the sole administrator of National Tax Adviser Occupational Qualification Exam tests in China.
These five clients represented an aggregate of 58.9% of our total net revenues for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
Sales and Business Development
Our sales and business development department, primarily composed of members of our senior management and professional sales team, is responsible for identifying and developing new markets and client opportunities for our product and service offerings.
For our computer-based testing services, we target key governmental agencies, professional associations, enterprises and other potential clients to help them develop standardized certification, qualification or assessment policies. Once we identify a potential client, we generally submit an initial proposal outlining the services we can provide based on our analysis of their test-related needs. We may develop and conduct trial tests tailored to the clients needs based on the terms of a memorandum of understanding signed with the client. We generally enter into a final contract with the client only after successful completion of the trial tests. During this process, we also actively seek opportunities to cross-sell and up-sell our services, including online education services and ancillary testing services to the client. The following diagram illustrates the key stages in our testing services business development process.
![]()
Marketing
To generate demand and market awareness, we engage in a variety of marketing activities to promote our product and service offerings. We host and invite potential clients, such as key governmental agencies and governing bodies, to industry conferences on topics such as the development of computer-based testing technologies. We also attend conferences and trade shows to demonstrate and promote our technologies, product and service offerings. We conduct marketing for our service offerings through promotional activities in cooperation with local governmental departments and educational institutions and through our local sales agents. Our on-campus marketing activities include promoting the licensure and certification tests linking to our ATA brand name, through prominently placed marketing materials like posters and other advertising means. We promote wider recognition of our ATA brand by placing our logo prominently outside ATA authorized test centers and in test and course program materials. We are also developing joint marketing efforts with certain independent operators of our ATA authorized test centers.
Competition
In the computer-based testing services market, we compete primarily on the basis of technology, price, management experience, established infrastructure, reputation and brand. We believe that our overall testing services and technologies, along with our nationwide test center network, provide us with a competitive advantage. We believe that we are currently the market leader in computer-based testing services in China due to a combination of our experience in and familiarity with the China computer-based testing services market, our advanced technologies, our large nationwide network of test centers, our established relationships with key test sponsors and governmental agencies and our competitive cost levels.
To our knowledge, based on interactions with clients and others in the market, we believe that we have the largest test center network of any commercial computer-based testing service provider in China. We had 3,147 authorized test centers in China, including centers in every province in China, as of March 31, 2017. Our vast network of test centers allows our clients to administer large-scale nationwide computer-based tests in a consistent, secure and cost-effective manner. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, approximately 12.2 million tests were delivered using our computer-based testing technologies and services, and our capacity for test delivery, which can be easily expanded if necessary, is already more than 1,200,000 tests per day.
For our HR Select employee assessment solution, while there are other companies providing recruitment services to corporate human resources departments, we are differentiated by our comprehensive service and focus on offering more professional testing services with proprietary testing contents and technologies.
While we anticipate new market entrants and increased efforts by existing international players to expand their presence in China, we believe that relatively high entry barriers, such as the time and costs associated with establishing a large-scale test center network, will make it difficult for new entrants or international competitors to quickly gain market share from us in China. We believe that potential domestic entrants lack the technology and commercial relationships that we possess. International competitors will likely face challenges in establishing effective relationships with key Chinese government and industry test sponsors or local educational institutions.
Seasonality
We have experienced seasonality and expect in the future to continue to experience seasonality in net revenues and accounts receivable related to our test delivery services, with the quarters ending June 30 and December 31 typically having higher net revenues from testing services and the quarters ending September 30 and March 31 typically having lower net revenues from testing services. This is primarily because the tests from which we derive substantial revenues are mostly delivered in the quarters ending June 30 and December 31.
Regulation
This section sets forth a summary of the most significant laws, regulations, policies and requirements that affect our business activities in China, the industries in which we operate, and our shareholders right to receive dividends and other distributions from us.
Regulation of the Software Industry
In China, holders of computer software copyrights enjoy protection under the Copyright Law of the Peoples Republic of China, or the Copyright Law. Under the Copyright Law, Chinas State Council and the State Copyright Administration have also promulgated various regulations relating to the protection of software copyrights in China. Under these regulations, computer software that is independently developed and exists in a physical form will be protected, and software copyright owners may license or transfer their software copyrights to others. Registration of software copyrights and exclusive licensing and transfer contracts with the Copyright Protection Center of China (previously, the State Copyright Administration) or its local branches are encouraged. Such registration is not mandatory under Chinese law, but can enhance the protections available to the registering parties. For example, the registration certificate serves an evidentiary function enabling the registering parties to prove they have protectable rights. We have registered 163 software copyrights with the NCA as of March 31, 2017.
Chinas Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (and its predecessors), or MIIT, has promulgated regulations to regulate the production, sale, import or export of software products in China. Under these regulations, all domestically produced software products to be operated or sold in China must be duly registered and filed with the provincial branches of MIIT. We have complied with the registration and filing requirements necessary to sell our software products in China. These registrations generally remain in effect for five years and are subject to renewal.
Regulation of Vocational Education
Chinese laws and regulations impose restrictions on foreign investment in educational institutions in China. However, Chinese laws and regulations do not impose restrictions on foreign investment in companies providing course and test content or related products and services to educational institutions. According to the Catalog of Industries for Guiding Foreign Investment amended in 2015, foreign investment in non-academic vocational education institutions is encouraged and there is no limitation to the maximum percentage of foreign ownership in a company operating non-academic vocational education business.
In addition, the Chinese government has issued a series of circulars and regulations promoting the development of vocational education, including The Decision to Enhance the Promotion of the Reform and Development of Vocational Education, The Decision to Enhance the Development of Vocational Education and The Decision to Enhance the Development of Modern Vocational Education published by the State Council on September 24, 2002, October 28, 2005 and May 2, 2014, respectively. These circulars and regulations require all levels of governments in China to intensify their support for vocational education and to gradually increase the financial resources that local and provincial governments allocate to vocational education.
Regulations regarding Internet Content Provider Licensure Requirements
We planned to engage in online testing preparation business, which are subject to PRC regulations including but not limited to Telecommunications Regulations, the Administrative Rules on Foreign-Invested Telecommunications Enterprises, the Notice on Strengthening the Administration of Foreign Investment in Operating Value-added Telecom Business, the Internet Information Services Administrative Measures, and Certain Rules on Regulating the Order of Internet Information Service Market. ATA Online previously held an ICP license issued by the Beijing Telecommunications Administration Bureau, a local branch of the MIIT, which allows ATA Online to provide Internet content distribution services. However, as ATA Online has not engaged in online testing preparation business since its incorporation, ATA Online deregistered its ICP license in 2015. Under PRC law, ATA Online is not required to hold an ICP license.
In the opinion of Jincheng Tongda & Neal Law Firm, our PRC legal counsel:
· the ownership structures of our wholly-owned subsidiaries in China are in compliance with existing published Chinese laws and regulations; and
· the business operations of our company, all of our Chinese subsidiaries, as described in this annual report, are in compliance with existing published Chinese laws and regulations in all material aspects.
Regulation of Online and Distance Education
Pursuant to the Administrative Regulations on Educational Web sites and Online and Distance Education Schools issued by the Ministry of Education in 2000, educational web sites and online education schools may provide education services in relation to higher education, elementary education, pre-school education, teaching education, occupational education, adult education, other education and public educational information services. Educational web sites refers to organizations providing education or education-related information services to web site visitors by means of a database or online education platform connected via the Internet or an educational television station through an Internet service provider, or ISP. Online education schools refer to education web sites providing academic education services or training services with the issuance of various certificates.
Setting up educational web sites and online education schools is subject to approval from relevant education authorities, depending on the specific types of education provided. Any educational web site and online education school shall, upon receipt of approval, indicate on its web site such approval information as well as the approval date and file number.
According to the Administrative License Law promulgated by the Standing Committee of the National Peoples Congress on August 27, 2003 and effective as of July 1, 2004, only laws promulgated by the National Peoples Congress and regulations and decisions promulgated by the State Council may set down administrative license. On June 29, 2004, the State Council promulgated the Decision on Setting Down Administrative Licenses for the Administrative Examination and Approval Items Really Necessary to be Retained, in which the administrative license for online education schools was retained, while the administrative license for educational websites was not retained. On January 28, 2014, the State Council promulgated the Decision to Cancel or to Delegate another Batch of Administrative Approval Items to Lower Level, in which the administrative license for online education schools was cancelled for higher education. On February 3, 2016, the State Council promulgated the Decision of State Council to Cancel the Second Batch of Administrative Approval Items (152 Items) that Delegated to Lower Level, in which the administrative license for online education schools and educational websites were cancelled.
Regulation of Broadcasting Audio-Visual Programs through the Internet or Other Information Network
The State Administration of Radio, Film and Television, or SARFT, promulgated the Rules for Administration of Broadcasting of Audio-Video Programs through the Internet and Other Information Networks, or the Broadcasting Rules, in 2004, which became effective on October 11, 2004. The Broadcasting Rules apply to the activities of broadcasting, integration, transmission, downloading of audio-video programs with computers, televisions or mobile phones as the main terminals and through various types of information networks. Pursuant to the Broadcasting Rules, a Permit for Broadcasting Audio-video Programs via Information Network is required to engage in these Internet broadcasting activities. On April 13, 2005, the State Council announced a policy on private investments in businesses in China that relate to cultural matters, which prohibits private investments in businesses relating to the dissemination of audio-video programs through information networks. On April 25, 2016, the SARFT promulgated the Private Network and Directional Broadcasting Audio-Video Programs Regulations, which came into effect on June 1, 2016 and replaced the Broadcasting Rules. The Broadcasting Audio-Video Programs Regulations provide, among other things, that a Permit for Broadcasting Audio-Video Programs via Information Network is required for engaging in broadcasting services through private network and directional communication. According to such Regulations, the Broadcasting Services through Private Network and Directional Communication shall mean the services and activities provided to the public through the private transmission channels that include internet, LAN and VPN based on Internet and through the receiving terminals of televisions, and other handheld electronic equipment, and such services and activities include the activities of content supply, integrated broadcast control, transmission and distribution with IPTVs, private-network mobile televisions, internet televisions. According to such Regulations, only the entities wholly or substantially owned by the State could apply for such Permit.
On September 2, 2016, the SARFT issued a Notice on Problems regarding Strengthening the Administration of Internet Audio-video Programs Live Broadcasting Services, which provides that (i) the provision of audio-video live broadcasting of important political, military, economic, social, cultural, sports and other activities and events and (ii) the provision of audio-video live broadcasting of cultural activities by general social organizations, sports events and like activities require an audio-video program transmission license.
On November 4, 2016, the Cyberspace Administration of China promulgated the Provisions on the Administration of Online Live Broadcasting Services, which became effective as of December 1, 2016. Such Provisions provide that anyone who provides online live broadcasting services through online performances, internet video/audio programs and so forth, shall obtain relevant qualifications as required by laws and regulations.
In November 2016, the SARFT issued a Notice on Strengthening the Administration of Audio-video Programs Transmission on Weibo, WeChat and Other Internet Social Networking Platforms, which further clarifies that anyone who operates internet audio/video services through Weibo, WeChat and other internet social networking platforms must obtain an audio-video program transmission license and operate its business pursuant to the scope as provided in such license.
On December 20, 2007, SARFT and MIIT issued the Internet Audio-Video Program Measures, which became effective on January 31, 2008 and was revised on August 28, 2015. Among other things, the Internet Audio-Video Program Measures stipulate that no entities or individuals may provide Internet audio-video program services without a license for disseminating audio-video programs through information network issued by SARFT or its local counterparts or completing the relevant registration with SARFT or its local counterparts and only entities wholly owned or controlled by the PRC government may engage in the production, editing, integration or consolidation, and transfer to the public through the Internet, of audio-video programs, and the provision of audio-video program uploading and transmission services. On February 3, 2008, SARFT and MIIT jointly held a press conference in response to inquiries related to the Internet Audio-Video Program Measures, during which SARFT and MIIT officials indicated that providers of audio-video program services established prior to the promulgation date of the Internet Audio-Video Program Measures that do not have any regulatory non-compliance records can re-register with the relevant government authorities to continue their current business operations. After the conference, the two authorities published a press release that confirms the above guidelines. On September 15, 2009, SARFT promulgated the Notice on Several Issues regarding the license for disseminating audio-video programs through information network. The Notice restates the necessity of applying for such license and sets forth the legal liabilities for those providing Internet audio-video program services without the license.
Regulations Relating to Internet Content and Information Security
Internet content in the PRC is regulated and restricted by the PRC government. The Administrative Measures on Internet Information Services, which was amended in 2011, specify that internet information services regarding news, publications, education, medical and health care, pharmacy and medical appliances, among other things, are to be examined, approved and regulated by the relevant authorities. Internet information providers are prohibited from providing services beyond those included in the scope of their ICP licenses or filings. Furthermore, these measures clearly specify a list of prohibited content. Internet information providers are prohibited from producing, copying, publishing or distributing information that is humiliating or defamatory to others or that infringes the lawful rights and interests of others. Internet information providers that violate the prohibition may face criminal charges or administrative sanctions by the PRC authorities. Internet information providers must monitor and control the information posted on their websites. If any prohibited content is found, they must remove the offending content immediately, keep a record of it and report to the relevant authorities.
Internet information in the PRC is also regulated and restricted from a national security standpoint. In 2009, the Standing Committee of the National Peoples Congress has enacted the Decision of the Standing Committee of the National Peoples Congress on Preserving Computer Network Security, which may subject violators to criminal punishment for any effort to: (1) gain improper entry into a computer or system of strategic importance; (2) disseminate politically disruptive information; (3) leak state secrets; (4) spread false commercial information; or (5) infringe intellectual property rights.
In addition, the Standing Committee of the National Peoples Congress promulgated the Cyber Security Law of the Peoples Republic of China, or the Cyber Security Law, which took effect on June 1, 2017, to protect cyberspace security and order. Pursuant to the Cyber Security Law, any individual or organization using the network must comply with the constitution and the applicable laws, follow the public order and respect social moralities, and must not endanger cyber security, or engage in activities by making use of the network that endanger the national security, honor and interests, or infringe on the fame, privacy, intellectual property and other legitimate rights and interests of others. The Cyber Security Law sets forth various security protection obligations for network operators, which are defined as owners and administrators of networks and network service providers, including, among others, complying with a series of requirements of tiered cyber protection systems; verifying users real identity; localizing the personal information and important data gathered and produced by key information infrastructure operators during operations within the PRC; and providing assistance and support to government authorities where necessary for protecting national security and investigating crimes.
Regulation of Domain Names and Web Site Names
PRC law requires owners of Internet domain names to register their domain names with qualified domain name registration agencies approved by MIIT and obtain a registration certificate from such registration agencies. A registered domain name owner has an exclusive use right over its domain name. Unregistered domain names may not receive proper legal protections and may be misappropriated by unauthorized third parties. As of March 31, 2016, we have registered 284 domain names relating to our web sites, including www.atai.net.cn, the primary URL for our web site, with the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers and the China Internet Network Information Center, a domain name registration service provider in China.
PRC law requires entities operating commercial web sites to register their web site names with SAIC or its local offices and obtain a commercial web site name registration certificate. If any entity operates a commercial web site without obtaining such certificate, it may be charged a fine or suffer other penalties by the SAIC or its local offices. Our web sites used in connection with our testing and education services are considered non-commercial web sites as we do not provide products and services through those web sites, and therefore the names of those web sites are not required to be registered with SAIC. ATA Online has registered the web site name used in connection with the online education services with Beijing municipal SAIC.
Regulation of Privacy Protection
PRC law does not prohibit Internet content providers from collecting and analyzing personal information from their users. PRC law prohibits Internet content providers from disclosing to third parties any information transmitted by users through their networks unless otherwise permitted by law. If an Internet content provider violates these regulations, MIIT or its local offices may impose penalties and the Internet content provider may be liable for damages caused to its users.
On July 16, 2013, the MIIT issued the Order for the Protection of Telecommunication and Internet User Personal Information. Most requirements under the order that are relevant to internet content provision operators are consistent with pre-existing requirements, but the new requirements are often more stringent and have a wider scope. If an internet content provision operator wishes to collect or use personal information, it may do so only if such collection is necessary for the services it provides. Further, it must disclose to its users the purpose, method and scope of any such collection or use, and must obtain consent from its users whose information is being collected or used. Internet content provision operators are also required to establish and publish their rules relating to personal information collection or use, keep any collected information strictly confidential, and take technological and other measures to maintain the security of such information. Internet content provision operators are required to cease any collection or use of the user personal information and de-register the relevant user account when a given user stops using the relevant internet service. Internet content provision operators are further prohibited from divulging, distorting or destroying any such personal information, or unlawfully selling or providing such information to other parties. In addition, if an internet content provision operator appoints an agent to undertake any marketing and technical services that involve the collection or use of personal information, the internet content provision operator is still required to supervise and manage the protection of such information. As for penalties, violators may face warnings, fines, and disclosure to the public and, in most severe cases, criminal liability under the order.
On November 7, 2016, the Standing Committee of the National Peoples Congress issued the Internet Security Law of the Peoples Republic of China, or the Internet Security Law, which took effect on June 1, 2017. The Internet Security Law requires providers of services over Internet networks to keep user information that they have collected in strict confidence and to establish improved systems for the protection of user information. Such service providers must provide notice of the purpose, methods and scope of their collection and use of user information, and obtain the consent of each person whose personal information will be collected. Providers of services over Internet networks may not collect any personal information that is not related to the services they provide, or disclose or tamper with personal information that they have collected, unless such information is encoded to prevent identification of individuals whose information is so disclosed or tampered with. Service providers who do not comply with the Internet Security Law may be subject to fines, suspension of their businesses, shutdown of their websites, and revocation of their business licenses.
Regulation of Foreign Exchange
The PRC government imposes restrictions on the convertibility of the Renminbi and on the collection and use of foreign currency by PRC entities. Under current regulations, the Renminbi is convertible for current account transactions, which include dividend distributions, interest payments, and the import and export of goods and services. Conversion of Renminbi into foreign currency and foreign currency into Renminbi for capital account transactions, such as direct investment, portfolio investment and loans, however, is still generally subject to the prior approval of SAFE.
Under current PRC regulations, foreign-invested enterprises such as our PRC subsidiaries are required to apply to SAFE or its designated banks for Foreign Exchange Registration. With such a registration, a foreign-invested enterprise may open foreign exchange bank accounts at banks authorized to conduct foreign exchange business by SAFE and may buy, sell and remit foreign exchange through such banks, subject to documentation and approval requirements. Foreign-invested enterprises are required to open and maintain separate foreign exchange accounts for capital account transactions and current account transactions. In addition, there are restrictions on the amount of foreign currency that foreign-invested enterprises may retain in such accounts.
According to Article 22 of the Regulations on the Foreign Exchange System of the Peoples Republic of China, if the Companys PRC subsidiaries liquidate, the Renminbi distributable to its foreign shareholders after the liquidation and payment of relevant taxes can be freely converted into foreign currency and remitted abroad. Therefore, there are no legal impediments to remitting the proceeds from a liquidation of our PRC subsidiaries outside of China to investors who are not PRC nationals.
Further, SAFE promulgated a new circular (known as Circular 142) in August 2008 with respect to the administration of conversion of foreign exchange capital contributions of a foreign invested enterprise. The circular clarifies that Renminbi converted from foreign exchange capital contributions can only be used for the activities within the approved business scope of such foreign invested enterprise and cannot be used for domestic equity investments unless otherwise permitted.
In addition, SAFE also strengthened its oversight over the flow and use of Renminbi converted from the foreign currency denominated capital of a foreign-invested company. The use of such Renminbi may not be changed without approval from SAFE, and such Renminbi may not be used to repay Renminbi loans if the proceeds of such loans have not yet been used. Violations of Circular 142 may result in severe penalties, including substantial fines as set forth in the related foreign exchange administration rules. In addition, SAFE promulgated a circular on November 9, 2010, or Circular 59, which tightens the regulation over settlement of the fund which is raised from overseas offerings such as our initial public offering and follow-on public offering and is transferred back to the PRC and requires that the settlement of such fund must be consistent with the description in the prospectuses for the initial public offering and follow-on public offering. Furthermore, it has recently come to our attention that SAFE issued an internal guideline to its local counterparts, referred to as Circular 45, in November 2011. Circular 45 has never been formally announced by SAFE to the public or posted on SAFEs website. Based on the version made publicly available by certain local governmental authorities on their websites, we understand that Circular 45 requires SAFEs local counterparts to strengthen the control imposed by Circulars 142 and 59 over the conversion of a foreign-invested companys capital contributed in foreign currency into RMB. Circular 45 stipulates that a foreign-invested companys RMB funds, if converted from such companys capital contributed in foreign currency, may not be used by such company to (i) extend loans (in the form of entrusted loans), (ii) repay borrowings between enterprises, or (iii) repay bank loans it has obtained and on-lent to third parties.
On May 10, 2013, SAFE released Circular 21, which came into effect on May 13, 2013. According to Circular 21, SAFE has simplified the foreign exchange administration procedures with respect to the registration, account openings and conversions, receipt and payment, settlements and sale of foreign exchange in relation to foreign direct investment.
SAFE promulgated the Circular of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Reforming the Management Approach regarding the Settlement of Foreign Exchange Capital of Foreign-invested Enterprises, or SAFE Circular 19, on March 30, 2015, which abolished Circular 142. According to SAFE Circular 19, up to all of the foreign exchange capital in the capital account of foreign-invested enterprises can be settled at the banks based on the actual operation needs of the foreign-invested enterprises. The capital in Renminbi obtained by foreign-invested enterprises from the discretionary settlement of foreign exchange capital shall be managed under the account pending foreign exchange settlement payment. The expenditure scope of such account includes: the expenditure within the scope of business, the payment of the capital of domestic equity investment and deposits in Renminbi, the repayment of the used loans in Renminbi, the purchase payment of foreign exchange or direct external repayment of foreign debts or other expenditure approved by the foreign exchange bureaus, but the capital of foreign-invested enterprises and capital in Renminbi obtained by them from foreign exchange settlement shall not be used for the following purposes: (1) directly or indirectly used for the payment beyond the business scope of the enterprises or the payment prohibited by national laws and regulations; (2) directly or indirectly used for investment in securities unless otherwise provided by laws and regulations; (3) directly or indirectly used for granting the entrust loans in Renminbi (unless permitted by the scope of business), repaying the inter-enterprise borrowings (including advances by the third party) or repaying the bank loans in Renminbi that have been sub-lent to the third party; and (4) paying the expenses related to the purchase of real estate not for self-use, except for the foreign-invested real estate enterprises.
On February 13, 2015, the SAFE promulgated the Notice on Further Simplifying and Improving the Policies of Foreign Exchange Administration Applicable to Direct Investment, or SAFE Circular 13, which became effective on June 1, 2015. Pursuant to SAFE Circular 13, annual foreign exchange inspection of direct investment is not required anymore and the registration of existing equity is required. SAFE Circular 13 also grants the authority to banks to directly examine and process foreign exchange registration with respect to both domestic and overseas direct investment.
Regulation of Foreign Exchange in Certain Onshore and Offshore Transactions
SAFE promulgated the Circular on Relevant Issues Concerning Foreign Exchange Control on Domestic Residents Offshore Investment and Financing and Roundtrip Investment through Special Purpose Vehicles, or SAFE Circular 37, on July 4, 2014. SAFE Circular 37 requires PRC residents to register with local branches of SAFE in connection with their direct establishment or indirect control of an offshore entity, for the purpose of overseas investment and financing, with such PRC residents legally owned assets or equity interests in domestic enterprises or offshore assets or interests, referred to in SAFE Circular 37 as a special purpose vehicle. SAFE Circular 37 further requires amendment to the registration in the event of any significant changes with respect to the special purpose vehicle, such as increase or decrease of capital contributed by PRC individuals, share transfer or exchange, merger, division or other material event. In the event that a PRC shareholder holding interests in a special purpose vehicle fails to fulfill the required SAFE registration, the PRC subsidiaries of that special purpose vehicle may be prohibited from making profit distributions to the offshore parent and from carrying out subsequent cross-border foreign exchange activities, and the special purpose vehicle may be restricted in its ability to contribute additional capital into its PRC subsidiary. Moreover, failure to comply with the various SAFE registration requirements described above could result in liability under PRC law for evasion of foreign exchange controls.
Our significant shareholder, Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, has completed his registration with SAFE, and we have urged our other Chinese resident shareholders to register under SAFE Circular 37 and they are preparing for such application. However, we cannot assure you that the application will be accepted by SAFE.
Failure by such shareholders to comply with SAFE Circular 37 could subject us to fines or legal sanctions, restrict our overseas or cross-border investment activities, limit our subsidiaries ability to make distributions or pay dividends or affect our ownership structure, which could adversely affect our business and prospects.
Regulation of Overseas Listings
On August 8, 2006, six PRC regulatory agencies, including the Chinese Securities Regulatory Commission, or CSRC, promulgated the Provisions Regarding Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprise by Foreign Investors, or the M&A Rule, which became effective on September 8, 2006 without retroactive effect and was amended by the PRC Ministry of Commerce on June 22, 2009. The M&A Rule, among other things, requires that an offshore company controlled by PRC companies or individuals that has acquired a PRC domestic company for the purpose of listing the PRC domestic companys equity interest on an overseas stock exchange must obtain the approval of the CSRC prior to the listing and trading of such offshore companys securities on an overseas stock exchange. On September 21, 2006, the CSRC, pursuant to the M&A Rule, published on its official web site procedures specifying documents and materials required to be submitted to it by offshore companies seeking CSRC approval of their overseas listings.
We believe CSRC approval was not required for our initial public offering in February 2008 because the CSRC approval required under the M&A Rule only applies to an offshore company that has acquired a domestic PRC company for the purpose of listing the domestic PRC companys equity interest on an overseas stock exchange, while (i) we obtained our equity interest in each of our PRC subsidiaries by means of direct investment other than by acquisition of the equity or assets of a PRC domestic company in 2008, (ii) our former contractual arrangements with ATA Online do not constitute the acquisition of ATA Online, (iii) the M&A Rule does not apply to the acquisition by ATA Learning, a wholly foreign owned foreign enterprise, and (iv) although Article 11 of M&A Rule prohibits the circumvention of the M&A Rule through establishing FIEs, ATA Learning was established in 2003 before the M&A Rule was promulgated, which makes this acquisition not a circumvention of the M&A Rule. See Item 3.D. Key Information Risk Factors Risks Relating to Regulation of Our Business If CSRC or another PRC regulatory agency determines that CSRC approval was required in connection with our initial public offering, we may become subject to penalties.
SAFE Regulations on Employee Share Options
On February 15, 2012, SAFE issued the Notice on Issues concerning the Foreign Exchange Administration for Domestic Individuals Participating in Stock Incentive Plan of Overseas Publicly-Listed Company, or the Stock Option Rules. According to the Stock Option Rules, PRC residents who participate in an employee share incentive plan of an overseas publicly-listed company are required to register with the SAFE and complete certain other procedures. These participates should retain a PRC agent, which can be a branch or representative office of the overseas listed company in China, a Chinese institution which has controlling relationship or actual control relationship with the offshore listed company, or a Chinese institution qualified for asset custody business, to handle various foreign exchange matters associated with their employee share incentive plan. The PRC agent should file on behalf of the PRC resident an application with SAFE to register such employee share incentive plan, apply annually for a quota for the payment of foreign currencies in connection with the exercise of the employee share options by the PRC resident and open a special foreign exchange account at a PRC domestic bank to hold the funds required in connection with the share incentive plan. In addition, the PRC agent is required to amend the SAFE registration with respect to the stock incentive plan if there is any material change to the employee share incentive plan, PRC agent or overseas entrusted institution.
In addition, the State Administration of Taxation has issued a few circulars concerning employee share options. Under these circulars, our employees working in China who exercise share options will be subject to PRC individual income tax. Our PRC subsidiaries have obligations to file documents relating to employee share options with relevant tax authorities and withhold individual income taxes of those employees who exercise their share options. If our employees fail to pay and we fail to withhold their income taxes, we may face sanctions imposed by tax authorities or other PRC government authorities.
C. Organizational Structure
For information on our organizational structure and a detailed description of the Companys significant subsidiaries, see Item 4.A. History and Development of the Company.
D. Property, Plant and Equipment
Our principal executive offices are located in approximately 3,023 square meters of office space used by us at 1/F East Gate, Building No.2, Jian Wai Soho, No.39 Dong San Huan Zhong Road, Chao Yang District, Beijing 100022, China. We also own 2,124 square meters of office space at Tower E, 6 Gongyuan West Street, Jian Guo Men Nei, Beijing 100005, China, which we have leased to two tenants. We also occupy approximately 2,816 square meters of total leased office space in our subsidiaries and branches located in Shanghai, Wuhan, Nanjing, Guangzhou and Xian. We believe that our existing facilities are adequate for our current requirements and that additional space can be obtained on commercially reasonable terms to meet our future requirements.
ITEM 4A. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS
A. Operating Results
Overview
Our Business
We believe that we are the leading provider of computer-based testing services in China, based on test delivery capacity and geographic coverage. We offer comprehensive services for the creation and delivery of computer-based tests utilizing our nation-wide test delivery platform, proprietary testing technologies and extensive experience in providing testing services in China. Our total net revenues increased to RMB 472.4 million ($68.6 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 417.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 and RMB 350.2 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, respectively. We had net income of RMB 23.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, RMB 26.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, and net loss of RMB 10.0 million ($1.4 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
We started our business in 1999 focusing on providing computer-based testing services to test sponsors. Our testing services revenues have grown primarily as a result of increases in the number of testing services clients and the number of test takers who take tests created or delivered using our testing technologies. Revenues from testing services accounted for 91.1%, 92.2% and 91.0% of our total net revenues in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively. We expect our testing services revenues to continue to be the largest source of our total net revenues. In March 2009, we launched HR Select, an employee assessment solution that utilizes our proprietary software and large test titles to assist companies in streamlining and optimizing their employee selection and assessment processes. HR Select offers tools for filtering and categorizing employee candidates, testing candidates and analyzing the test results. We are also a distributor and administrator of certain TOEIC exams to our institutional clients in China. Revenues from HR Select and distribution and administration of TOEIC exams are included in testing services revenues. The following graph shows the growth in the number of tests delivered using our testing technologies for the twelve months ended March 31, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017.
Number of Exams Delivered (1)
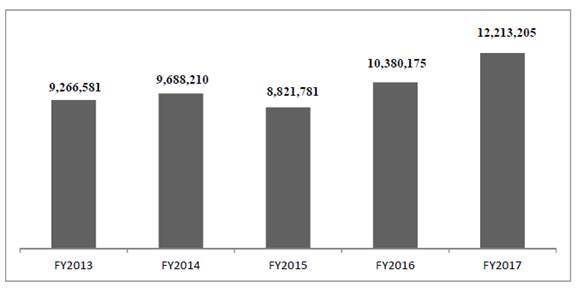
(1) Includes free tests delivered for business development purposes. The number of tests delivered excluding the free tests in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017 was 8,744,859, 9,411,226, 8,767,389, 10,258,866 and 12,127,203, respectively.
We also offer targeted online education services for certain professional licensure and certification tests in the securities and banking industries. ATA operates online education web sites and training platforms to help candidates across China fulfill their continuing educational requirement after passing their professional licensure and certification tests for the China Futures Association and CBA. Revenues from our online education services accounted for 1.6%, 1.2% and 1.6% of our total revenue in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
As of March 31, 2017, we operated our business and generated our net revenues primarily through our wholly-owned subsidiaries in China, ATA Testing, ATA Learning and ATA Online. Before ATA Online became our wholly-owned subsidiary in May 2015, due to PRC laws and regulations restricting foreign ownership in distributors of Internet content, ATA BVI, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Onlines shareholders entered into a series of contractual arrangements, through which we effectively controlled and enjoyed the economic benefits of ATA Online. As a result of those contractual arrangements, under U.S. GAAP, we were considered the primary beneficiary of ATA Online. Accordingly, we consolidated ATA Onlines results in our consolidated financial statements based on the contractual arrangements pursuant to the variable interest entity agreements, or VIE agreements, in accordance with U.S. GAAP until ATA Online became our wholly-owned subsidiary in May 2015. Since May 2015, we restructured our testing services business and online education services into ATA Online for purposes of listing it separately on the New Third Board. In connection therewith, we terminated the abovementioned contractual arrangements. See Item 4.A. Information on the Company History and Development of the Company.
Factors Affecting Our Results of Operations
The key factors affecting our results of operations are:
· growth in Chinas professional services sector resulting in increasing demand for qualified and certified talent in China and in the finance industry in particular;
· overall economic growth and rising income levels in China contributing to increased spending on education, testing and test preparation;
· government and industry initiatives to standardize and license professionals in industries such as securities, futures, banking, law and accounting;
· growth in the use of computer-based tests and performance-based tests and willingness of test sponsors to outsource test content development and delivery for sophisticated computer-based tests as well as online education programs;
· the increasing importance of identifying qualified talent contributing to increasing demand for testing and certification programs that can confirm the qualifications of the applicant or job seeker; and
· our ability to continue to introduce new services and testing platforms and the market success of such services and platforms, such as our EzTest, distribution and administration of certain test titles.
Although we anticipate the above factors will continue to increase demand for our products and services in China, a slowing or reversal of any of the above factors could cause our revenue growth to slow or stop, or to not grow as fast as we might expect.
In addition, our results of operations have been, and may continue to be, significantly affected by the following factors:
· share-based compensation;
· the impact of PRC tax policies, including certain preferential tax rates;
· the relative proportion of our net revenues derived from higher-gross margin and lower-gross margin service offerings; and
· the impacts of strategic investments.
Net Revenues
We derive revenues from sale of computer-based testing services, online education services, and other products and services. Our net revenues are presented net of PRC business taxes and value added tax. The following table sets forth a breakdown of our total net revenues for the periods.
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of net |
|
|
|
% of net |
|
|
|
|
|
% of net |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
revenues |
|
RMB |
|
revenues |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
revenues |
|
|
|
|
(in thousands, except or percentages) |
| ||||||||||||
|
Net Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Testing services |
|
319,055 |
|
91.1 |
% |
384,800 |
|
92.2 |
% |
430,057 |
|
62,479 |
|
91.0 |
% |
|
Online education services |
|
5,711 |
|
1.6 |
% |
4,897 |
|
1.2 |
% |
7,462 |
|
1,084 |
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Other |
|
25,392 |
|
7.3 |
% |
27,443 |
|
6.6 |
% |
34,867 |
|
5,066 |
|
7.4 |
% |
|
Total net revenues |
|
350,158 |
|
100.0 |
% |
417,140 |
|
100.0 |
% |
472,386 |
|
68,629 |
|
100.0 |
% |
Testing Services
We derive testing services revenues primarily from fees charged to test sponsors, including governmental agencies and other sponsors of licensure and certification tests, for our test delivery services. We also offer testing services to private enterprises as part of our HR Select employee assessment solution and administer TOEIC and ACT exams in China.
We offer our clients a comprehensive set of services for the compilation, delivery and analysis of computer-based tests using our E-testing platform, as well as logistical services such as test registration and fee collection. We generate revenues from our test delivery services through fees charged to test sponsors based on the total number of test takers taking a requested test or tests taken by test takers. Our clients typically pay us within two to six months after delivery of the test. We recognize revenue for test delivery services upon completion of the relevant test.
We have experienced seasonality and expect in the future to continue to experience seasonality in net revenues and accounts receivable related to our test delivery services, with the quarters ending June 30 and December 31 typically having higher net revenues from testing services and the quarters ending September 30 and March 31 typically having lower net revenues from testing services. This is primarily because the tests from which we derive substantial revenues are mostly delivered in the quarters ending June 30 and December 31.
Significant Factors Affecting Testing Services
The most significant factor directly affecting our revenues from fees charged for our testing services are the number of tests taken. The number of tests taken is driven by our ability to secure contracts with test sponsors for the creation and delivery of computer-based test titles popular with test takers. The volume of tests we offer is determined by the willingness of test sponsors to use our services. Our revenues from fees charged for our testing services are also affected by the price we can charge per test, which generally remains fairly stable once we are engaged by a test sponsor to help deliver a particular test.
Demand and pricing for a test is affected by whether a certification, licensure or qualification test associated with certain profession, career or job position is considered desirable by potential test takers. Some industries may experience fluctuations in the number of people attempting to become qualified to participate in the industry, which will depend on the overall health of the relevant industry, changes in average salary levels in the relevant industry, the popularity of certain types of careers and employers, governmental policies that impact the relevant industry, or other factors.
In addition, obtaining contracts from test sponsors for new test titles and to upgrade existing test titles often requires considerable time and resources. Many of our clients administer tests to a large number of people on a regular basis, and maintaining consistency and stability from year to year in the test delivery format is important to them. The decision process involved in adopting a new type of test or a new test delivery format can be difficult and complex. These factors often result in significant delays in our ability to secure contracts, and make it difficult to predict our revenues from fees paid by test sponsors in any given year. On the other hand, for test sponsors that administer many tests on a regular basis, our ability to secure an initial contract and to effectively meet their test delivery requirements under the contract can help us obtain future test title contracts from that test sponsor. This enables us to increase and diversify our revenues and to hinder competitors from obtaining contracts with that test sponsor.
Online Education Services
We derive online education services revenues from the provision of online education services.
ATA provides online education services for the China Futures Association and CBA by operating online education web sites and training platforms for securities and banking professionals who are required to fulfill continuing educational requirements after passing their professional licensure and certification tests. The online training entitles the end users access to online education services during a specified service period, which normally ranges between 90 to 360 days from the activation. Revenue of online education services is recognized over the service period commencing at the point of time the users access to the online training is activated and ending at the point of time the user completes the training hours. As of each reporting date, review will be conducted on all membership accounts. If the online training sold to the end users are not activated before the expiration date, related online service revenue is recognized on the expiration date. Fees from online training platform maintenance service are recognized, when collectability is reasonably assured, on a straight-line basis over the contractual period.
Significant Factors Affecting Online Education Services
A number of factors affect our revenues from online education services As our online education services aim to help test takers who passed professional licensure and certification tests fulfill their post-qualification continuing educational requirements, demand for our online education services primarily depends on whether such continuing educational requirements will still be in place going forward. In addition, as we historically offered online education services for tests that are delivered through our test delivery platform, our ability to grow our online education services is also affected by the willingness of our test sponsor clients to permit us to provide online education services for their tests. Some test sponsor clients may not permit us to provide online education services in relation to tests for which we provide test delivery and other services due to a perceived conflict of interest. Furthermore, demand for online education services for a particular test also depends on the relative level of importance or difficulty of the test, with greater demand for online education services for more important and more difficult tests. Therefore, our ability to secure test delivery services contracts for more important and more difficult tests may affect our online education services. Moreover, because we generally do not develop the learning content used in our online education services, our ability to license online education learning content and materials from the relevant test sponsor or third party content provider is also critical for continuing our offer of online education services.
Other Revenues
We derive other revenues from test content creation services, delivery of certificates to passing candidates, licensing fees paid to us by operators of our ATA authorized test centers, and other fees and services.
Test content creation services. Our test content creation services include the installation of our technology on client testing platforms, the conversion of paper-based test items into computer-based tests items, and other related services. We charge service fees for these test content creation services.
Certificate delivery. Many of our testing services clients charge passing candidates a separate fee to receive a certificate for a test passed. We deliver upon request, and charge a per-certificate fee for delivery of certificates to these candidates.
Licensing fees from ATA authorized test centers. We license our ATA name and E-testing platform technology and provide ongoing technical support, upgrades and training during the contract period in exchange for license fees.
Test administration software products. We offer our test administration software products to our clients and charge a per-software copy price for the software.
Other fees and services. From time to time and as requested by our clients, we may provide IT consulting and system integration services and other testing-related services to our clients. We also generated rental income by leasing our own property.
Cost of Revenues
Our cost of revenues consists primarily of test monitoring costs, payroll compensation, royalty fees and other related costs, all of which are directly attributable to the provision of our testing services, online education services and our other services. The following table shows our cost of revenues and gross profit for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
% |
|
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
| ||||||||||||
|
Net Revenues |
|
350,158 |
|
100.0 |
% |
417,140 |
|
100.0 |
% |
472,386 |
|
68,629 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
Cost of Revenues |
|
172,539 |
|
49.3 |
% |
208,017 |
|
49.9 |
% |
239,853 |
|
34,846 |
|
50.8 |
% |
|
Gross Profit |
|
177,619 |
|
50.7 |
% |
209,123 |
|
50.1 |
% |
232,533 |
|
33,783 |
|
49.2 |
% |
Test Monitoring Costs
Test monitoring costs consist of fees paid to test centers, including a fixed fee per test taker, which varies for different tests, to hire test proctors, to rent testing facilities and for the peripheral items used for the provision of our testing services, and signage used to identify and brand our ATA authorized test centers.
Payroll Compensation
Payroll compensation consists of base salary and related welfare benefits paid to staff in our services implementation and customer support departments.
Royalty Fees
Royalty fees primarily consist of fees paid to ETS for the distribution right in Mainland China for TOEIC exams, license fees paid to Saville Assessment for its psychometric assessment tests used in our HR Select service and license fees paid to CBA for the development and operation of its related online training platform.
Factors Affecting Gross Margin
Our gross margin is primarily affected by our revenue per test and test-related costs, including test monitoring costs, payroll compensation and royalty fees. Gross margin for different test titles varies and is typically lower for initial deliveries.
Operating Expenses
Our operating expenses consist of general and administrative expenses, sales and marketing expenses, research and development expenses, provision for doubtful accounts and impairment of intangible assets.
General and Administrative Expenses
Our general and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and benefits, travel, administration and share-based compensation expenses for our administrative, management and finance personnel, as well as other expenses including professional fees, office expenses and rental costs.
Sales and Marketing Expenses
Our sales and marketing expenses consist primarily of salaries and benefits, travel, and share-based compensation expenses for our sales and marketing personnel, as well as other expenses including sales agency fees, conference hosting expenses, advertising and promotional expenses, entertainment expenses and other sales and marketing expenses.
Research and Development Expenses
Our research and development expenses consist primarily of costs of equipment used in our research and development activities, salaries and benefits for our research and development personnel, cost of outsourcing services and other costs relating to the design, development, testing and enhancement of our products and services.
Provision for Doubtful Accounts
The provision for doubtful accounts represents our best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses resulting from our customers or non-customer business partners inability to make required payments. We consider the age of doubtful receivable, historical collection experience, and business partners individual conditions.
Impairment of Intangible Assets
The impairment of intangible assets is the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair value of our intangible assets such as brands and trademarks, relationships with test sponsors and customers, or other intangibles.
Taxation
Cayman Islands and British Virgin Islands
Under the current laws of the Cayman Islands and the British Virgin Islands, the Company and ATA BVI are not subject to income tax. In addition, upon any payments of dividends by the Company or ATA BVI, no Cayman Islands or British Virgin Islands withholding tax is imposed.
Hong Kong
Xing Wei did not derive any income that is subject to Hong Kong profits tax for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017. Accordingly, no provision for Hong Kong profits tax was required. The payment of dividends by Hong Kong companies is not subject to any Hong Kong withholding tax.
Peoples Republic of China
Our subsidiaries operating in the PRC are subject to PRC taxes as described below:
Enterprise income tax. Effective from January 1, 2008, the EIT Law imposes a tax rate of 25% on all enterprises, including foreign-invested enterprises, and terminates many of the tax exemptions, reductions and preferential treatments available under previous tax laws and regulations. Under the EIT Law, qualified high-and-new technology enterprises eligible for key support from the State (HNTE) are entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% and subject to an annual review during the valid period of their HNTE certificates. In December 2008, ATA Testing was recognized as a HNTE and obtained a HNTE certificate, which entitled ATA Testing to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years from 2008 to 2010. ATA Testing successfully renewed its HNTE certificate for another three years starting from 2011, and therefore it is entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% retroactively from January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2013. In October 2014, ATA Testing successfully renewed its HNTE certificate for another three years from 2014 and therefore it is entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2014 to 2016. ATA Testing is currently in the process of re-applying for its HNTE certificate for another three years. Upon a successful renewal, ATA Testing should be entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% retroactively from January 1, 2017. In December 2009, each of ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data received approval from the tax authority that it qualified as an HNTE for three years, entitling them to a preferential income tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2009 to 2011. From May 2012 to July 2012, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data successfully renewed their HNTE certificates, respectively, for another three years from 2012 and therefore are entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2012 to 2014. In November 2015, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data successfully renewed their HNTE certificates, respectively, for another three years from 2015 and therefore are entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% for calendar years 2015 to 2017. In the event ATA Testing, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data are unable to renew their HNTE certificates, they will be subject to the standard statutory enterprise income tax rate of 25%. See Item 3. Key InformationD. Risk FactorsRisks Relating to Regulation of Our BusinessThe discontinuation of any of the preferential tax treatments currently enjoyed by our subsidiaries in the PRC could materially increase our tax obligations. Zhongxiao Zhixing Education Technology (Beijing) Limited (Zhongxiao Zhixing), a PRC subsidiary of Xing Wei, is subject to an income tax of 25%. Beijing Puhua Huitong Education Technology Co., Limited (Puhua Technology), a PRC subsidiary of ATA Online, is also subject to an income tax of 25%.
In addition, under the EIT Law, an enterprise established under the laws of a foreign country or region whose de facto management body is located within the PRC territory is considered a resident enterprise and will generally be subject to the enterprise income tax at the rate of 25% on its global income. According to the Implementation Rules to the EIT Law, de facto management body refers to a managing body that exercises, in substance, overall management and control over the production and business, personnel, accounting and assets of an enterprise. We have determined that our overseas entities are not PRC resident enterprises for PRC income tax purposes. However, if we and our overseas entity were considered PRC resident enterprises, we would be subject to the enterprise income tax at the rate of 25% on our global income. See Item 3. Key InformationD. Risk FactorsRisks Relating to Regulation of Our BusinessUnder the EIT Law, we may be classified as a resident enterprise of China. Such classification will likely result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and U.S. holders of our ADSs or common shares, and Item 10.E. Additional Information Taxation Peoples Republic of China Taxation.
In addition, the EIT Law revokes the exemption of withholding tax on dividends paid by a PRC enterprise to its foreign investors under the old tax law and its Implementation Rules provide that a withholding tax of 10% (or other applicable withholding tax rates based on tax treaties between the PRC and other jurisdictions) will generally be applicable to dividends payable to foreign investors. To the extent we and our overseas entity are not considered as PRC resident enterprises, the dividends that our PRC subsidiaries pay to us will be subject to this withholding tax. See Item 3. Key InformationD. Risk FactorsRisks Relating to Regulation of Our BusinessUnder the EIT Law, we may be classified as a resident enterprise of China. Such classification will likely result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and U.S. holders of our ADSs or common shares. The undistributed earnings generated before January 1, 2008 shall be exempt from withholding tax when such earnings are distributed to the foreign investor in the year 2008 or thereafter. As of March 31, 2017, we have accrued withholding tax of RMB 22,620,872 on undistributed earnings of RMB 226,208,715 generated by our PRC consolidated entities since January 1, 2008 as we have changed our plan with respect to distribution of earnings from our PRC subsidiaries and do not believe the indefinite reinvestment exception for not recognizing deferred tax liability is met. We announced declaration of a cash dividend of $0.205 per common share, or $0.41 per ADS on June 1, 2017.
Under applicable Chinese tax laws, foreign-invested enterprises and domestic Chinese companies may carry forward tax losses up to five years. In view of cumulated losses noted by certain of our PRC subsidiaries and affiliated entity, as of March 31, 2017, we provided full valuation allowance for their deferred income tax assets after consideration of the scheduled reversal of existing deferred income tax liabilities.
VAT pilot program and VAT exemption of offshore outsourcing services. ATA Testing, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data subject to VAT at a rate of 6% for net revenues (i.e. VAT excluded) generated from service and license fees under the VAT pilot program under which Business Tax is being replaced by VAT gradually. This VAT is not a deduction from revenue in our consolidated statements of operations. Zhongxiao Zhixing is subject to VAT at a rate of 3% since it is classified as a Small Scale VAT payer.
Critical Accounting Policies
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP, which requires us to make judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of our assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities on the date of each set of consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during each financial reporting period. We continually evaluate these estimates and assumptions based on the most recently available information, our own historical experience and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Since the use of estimates is an integral component of the financial reporting process, actual results could differ from those estimates as a result of changes in our estimates or changes in the facts or circumstances underlying our estimates and assumptions.
An accounting policy is considered to be critical if it requires an accounting estimate to be made based on assumptions about matters that are highly uncertain at the time such estimate is made, and if different accounting estimates that reasonably could have been used, or changes in the accounting estimates that are reasonably likely to occur periodically, could materially impact the consolidated financial statements. Some of our accounting policies require higher degrees of judgment than others in their application. We consider the policies discussed below to be critical to an understanding of our consolidated financial statements as their application places the most significant demands on our managements judgment. When reviewing our consolidated financial statements, you should take into account:
· our critical accounting policies discussed below;
· the related judgments made by us and other uncertainties affecting the application of these policies;
· the sensitivity of our reported results to changes in prevailing facts and circumstances and our related estimates and assumptions; and
· the risks and uncertainties described under Item 3.D. Key Information Risk Factors.
See Note (2) to our audited consolidated financial statements for additional information regarding our significant accounting policies.
Bad Debt Allowance
We perform ongoing credit evaluations of our customers financial conditions and generally do not require collateral on accounts receivable.
The activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts for accounts receivable for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 is as follows:
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
Beginning allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
4,688,433 |
|
5,003,118 |
|
4,875,266 |
|
708,285 |
|
|
Additions charged to (reversal of) bad debt expense |
|
845,965 |
|
(127,852 |
) |
524,460 |
|
76,194 |
|
|
Write-off of accounts receivable |
|
(531,280 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ending allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
5,003,118 |
|
4,875,266 |
|
5,399,726 |
|
784,479 |
|
Income Taxes
We assess the likelihood that our net deferred income tax assets will be realized. To the extent that we believe that it is more likely than not that some portion or the entire amount of deferred income tax assets will not be realized, we establish a valuation allowance.
In assessing the realizability of deferred income tax assets, we consider whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred income tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible or tax loss carried forward are utilized. We consider the scheduled reversal of deferred income tax liability, projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment.
As of March 31, 2017, we believe it is more likely than not that we will realize the deferred income tax assets, net of the valuation allowance of RMB 41.2 million ($6.0 million). The amount of the deferred income tax assets considered realizable as of March 31, 2017 could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future taxable income are reduced.
For each of the year ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, we had no unrecognized tax benefits relating to uncertain tax positions. Also, we do not expect that the amount of unrecognized tax benefits will significantly increase within the next twelve months.
According to the PRC Tax Administration and Collection Law, the statute of limitations is three years if the underpayment of taxes is due to computational errors made by the taxpayer or the withholding agent. The statute of limitations is extended to five years under special circumstances where the underpayment of taxes is more than RMB 100,000. In the case of transfer pricing issues, the statute of limitations is ten years. There is no statute of limitations in the case of tax evasion. The income tax return of each of our companys PRC consolidated entities is subject to examination by the relevant tax authorities for the calendar tax years beginning in 2012.
Share-based payment
We measure the cost of employee share options or similar equity instruments based on the grant date fair value of the award and recognize that cost over the period during which an employee is required to provide services in exchange for the award, which generally is the vesting period. When no future services are required to be performed by the employee in exchange for an award of equity instruments, and if such award does not contain a performance or market condition, the cost of the award is expensed on the grant date. When there is a modification of the terms and conditions of an award of equity instruments, our company measures the pre-modification and post-modification fair value of the equity instruments as of the modification date and recognizes the incremental value as compensation cost over the remaining service period.
When there is a change in the grantee status from an employee to a non-employee, if grantee retains the awards on a change in status and continues to provide substantive services to our company, the change in status results in a new measurement date for the unvested awards with compensation costs measured as if the awards were newly issued to the grantee on the date of the change in status. If grantee retains the awards on a change in status and is not required to provide substantive services to the grantor subsequent to that change in status, the change in status is, in substance, an acceleration of the vesting of the arrangement.
Long-term investments
Equity method investments. Investment in common stock or in-substance common stock of an entity where we can exercise significant influence, but not control, is accounted for using the equity method. Under the equity method, the investment is initially recorded at cost and adjusted for our share of undistributed earnings or losses of the investees. Investment losses are recognized until the investment is fully written down as we do not guarantee the investees obligations nor it is committed to provide additional funding. When our carrying value in an equity method investment is reduced to zero, no further losses are recorded in our consolidated financial statements unless we guarantee obligations of the affiliated company or have committed additional funding. When the equity method accounted investees subsequently reports income, we will not record its share of such income until it exceeds the amount of its share of losses not previously recognized.
Cost method investments. Investments in equity of entities that are not considered debt securities or equity securities that have readily determinable fair values and over which we have no significant influence nor control, is accounted for using the cost method. Under the cost method, the investments are initially recorded at cost and recognized income as any dividends declared from distribution of investees earnings.
Available-for-sale investment. Available-for-sale investment is investment in convertible notes measured at fair value with unrealized gains and losses recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income.
We regularly evaluate the impairment of the long-term investments based on performance and the financial position of the investees as well as other evidence of market value. Such evaluation includes, but is not limited to, reviewing the investees cash position, recent financings, projected and historical financial performance, cash flow forecasts and financing needs. An impairment charge is recorded when the carrying amount of the investment exceeds its fair value and this condition is determined to be other-than-temporary.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth a summary, for the periods indicated, of our consolidated results of operations and each item expressed as a percentage of our total net revenues. Our historical results presented below are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for any future period.
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
% of net |
|
RMB |
|
% of net |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
% of net |
|
|
|
|
(In thousands, except for percentages) |
| ||||||||||||
|
Net revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Testing services |
|
319,055 |
|
91.1 |
% |
384,800 |
|
92.2 |
% |
430,057 |
|
62,479 |
|
91.0 |
% |
|
Online education services |
|
5,711 |
|
1.6 |
% |
4,897 |
|
1.2 |
% |
7,462 |
|
1,084 |
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Other |
|
25,392 |
|
7.3 |
% |
27,443 |
|
6.6 |
% |
34,867 |
|
5,066 |
|
7.4 |
% |
|
Total net revenues |
|
350,158 |
|
100.0 |
% |
417,140 |
|
100.0 |
% |
472,386 |
|
68,629 |
|
100 |
% |
|
Cost of revenues |
|
172,539 |
|
49.3 |
% |
208,017 |
|
49.9 |
% |
239,853 |
|
34,846 |
|
50.8 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
177,619 |
|
50.7 |
% |
209,123 |
|
50.1 |
% |
232,533 |
|
33,783 |
|
49.2 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
36,837 |
|
10.5 |
% |
36,529 |
|
8.8 |
% |
43,430 |
|
6,310 |
|
9.2 |
% |
|
Sales and marketing |
|
45,186 |
|
12.9 |
% |
42,646 |
|
10.2 |
% |
47,824 |
|
6,948 |
|
10.1 |
% |
|
General and administrative |
|
64,759 |
|
18.5 |
% |
78,341 |
|
18.8 |
% |
69,078 |
|
10,035 |
|
14.7 |
% |
|
Impairment of intangible assets |
|
310 |
|
0.1 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for (reversal of) doubtful accounts |
|
846 |
|
0.2 |
% |
(128 |
) |
0 |
% |
694 |
|
101 |
|
0.1 |
% |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
147,938 |
|
42.2 |
% |
157,388 |
|
37.8 |
% |
161,026 |
|
23,394 |
|
34.1 |
% |
|
Other operating income |
|
2,078 |
|
0.6 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from operations |
|
31,759 |
|
9.1 |
% |
51,735 |
|
12.3 |
% |
71, 507 |
|
10,389 |
|
15.1 |
% |
|
Share of losses of equity method investments |
|
(2,197 |
) |
(0.6 |
)% |
(8,829 |
) |
(2.1 |
)% |
(16,121 |
) |
(2,342 |
) |
(3.4 |
)% |
|
Impairment loss of long-term investments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(32,199 |
) |
(4,678 |
) |
(6.7 |
)% |
|
Gain from disposal of long-term investment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,600 |
|
232 |
|
0.3 |
% |
|
Interest income |
|
4,136 |
|
1.2 |
% |
3,573 |
|
0.9 |
% |
3,914 |
|
569 |
|
0.8 |
% |
|
Foreign currency exchange loss, net |
|
(1,067 |
) |
(0.3 |
)% |
(1,506 |
) |
(0.4 |
)% |
(73 |
) |
(11 |
) |
(0.0 |
)% |
|
Earnings before income tax |
|
32,631 |
|
9.4 |
% |
44,973 |
|
10.7 |
% |
28,628 |
|
4,159 |
|
6.1 |
% |
|
Income tax expense |
|
9,575 |
|
2.7 |
% |
18,922 |
|
4.5 |
% |
38,597 |
|
5,607 |
|
8.2 |
% |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
23,056 |
|
6.7 |
% |
26,051 |
|
6.2 |
% |
(9,969 |
) |
(1,448 |
) |
(2.1 |
)% |
|
Net income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(253 |
) |
(36 |
) |
(0.0 |
)% |
|
Net income (loss) attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
23,056 |
|
6.7 |
% |
26,051 |
|
6.2 |
% |
(9,716 |
) |
(1,412 |
) |
(2.1 |
)% |
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
Basic and diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
(0.03 |
) |
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2017 Compared to Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2016
Net Revenues
Our total net revenues increased by RMB 55.3 million, or 13.2%, to RMB 472.4 million ($68.6 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 417.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily as a result of an increase in net revenues from testing services.
Testing services. Testing services net revenues increased by RMB 45.3 million, or 11.8%, to RMB 430.1 million ($62.5 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 384.8 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to the increased number of tests taken for certain large existing exams, including CICPA and AMAC, the addition of the National Tour Guide Qualification Exam and Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Field Professionals Qualification Exam, and the increase in volume of certain other exams. Our net revenues from testing services provided to CICPA and AMAC, in aggregate, increased from RMB 99.7 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 to RMB 178.1 million ($25.9 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017. We generated RMB 16.2 million ($2.4 million) net revenues, in aggregate, from our newly provided testing services for the National Tour Guide Qualification Exam and Housing and Urban-Rural Construction Field Professionals Qualification Exam in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017. The increase was partially offset by the loss of our SAC exam, which contributed revenue of RMB 67.0 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. The total number of billable tests delivered increased to 12,127,203 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from 10,258,866 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.
Online education services. Our revenues from online education services increased by RMB 2.6 million, or 52.4%, to RMB 7.5 million ($1.1 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 4.9 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to increase in revenue from our online education services provided for certain large customers.
Other revenues. Other revenues increased by RMB 7.5 million, or 27.1%, to RMB 34.9 million ($5.1 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 27.4 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to (i) increase in revenue derived from services delivered in relation to the National Tour Guide Qualification Exam of RMB 4.1 million and (ii) increase in rental income of RMB 0.6 million.
Gross Profit
Our gross profit increased by RMB 23.4 million, or 11.2%, to RMB 232.5 million ($33.8 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 209.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. Our gross margin decreased to 49.2% in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2017 from 50.1% in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2016. The decrease in gross margin was primarily due to increased labor costs associated with salary increases by RMB 4.6 million, as well as a change in revenue mix.
Operating Expenses
Our operating expenses increased by RMB 3.6 million, or 2.3%, to RMB 161.0 million ($23.4 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 157.4 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.
General and administrative expenses. Our general and administrative expenses decreased by RMB 9.2 million, or 11.8%, to RMB 69.1 million ($10.0 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 78.3 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to decrease in (i) tax expenses and professional services fees incurred in connection with the reorganization of ATA Online in preparation for its New Third Board listing of RMB 8.1 million, (ii) share-based compensation expenses of RMB 3.5 million.
Sales and marketing expenses. Our sales and marketing expenses increased by RMB 5.2 million, or 12.1%, to RMB 47.8 million ($6.9 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 42.6 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to increased expenses of RMB 3.4 million we incurred as a result of our enhanced pre-sales marketing and promotion efforts and increased labor cost of our marketing personnel of RMB 1.4 million. Sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of our total net revenues decreased slightly to 10.1% in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from 10.2% in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.
Research and development expenses. Our research and development expenses increased by RMB 6.9 million, or 18.9%, to RMB 43.4 million ($6.3 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 36.5 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to the increased labor cost of RMB 4.4 million we paid to our research and development personnel and consultants relating to our new K-12 initiatives of RMB 1.5 million.
Provision for doubtful accounts. Accrual of bad debt expenses was RMB 0.7 million ($0.1 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, compared to reversal of bad debt expenses of RMB 0.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to the reversal of the collection of certain long aging receivable during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.
Impairment Loss of long-term investments
We recorded impairment loss of RMB 32.2 million ($4.7 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 related to our investments in certain companies providing online education and K-12 related services, which failed to meet the expected milestones and operation forecasts and encountered shortage of working capital resulted from continuous negative operating cash flows.
Interest Income
Our interest income increased to RMB 3.9 million ($0.6 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 from RMB 3.6 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, primarily due to the average cash balance increase compared to the prior year.
Foreign Currency Exchange Gains (Losses), Net
Our net foreign currency exchange loss primarily reflects the effects of exchanging from Renminbi to U.S. dollar and devaluation of Renminbi against U.S. dollar in relation to the re-measurement of Renminbi denominated bank deposits held by overseas entities, whose functional currency is U.S. dollar. We recorded a net foreign currency exchange loss of RMB 0.1 million ($0.01 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, compared with a net loss of RMB 1.5 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. The decrease in foreign exchange loss was primarily because a large amount of Renminbi was exchanged for U.S. dollar at our overseas bank accounts for long term investment in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, while no such exchange occurred in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
Income Tax Expense
We had income tax expense of RMB 38.6 million ($5.6 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, compared to RMB 18.9 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. The increase in our income tax expense was primarily due to accrual of withholding tax of RMB 22.6 million ($3.3 million) in connection with all undistributed earnings generated by our PRC consolidated entities since January 1, 2008 as we do not believe the permanent reinvestment exception for not recognizing deferred tax liability is met due to change of our investment plan.
Net Loss
As a result of the above factors, we had net loss of RMB 10.0 million ($1.4 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, compared to net income of RMB 26.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. The loss was primarily due to an accrual of RMB 22.6 million withholding taxes in connection with all undistributed earnings of PRC subsidiaries since January 1, 2008, as well as impairment losses of RMB 32.2 million and investment losses of RMB 16.1 million associated with certain strategic investments, which was offset by the increase of gross profit of RMB 23.4 million, driven by the robust revenue increase of RMB 55.3 million.
We had a basic loss per common share and diluted loss per common share of RMB 0.21 ($0.03) and RMB 0.21 ($0.03) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 compared to a basic earnings per common share and diluted earnings per common share of RMB 0.57 and RMB 0.57 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2016 Compared to Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2015
Net Revenues
Our total net revenues increased by RMB 66.9 million, or 19.1%, to RMB 417.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 350.2 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, primarily as a result of an increase in net revenues from testing services.
Testing services. Testing services net revenues increased by RMB 65.7 million, or 20.6%, to RMB 384.8 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 319.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, primarily due to the addition of the AMAC and CCTAA exams, and increases in the volume of certain other exams. We generated RMB 118.4 million net revenues, in aggregate, from AMAC, CCTAA and CICPA in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. Our net revenues from TOEIC and HR Select increased from RMB 76.8 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015 to RMB 86.3 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 due to on-campus recruitment tests. The total number of billable tests delivered increased to 10,258,866 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from 8,767,389 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Online education services. Our revenues from online education services decreased by RMB 0.8 million, or 14.3%, to RMB 4.9 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 5.7 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Other revenues. Other revenues increased by RMB 2.0 million, or 8.1%, to RMB 27.4 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 25.4 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, primarily due to increase in rental income.
Gross Profit
Our gross profit increased by RMB 31.5 million, or 17.7%, to RMB 209.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 177.6 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015. Our gross margin decreased slightly to 50.1% in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2016 from 50.7% in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015.
Operating Expenses
Our operating expenses increased by RMB 9.5 million, or 6.4%, to RMB 157.4 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 147.9 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
General and administrative expenses. Our general and administrative expenses increased by RMB 13.5 million, or 21.0%, to RMB 78.3 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 64.8 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, primarily due to increases in professional service expenses relating to ATA Onlines New Third Board listing and share-based compensation expenses.
Sales and marketing expenses. Our sales and marketing expenses decreased by RMB 2.6 million, or 5.6%, to RMB 42.6 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 45.2 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015. Sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of our total net revenues decreased to 10.2% in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from 12.9% in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Research and development expenses. Our research and development expenses decreased by RMB 0.3 million, or 0.8%, to RMB 36.5 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 36.8 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Provision for doubtful accounts. Reversal of bad debt expenses was RMB 0.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, compared to accrual of bad debt expenses of RMB 0.8 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, primarily due to our cash collection of several long aging accounts.
Impairment of intangible assets. Our impairment of intangible assets was RMB nil in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 compared to RMB 0.3 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Interest Income
Our interest income decreased to RMB 3.6 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 4.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, primarily due to the decrease of Chinas benchmark interest rate.
Foreign Currency Exchange Gains (Losses), Net
Our net foreign currency exchange loss primarily reflects the effects of exchanging from Renminbi to U.S. dollar and devaluation of Renminbi against U.S. dollar in relation to the re-measurement of our Renminbi denominated bank deposits held by overseas entities, whose functional currency is U.S. dollar. We recorded a net foreign currency exchange loss of RMB 1.5 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, compared with a net loss of RMB 1.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Income Tax Expense
We had income tax expense of RMB 18.9 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, compared to RMB 9.6 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015. The increase in our income tax expense was primarily due to the increase in valuation allowance of deferred income tax assets from ATA Learning and ATA Testing.
Net Income
As a result of the above factors, our net income increased to RMB 26.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from net income of RMB 23.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
Our basic earnings per common share and diluted earnings per common share increased to RMB 0.57 and RMB 0.57 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 from RMB 0.49 and RMB 0.49 in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015.
B. Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have financed our working capital and capital expenditure requirements primarily through cash generated from operating activities.
As of March 31, 2017, we had RMB 222.4 million ($32.3 million) in cash. Our cash and cash equivalents were primarily deposited with reputable banks in China and Hong Kong. We intend to finance our future additional working capital and capital expenditure needs principally from cash generated from operating activities.
We believe our current cash and expected future cash flows from operating activities, particularly from testing services and online education services, is sufficient to meet our present working capital requirements. Our current expansion plans do not require significant capital commitments. We do not expect our short-term and long-term cash requirements to be materially different. If any future projects would require additional funding, outside financing might be pursued as needed. Nevertheless, we may require additional sources of liquidity in the event of changes in business conditions or other future developments. Factors affecting our sources of liquidity include our sales performance and changes in working capital. Any change in the significant factors affecting our revenues from testing services and online education services may cause material fluctuations in our cash generated from operations. See Item 5.A. Operating and Financial Review and ProspectusOperating ResultsNet Revenues for a description of these significant factors. Changes in working capital, including any significant shortening or lengthening of our accounts receivable cycle or client prepayment cycles, may also cause fluctuations in our cash generated from operations. If our sources of liquidity are insufficient to satisfy our cash requirements, we may seek to sell additional equity or debt securities to meet our cash needs. The sale of convertible debt securities or additional equity securities could result in dilution to our shareholders. The incurrence of indebtedness would result in debt service obligations and could result in operating and financial covenants that would restrict our operations. We cannot assure you that financing will be available in amounts or on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
The following table summarizes our net cash flows with respect to operating activities, investing activities and financing activities in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017:
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
| ||||||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
45,852 |
|
64,505 |
|
61,545 |
|
8,941 |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
(52,759 |
) |
(36,801 |
) |
(93,952 |
) |
(13,649 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
(63,661 |
) |
(20,310 |
) |
7,250 |
|
1,053 |
|
|
Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash |
|
(1,084 |
) |
(21 |
) |
(63 |
) |
(9 |
) |
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash |
|
(71,652 |
) |
7,373 |
|
(25,220 |
) |
(3,664 |
) |
|
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
|
311,947 |
|
240,295 |
|
247,668 |
|
35,982 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
|
240,295 |
|
247,668 |
|
222,448 |
|
32,318 |
|
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was RMB 61.5 million ($8.9 million) in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, mainly attributable to cash collection from revenues of RMB 462.5 million ($67.2 million), partially offset by cash paid for test monitoring costs and royalty fees of RMB 166.6 million ($24.2 million) and cash paid for payroll and other operating expenses of RMB 234.4 million ($34.1 million).
Net cash provided by operating activities was RMB 64.5 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016, mainly attributable to cash collection from revenues of RMB 412.8 million, partially offset by cash paid for test monitoring costs and royalty fees of RMB 145.4 million and cash paid for payroll and other operating expenses of RMB 202.9 million.
Net cash provided by operating activities was RMB 45.9 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015, mainly attributable to cash collection from revenues of RMB 385.1 million, partially offset by cash paid for test monitoring costs and royalty fees of RMB 121.2 million and cash paid for payroll and other operating expenses of RMB 218.0 million.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 of RMB 94.0 million ($13.6 million) was primarily attributable to payment of RMB 89.9 million made for long-term investments and payment of RMB 9.9 million made for capital expenditures, partially offset by proceeds of RMB 5.5 million received from disposal of certain equity interests of an affiliate company.
Net cash used in investing activities in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 of RMB 36.8 million was primarily attributable to equity investments and amount due from shareholder of RMB 10.0 million in connection with the termination of VIE agreements (see the discussion in Note (17) of the consolidated financial statements included in this annual report). Amount due from shareholder was received in full in June 2017.
Net cash used in investing activities in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2015 of RMB 52.8 million was primarily attributable to capital expenditures for leasehold improvements and equity investments.
Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2017 of RMB 7.3 million ($1.1 million) was primarily attributable to RMB 34.0 million investment prepayment made by third-party investors to one of our subsidiaries and RMB 3.4 million cash received from short-term loan ATA BVI borrowed during the year, which was partially offset by RMB 30.0 million cash paid as collateral for financial standby letter of credit. In June 2017, the short term loan ATA BVI borrowed was fully repaid and the RMB 30.0 million cash paid as collateral for financial standby letter of credit was released back to the company.
Net cash used in financing activities in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2016 of RMB 20.3 million was primarily attributable to repurchase of common shares.
Net cash used in financing activities in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015 was primarily attributable to payment of dividends. On May 30, 2014, we declared a special cash dividend of $0.205 per common share, or $0.41 per ADS. The total amount of cash dividend distributed was $9.5 million, which was paid from cash held by ATA Inc. The dividend was paid to all shareholders of record as of the close of business on June 30, 2014.
Capital Expenditures
The following table sets forth our historical capital expenditures for the periods indicated. Actual future capital expenditures may differ from the amounts indicated below.
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
| ||||||
|
Total capital expenditures |
|
14,836 |
|
3,087 |
|
9,932 |
|
1,443 |
|
Historically, our capital expenditures have been made primarily for the purchase of office space, leasehold improvements, software, computer equipment, servers and education assessment test caseware.
Foreign Currency Exchange
ATA Inc., ATA BVI and Xing Weis functional currency is U.S. dollar. As of March 31, 2017, we had RMB 222.4 million ($32.3 million) in cash and cash equivalents. The functional currency of our PRC subsidiaries is Renminbi. The non-Renminbi portion of our revenues primarily consists of U.S. dollar-denominated licensing fees and royalty payments, while the non-Renminbi portion of our expenditures primarily consists of professional fees and royalty payments, either denominated in U.S. dollars or Hong Kong dollars. Fluctuations in exchange rates, primarily those involving the U.S. dollar against the Renminbi, may affect our costs and operating margins and reported operating results. Under the current foreign exchange system in China, our operations in China may not be able to hedge effectively against currency risk, including any possible future Renminbi devaluation. See Item 3.D. Key Information Risk Factors Risks Relating to Doing Business in the Peoples Republic of China Fluctuations in exchange rates could result in foreign currency exchange losses.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standard Update (ASU) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This ASU requires an entity to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. An entity should also disclose sufficient quantitative and qualitative information to enable users of financial statements to understand the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers. In December 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which deferred the effective date of ASU No. 2014-09. In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-08, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net) which clarifies the implementation guidance on principal versus agent considerations. The guidance includes indicators to assist an entity in determining whether it controls a specified good or service before it is transferred to the customers. The new standard is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The new standard may be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect recognized as of the date of adoption. We plan to complete our evaluation in next fiscal year, including an assessment of the new expanded disclosure requirements and a final determination of the transition method we will use to adopt the new standard.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASC Topic 842, Leases through ASU No. 2016-02. ASC Topic 842 requires a lessee to recognize all leases, including operating leases, on balance sheet via a right-of-use asset and lease liability, unless the lease is a short-term lease. All (or a portion of) fixed payments by the lessee to cover lessor costs related to ownership of the underlying assets, or executory costs, that do not represent payments for a good or service will be considered lease payments and reflected in the measurement of lease assets and lease liabilities by lessees. The new standard does not substantially change lessor accounting from current U.S. GAAP. The new standard also requires lessees and lessors to disclose more qualitative and quantitative information about their leases than current U.S. GAAP does. The standard is applied retrospectively, with elective reliefs. The new standard is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018 for a public business entity. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2016-02 will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, Compensation-Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. ASU No. 2016-09 was issued as part of the FASBs simplification initiative aimed at reducing costs and complexity while maintaining or improving the usefulness of financial information. This update involves several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, forfeitures, statutory tax withholding requirements, and classification in the statement of cash flows. This ASU is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted for any interim or annual period. If an entity early adopts the amendments in an interim period, any adjustments should be reflected as of the beginning of the fiscal year that includes that interim period, and the entity must adopt all of the amendments in the same period. We do not expect the adoption of ASU No. 2016-09 will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, which clarifies the presentation and classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2016-15 will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows - Restricted cash. This ASU requires companies to include cash and cash equivalents that have restrictions on withdrawal or use in total cash and cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows. This ASU is effective for public business entities for annual and interim periods in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. If an entity early adopts the amendments in an interim period, adjustments should be reflected at the beginning of the fiscal year that includes that interim period. The amendments in this ASU should be applied using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. We are currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2016-18 will have on our consolidated financial statements.
C. Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, Etc.
Research and development is important to our continued success. Our research and development initiatives are designed to improve our existing testing technologies and to develop new and innovative technologies. We conduct our research and development activities primarily in-house but may also from time to time outsource certain research and development activities. We have an experienced team of engineers with expertise in the fields of computing, software, system and test design and conversion. Our research and development team consisted 126 people as of March 31, 2017. We will continue to look selectively for experienced software engineers and other technology talent to further increase our technological capabilities. While we focus on development of technologies that can be commercialized and integrated into our service offerings in the short term, we also invest in the research and development of testing technologies for the medium and long term in preparation for the next generation and cutting-edge products and services. In addition, we are developing upgrades of our key technologies, including our E-testing, MTS and EzTest platforms. Our total expenses for research and development were RMB 36.8 million, RMB 36.5 million and RMB 43.4 million ($6.3 million) in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
D. Trend Information
Other than as disclosed elsewhere in this annual report, we are not aware of any trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments or events for the period from April 1, 2014 to March 31, 2017 that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our revenues, income, profitability, liquidity or capital resources, or that caused the disclosed financial information to be not necessarily indicative of future operating results or financial conditions.
E. Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not currently have, and do not expect in the future to have, any off-balance sheet arrangements or commitments. In our ongoing business, we do not plan to enter into transactions involving, or otherwise form relationships with, unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or commitments.
F. Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations
Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
The following table sets forth our contractual obligations as of fiscal year ended March 31, 2017:
|
|
|
Payment Due |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
Total |
|
Within 1 Year |
|
1-3 Years |
|
3-5 Years |
|
More than 5 Years |
|
|
|
|
(In thousands of RMB) |
| ||||||||
|
Operating Lease Obligations (1) |
|
37,739 |
|
14,078 |
|
22,251 |
|
1,410 |
|
|
|
|
Unconditional Purchase Obligation (2) |
|
6,134 |
|
4,838 |
|
1,296 |
|
|
|
|
|
(1) Our operating lease obligations comprise our office lease obligations for our offices in China. These office leases expire at different times over the period from the date of this annual report through May 2020, and will become subject to renewal. We will evaluate the need to renew each office lease on a case-by-case basis prior to its expiration.
(2) On August 11, 2011, we entered into an agreement with Saville which granted us a license to market, distribute, sell, promote, demonstrate, supply, install and support its products in Mainland China for 10 years. Each party may terminate this agreement at any time for any reason by giving the other party not less than twelve months written notice provided that the termination date shall not be earlier than the fifth anniversary of this agreement unless either party is in breach of this agreement.
Indebtedness
As of the date of this annual report, we do not have any outstanding debt, debt securities, contingent liabilities, mortgages, or liens.
G. Safe Harbor
This annual report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. See IntroductionForward-Looking Statements.
ITEM 6. DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES
A. Directors and Senior Management
The following table sets forth certain information relating to our directors and executive officers as of the date of this annual report. The business address of each of our directors and executive officers is 1/F East Gate, Building No. 2, Jian Wai Soho, No. 39 Dong San Huan Zhong Road, Chao Yang District, Beijing 100022, China.
|
Name |
|
Age |
|
Position |
|
Kevin Xiaofeng Ma |
|
53 |
|
Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer |
|
Andrew Yan |
|
59 |
|
Director |
|
Hope Ni |
|
45 |
|
Director |
|
Alec Tsui |
|
68 |
|
Director |
|
Zhilei Tong |
|
42 |
|
Director |
|
Amy Tung |
|
45 |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
Alex Tong |
|
54 |
|
Vice President of Business Development |
Kevin Xiaofeng Ma is co-founder, chairman of the board and chief executive officer of our company. Prior to co-founding our company, Mr. Ma co-founded Dynamic Technology Corporation and served as its chief executive officer from 1996 to 1998. From 1990 to 1996, Mr. Ma served as a general manager in the Hainan High-Tech Industry International Cooperation Center. Previously, Mr. Ma gained experience as a vice president at the Beijing MIDI High-Tech Center, as a director of Beijing Zhongjia Integrated Intelligent System Engineering, and as a reporter for China Radio International. Mr. Ma is a member of the board of directors of a number of private enterprises with operations in China, which do not compete with our business. Mr. Ma graduated from Nanjing University with a bachelors degree in economics.
Andrew Yan is a director of our company, and is an independent director pursuant to Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(a)(2). He is the founding managing partner of SAIF Partners IV, III and SB Asia Investment Fund II L.P., and president and executive managing director of Softbank Asia Infrastructure Fund. Before joining Softbank Asia Infrastructure Fund in 2001, Mr. Yan was a managing director and the head of the Hong Kong office of Emerging Markets Partnership, the management company of AIG Asian Infrastructure Funds from 1994 to 2001. From 1989 to 1994, he worked in the World Bank, the Hudson Institute and US Sprint Co. as an economist, research fellow and director for Asia respectively in Washington, DC. From 1982 to 1984, he was the chief engineer of Jianghuai Airplane Corp. He is currently an independent non-executive director of China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation, China Resources Land Limited and Cogobuy Group, non-executive director of Guodian Technology & Environment Group Corporation Limited, Ozner Water International Holding Limited, eSun Holdings Limited and China Huiyuan Juice Group Limited. He is also an independent director of BlueFocus Communication Group, TCL Corporation, ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd and Sky Solar Holdings Limited. He also holds directorship in several SAIF portfolio companies. Mr. Yan received a master of arts degree from Princeton University, and a bachelors degree in engineering from the Nanjing Aeronautic Institute.
Hope Ni has been an independent director of ATA Inc. and ATA Online. Ms. Ni is an executive director and the chief investment officer of Cogobuy Group (listed on the Main Board of The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong). Ms. Ni currently serves on the boards of JA Solar Holdings Co (NASDAQ: JASO) and Digital China Holdings Ltd. (Stock code: 00861.HK). From 2004 to 2007, Ms. Ni was the chief financial officer and director of Viewtran Group, Inc. (NASDAQ: VIEW), during which time, Viewtran Group increased market capitalization approximately seven times. In 2008, Ms. Ni served as the vice chairman of Viewtran Group, Inc. Prior to that, Ms. Ni spent six years as a practicing attorney at Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom LLP in New York and Hong Kong. Earlier in her career, Ms. Ni worked at Merrill Lynchs investment banking division in New York. Ms. Ni received her J.D. degree from University of Pennsylvania Law School and her B.S. degree in applied economics and business management from Cornell University.
Alec Tsui is an independent director on our board and ATA Online. Mr. Tsui is currently an independent non-executive director of a number of companies listed in Hong Kong, Philippines and on the Nasdaq Global Market, including, COSCO Shipping International (Hong Kong) Co Ltd., Pacific Online Limited, Summit Ascent Holdings Limited, Melco Resorts & Entertainment Limited, Melco Crown (Philippines) Resorts Corporation, Kangda International Environmental Company Limited and DTXS Silk Road Investment Holdings Company Limited. He was the chairman of the Hong Kong Securities Institute from 2001 to 2004. He was an advisor and a council member of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange from 2001 to 2002. He joined the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 1994 as an executive director of the finance and operations services division and became its chief executive in 1997. Prior to that, Mr. Tsui served at the Securities and Futures Commission of Hong Kong from 1989 to 1993. Mr. Tsui graduated from the University of Tennessee with a B.S. degree and a masters degree in industrial engineering. He completed a program for senior managers in government at the John F. Kennedy School of Government of Harvard University.
Zhilei Tong is a director of our board. Mr. Tong founded Chinese All Digital Publishing Group Co., Ltd. in 2000 and is currently the chairman and CEO of Chinese All Digital Publishing Group Co., Ltd. He is also the executive director of Shanghai Wenrui Investment co., Ltd., the executive director and CEO of Beijing ChineseAll Education Technology Development Co., Limited, the executive director of Shanghai ChineseAll Culture Development Co., Ltd., the chairman of Hubei ChineseAll Digital Publishing Co., Ltd. and the executive director of Hangzhou ChineseAll Information Technology Co., Ltd., the executive director of ChineseAll (Tianjin) Culture Development Co., Ltd., the executive director of ChineseAll Group Limited, the director of Beijing Yajieshanghui Consulting Co., Ltd., a representative of the 16th Peoples Congress of Beijing Dongcheng District, a member of the Secretary General in the All-China Youth Federation and secretary general in education subsector, the vice-chairman in Youth Federation of Dongcheng District of Beijing, the vice president of the Copyright Society of China, the vice president of China Audio-video and Digital Publishing Association, the vice-chairman of China Redactological Society. Mr. Tong received his bachelors degree from Tsinghua University and his IMBA degree from MIT and Tsinghua University.
Amy Tung is our Chief Financial Officer having assumed such role on April 1, 2017. Ms. Tung has been with the Company since 2006, serving in roles previously including the assistant to the CEO and vice president/financial controller. Prior to her service with ATA, Ms. Tung has held various financial and accounting positions with Bayer Healthcare Limited in Hong Kong, BEA Systems (Hong Kong) Limited, Bureau Veritas Consumer Products Services (Hong Kong) Limited, Agilent Technologies Hong Kong Limited, and Compaq Computer Limited. Ms. Tung received her masters degree in financial engineering from Columbia University and her MBA and bachelors degree in computer science from the Chinese University of Hong Kong. She is a fellow member of the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants and the Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
Alex Tong is our vice president in charge of business development. Prior to joining us in September 2005, Mr. Tong worked as a general manager for the Asia Pacific region at the Royal Institution of Charted Surveyors from 2003 to 2005. Prior to that, Mr. Tong worked for Thomson Prometric in the position of executive director from 1999 to 2003 and as the managing director at Pearson NCS Hong Kong Ltd. from 1997 to 1999. Mr. Tong graduated from University of Nottingham with a bachelors degree in education and a masters degree of philosophy in education and from the Chinese University of Hong Kong with an executive MBA.
B. Compensation
For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017, we and our subsidiaries paid aggregate cash compensation of approximately RMB 7.3 million ($1.1 million) to our directors and executive officers as a group, and 692,000 restricted shares were granted to directors and selected executive officers. We do not pay or set aside any amounts for pension, retirement or other benefits for our officers and directors.
Share Incentives
We adopted a share incentive plan, or the 2005 Plan, in April 2005, which was terminated in 2015. We adopted our 2008 Employee Share Incentive Plan, or the 2008 Plan, in January 2008. We amended and restated the 2008 Plan, or the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan, in December 2016, primarily to extend its term and expand the option pool thereunder to include the reserved but unissued common shares under the 2005 Plan. Our share incentive plans are intended to promote our success and to increase shareholder value by providing an additional means to attract, motivate, retain and reward selected directors, officers, employees and other eligible persons. An aggregate of 3,310,300 common shares are reserved for issuance under the 2005 Plan. Subject to any amendment of our Amended and Restated 2008 Plan by our directors, the maximum aggregate number of common shares that may be issued pursuant to all awards under the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan is 5,726,763 shares (which was increased from 3,026,763 shares under the 2008 Plan), plus, unless the board of directors determines a lesser amount, an annual increase on January 1 of each calendar year beginning in 2017 equal to the lesser of (x) one percent (1%) of the number of shares issued and outstanding on December 31 of the immediately preceding calendar year, and (y) 336,307 shares. As of March 31, 2017, 6,063,070 shares were authorized for issuance under the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan.
We have granted share options and restricted shares under the 2005 Plan, the 2008 Plan and the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan to selected directors, officers, employees and individual consultants and advisors. As of April 1, 2017, we have granted a total of 2,451,067 share options that are outstanding under such plans, of which 916,337 have vested. The contractual term of these options is ten years. As of April 1, 2017, we have also granted 2,700,000 restricted shares that are unvested and outstanding, and 60,000 restricted shares have vested in the year ended March 31, 2017.
Options and restricted shares granted under our share incentive plans generally do not vest unless the grantee remains under our employment or in service with us on the given vesting date.
Generally, if the grantees employment or service with us is terminated for cause, all such grantees options under our share incentive plans, vested and unvested, immediately terminate and become unexercisable. On the other hand, if the grantees employment or service with us is terminated for any reason other than for cause, all such grantees vested options terminate and become unexercisable 90 days, or three months following the grantees last day of employment or service with us, while generally all unvested options immediately terminate and become unexercisable. In circumstances where there is a death or total disability of the grantee, all such grantees vested options terminate and become unexercisable 12 months following the grantees last day of employment or service with us, while generally all unvested options immediately terminate and become unexercisable.
Our board of directors may amend, alter, suspend, or terminate our share incentive plans at any time, provided, however, that our board of directors must first seek the approval of the participants of our share incentive plans if such amendment, alteration, suspension or termination would adversely affect the rights of participants under any option granted prior to that date. Without further action by our board of directors, the 2005 Plan terminated in 2015 and the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan will terminate in 2026.
The table below sets forth the share option and restricted share grants made to our current directors and executive officers pursuant to our share incentive plans:
Share options
|
|
|
Number of Common |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Shares to be Issued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Upon Exercise of |
|
Exercise Price per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Name |
|
Options |
|
Common Share |
|
Date of Grant |
|
Vesting Start Date |
|
Date of Expiration |
| |
|
Hope Ni |
|
50,000 |
|
$ |
4.75 |
|
January 7, 2008 |
|
January 7, 2008 |
|
January 6, 2018 |
|
|
Alec Tsui |
|
50,000 |
|
$ |
4.75 |
|
January 28, 2008 |
|
January 28, 2008 |
|
January 27, 2018 |
|
|
Kevin Xiaofeng Ma |
|
1,469,460 |
|
$ |
2.24 |
|
February 10, 2015 |
|
February 10, 2015 |
|
February 9, 2025 |
|
|
Alex Tong |
|
100,000 |
|
$ |
1.705 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 16, 2027 |
|
|
Amy Tung |
|
100,000 |
|
$ |
1.705 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 16, 2027 |
|
Restricted shares
|
Name |
|
Restricted Shares |
|
Date of Grant |
|
Vesting Start Date |
|
|
Kevin Xiaofeng Ma |
|
200,000 |
|
May 30, 2011 |
|
June 1, 2011 |
|
|
|
|
90,000 |
|
February 10, 2015 |
|
February 10, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
133,000 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
|
Andrew Yan |
|
100,000 |
|
May 30, 2011 |
|
June 1, 2011 |
|
|
|
|
133,000 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
|
Hope Ni |
|
60,000 |
|
February 16, 2012 |
|
February 17, 2012 |
|
|
|
|
133,000 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
|
Alec Tsui |
|
60,000 |
|
February 16, 2012 |
|
February 17, 2012 |
|
|
|
|
133,000 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
|
Alex Tong |
|
100,000 |
|
June 13, 2013 |
|
June 13, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
|
Amy Tung |
|
30,000 |
|
February 16, 2012 |
|
February 17, 2012 |
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
June 13, 2013 |
|
June 13, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
100,000 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
January 17, 2017 |
|
C. Board Practices
Duties of Directors
Under Cayman Islands Law, our directors have a statutory duty of loyalty to act honestly in good faith with a view to our best interests. Our directors also have a duty to exercise the care, diligence and skills that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in comparable circumstances. In fulfilling their duty of care to us, our directors must ensure compliance with our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association. A shareholder has the right to seek damages if a duty owed by our directors is breached.
The functions and powers of our board of directors include, among others:
· convening shareholders annual general meetings and reporting its work to shareholders at such meetings;
· issuing authorized but unissued shares;
· declaring dividends and distributions;
· exercising the borrowing powers of our company and mortgaging the property of our company;
· approving the transfer of shares of our company, including the registering of such shares in our share register; and
· exercising any other powers conferred by the shareholders meetings or under our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association.
Terms of Directors
We have a board of five directors divided into class A, class B and class C directors. As of the date of this annual report, the class A directors are Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Zhilei Tong, the class B director is Andrew Yan, and the class C directors are Hope Ni and Alec Tsui. One third of our directors for the time being (or, if their number is not a multiple of three (3), the number nearest to but not greater than one third) shall retire from office every year at our annual general meeting of shareholders on a rotating basis. Our class A director Zhilei Tong and class C directors Hope Ni and Alec Tsui were re-elected at our 2016 annual general meeting. Our class B director Andrew Yan will retire from office and will be eligible for re-election at our 2017 annual general meeting. Our chief executive officer, which currently is Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, shall not, while holding office, be subject to retirement or be taken into account in determining the number of directors to retire in any year. Neither we nor our subsidiaries have any directors service contracts providing for benefits upon termination of employment.
Board Practices
Our board of directors has established an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nominations committee.
Audit Committee
Our audit committee consists of Hope Ni and Alec Tsui. Hope Ni is the chairman of our audit committee. Our board of directors has determined that Hope Ni and Alec Tsui are independent directors within the meaning of Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(a)(2) and meet the criteria for independence set forth in Rule 10A-3(b) of the Exchange Act. Hope Ni meets the criteria of an audit committee financial expert as set forth under the applicable rules of the SEC. The third seat on our audit committee is vacant in reliance on Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5615(a)(3), which permits a foreign private issuer like us to follow home country practices in relation to the composition of its audit committee. In this regard we have elected to adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Islands, which does not require us to have a three member audit committee or to fill all three seats on the audit committee at this time.
Our audit committee is responsible for, among other things:
· appointing the independent auditor;
· pre-approving all auditing and non-auditing services permitted to be performed by the independent auditor;
· annually reviewing the independent auditors report describing the auditing firms internal quality-control procedures, any material issues raised by the most recent internal quality-control review, or peer review, of the independent auditor and all relationships between the independent auditor and our company;
· setting clear hiring policies for employees and former employees of the independent auditor;
· reviewing with the independent auditor any audit problems or difficulties and managements responses;
· reviewing and approving all related party transactions on an ongoing basis;
· reviewing and discussing the annual audited financial statements with management and the independent auditor;
· reviewing and discussing with management and the independent auditor major issues regarding accounting principles and financial statement presentations;
· reviewing reports prepared by management or the independent auditor relating to significant financial reporting issues and judgments;
· discussing earnings press releases with management, as well as financial information and earnings guidance provided to analysts and rating agencies;
· reviewing with management and the independent auditor the effect of regulatory and accounting initiatives, as well as off-balance sheet structures, on our financial statements;
· discussing policies with respect to risk assessment and risk management with management, internal auditors and the independent auditor;
· timely reviewing reports from the independent auditor regarding all critical accounting policies and practices to be used by our company, all alternative treatments of financial information within U.S. GAAP that have been discussed with management and all other material written communications between the independent auditor and management;
· establishing procedures for the receipt, retention and treatment of complaints received from our employees regarding accounting, internal accounting controls, or auditing matters, and the confidential, anonymous submission by our employees of concerns regarding questionable accounting or auditing matters;
· annually reviewing and reassessing the adequacy of our audit committee charter;
· such other matters that are specifically delegated to our audit committee by our board of directors from time to time;
· meeting separately, periodically, with management, internal auditors and the independent auditor; and
· reporting regularly to the full board of directors.
Compensation Committee
Our compensation committee consists of Andrew Yan, Hope Ni and Alec Tsui. Andrew Yan is the chairman of our compensation committee. Our board of directors has determined that all of our compensation committee members are independent directors within the meaning of Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(a)(2).
Our compensation committee is responsible for:
· reviewing and approving our overall compensation policies;
· reviewing and approving corporate goals and objectives relevant to the compensation of our chief executive officer, evaluating our chief executive officers performance in light of those goals and objectives, reporting the results of such evaluation to the board of directors, and determining our chief executive officers compensation level based on this evaluation;
· determining the compensation level of our other executive officers;
· making recommendations to the board of directors with respect to our incentive-compensation plan and equity-based compensation plans;
· administering our equity-based compensation plans in accordance with the terms thereof; and
· such other matters that are specifically delegated to the compensation committee by our board of directors from time to time.
Nominations Committee
Our nominations committee consists of Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, Andrew Yan and Alec Tsui. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma is the chairman of the nominations committee. Although Nasdaq Stock Market Rules generally require all members of the nominations committee of a listed company to be independent directors within the meaning of Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(a)(2), Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5615(a)(3) permits a foreign private issuer like us to follow home country practices in relation to composition of its nominations committee. In this regard, we have elected to adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Islands, which does not require that any of the members of a companys nominations committee be independent directors.
Our nominations committee is responsible for, among other things:
· seeking and evaluating qualified individuals to become new directors as needed;
· reviewing and making recommendations to the board of directors regarding the independence and suitability of each board member for continued service; and
· evaluating the nature, structure and composition of other board committees.
Corporate Governance
Our board of directors has adopted a code of ethics, which is applicable to our senior executive and financial officers. In addition, our board of directors has adopted a code of conduct, which is applicable to all of our directors, officers, employees and advisors. Our code of ethics and our code of conduct are publicly available on our web site, http://www.atai.net.cn. In addition, our board of directors has adopted a set of corporate governance guidelines. The guidelines reflect certain guiding principles with respect to our boards structure, procedures and committees. The guidelines are not intended to change or interpret any law, or our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association.
Interested Transactions
A director may vote with respect to any contract or transaction in which he or she is interested, provided that the nature of the interest of any director in such contract or transaction is disclosed by him or her at or prior to its consideration and any vote in that matter.
D. Employees
We had 443, 446 and 483 employees as of March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively. As of March 31, 2017, we had 83 employees in sales and marketing, 126 in research and development, 206 in client service and support and 68 in general and administrative functions.
In April 2005, we adopted a share incentive plan, or the 2005 Plan. In January 2008, we adopted our 2008 share incentive plan, or the 2008 plan. We amended and restated the 2008 Plan, or the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan, in December 2016. We use our share incentive plans as an additional means to further attract, motivate, retain and reward selected directors, officers, employees and third-party consultants and advisors. For more information, see Item 6.B. Directors, Senior Management and Employees Compensation Share Incentives. We believe these initiatives have contributed to our ability to attract and retain talent.
As required by Chinese laws and regulations, we participate in various employee benefit plans that are organized by municipal and provincial governments, including housing, pension, medical and unemployment benefit plans. We make monthly payments to these plans in respect of each employee based on the employees compensation. We believe that we maintain a good working relationship with our employees and we have not experienced any significant labor disputes. Our employees have not entered into any collective bargaining agreements.
According to our contracts with our employees, our employees are generally prohibited from engaging in any activities that compete with our business during the period of their employment and for two years after termination of their employment with us. Furthermore, all employees are prohibited, for a period of two years following termination, from soliciting other employees to leave us and, for a period of five years following termination, from soliciting our existing clients. However, we may have difficulty enforcing these non-competition and non-solicitation terms in China because the Chinese legal system, especially with respect to the enforcement of such terms, is still developing.
E. Share Ownership
The following table sets forth information with respect to the beneficial ownership, within the meaning of Section 13(d)(3) of the Exchange Act, of our common shares as of June 22, 2017 by:
· each person known to us to own beneficially more than 5% of our common shares, and
· each of our directors and executive officers
|
|
|
Common shares beneficially owned |
| ||
|
|
|
Number (1) |
|
Percent (2) |
|
|
Directors and Executive Officers: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kevin Xiaofeng Ma(3) |
|
24,583,792 |
|
50.0 |
% |
|
Andrew Yan |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
Hope Ni |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
Alec Tsui |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
Zhilei Tong |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
Alex Tong |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
Amy Tung |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
Directors and Executive Officers Combined |
|
25,602,792 |
|
52.0 |
% |
|
Principal Shareholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Joingear Limited(4) |
|
18,427,074 |
|
38.0 |
% |
|
HSBC International Trustee Limited(5) |
|
9,843,988 |
|
20.3 |
% |
|
Able Knight Development Limited(3) |
|
4,998,988 |
|
10.3 |
% |
|
Lijun Mai(6) |
|
4,845,000 |
|
10.0 |
% |
|
Cheng-Yaw Sun(7) |
|
3,400,000 |
|
7.0 |
% |
* Beneficially owns less than 1% of our common shares.
(1) The number of common shares beneficially owned by each of the listed persons includes common shares that such person has the right to acquire within 60 days after June 22, 2017.
(2) Percentage of beneficial ownership for each of the persons listed above is determined by dividing (i) the number of common shares beneficially owned by such person by (ii) the total number of common shares outstanding, plus the number of common shares such person has the right to acquire within 60 days after June 22, 2017. The total number of our common shares outstanding as of June 22, 2017 is 48,436,886.
(3) Includes (i) (a) 423,000 common shares and (b) options to purchase 734,730 common shares held by Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, (ii) 4,998,988 common shares held by Able Knight Development Limited, which is a British Virgin Islands company ultimately wholly-owned by HSBC International Trustee Limited as trustee of an irrevocable trust constituted under the laws of the Cayman Islands with Kevin Xiaofeng Ma as the settlor and certain family members of Kevin Xiaofeng Ma as the beneficiaries and (iii) 18,427,074 common shares held by Joingear Limited, which is a British Virgin Islands company with 50.01% and 49.99% of its issued and outstanding share capital owned by Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and ChineseAll Education Group Limited, respectively. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma is the sole director of Able Knight Development Limited. The business address of Able Knight Development Limited is Portcullis TrustNet Chambers, P.O. Box 3444, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Zhilei Tong are directors of Joingear Limited. The business address of Joingear Limited is OMC Chambers, P.O. Box 3152, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands.
(4) Includes (i) (a) 12,707,436 common shares and (b) 2,787,320 ADSs, representing 5,574,640 common shares held by Joingear Limited, based on Schedule 13D Amendment No. 1 filed jointly by Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, Able Knight Development Limited, Precious Time Holdings Limited, Ma Family Trust and Joingear Limited on March 23, 2016; and (ii) (a) 100,000 common shares and (b) 22,499 ADSs, representing 44,998 common shares transferred from New Beauty Holdings Limited to Joingear Limited on April 5, 2016 and June 20, 2016, respectively. Joingear Limited is a British Virgin Islands company. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Zhilei Tong are directors of Joingear Limited.
(5) Based on a report provided by HSBC International Trustee Limited on May 4, 2017. Includes 4,998,988 common shares and 2,422,500 ADSs (representing 4,845,000 common shares) held by HSBC International Trustee Limited solely in its capacity as trustee of various trusts. These trusts include Able Knight Development Limited, holding 4,998,988 common shares, Mutual Step Holdings Limited, holding 822,500 ADSs (representing 1,645,000 common shares), Art Grace Development Limited, holding 800, 000 ADSs (representing 1,600,000 common shares) and Art Kind Technology Limited, holding 800, 000 ADSs (representing 1,600,000 common shares). The registered address of HSBC International Trustee Limited is 21 Collyer Quay, #09-01 HSBC Building, Singapore 049320.
(6) Based on a Schedule 13G filed jointly by Lijun Mai, Mutual Step Holdings Limited, Magnificent Trio Company Limited, Wealth Trust, Art Kind Technology Limited, New Knight Holdings Limited, Sunrise Trust, Art Grace Development Limited, Unique Icon Limited and Value Trust on February 17, 2009. Includes 1,645,000 common shares held by Mutual Step Holdings Limited, 1,600,000 common shares held by Art Kind Technology Limited and 1,600,000 common shares held by Art Grace Development Limited. Each of Mutual Step Holdings Limited, Art Kind Technology Limited and Art Grace Development Limited is a British Virgin Islands company ultimately wholly-owned by HSBC International Trustee Limited as trustee of an irrevocable trust constituted under the laws of Cayman Islands with Lijun Mai or certain family members of Lijun Mai as the settler and beneficiaries. Lijun Mai is the sole director of Mutual Step Holdings Limited. The business address of each of Mutual Step Holdings Limited, Art Kind Technology Limited and Art Grace Development Limited is Portcullis TrustNet Chambers, P.O. Box 3444, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands.
(7) Based on Schedule 13D filed jointly by Cheng-Yaw Sun, Twittering World Limited and Xing Wei Institute Inc. on November 22, 2013. Includes 936,936 common shares and 531,532 ADSs (representing 1,063,064 common shares) held of record by Twittering World Limited and 1,400,000 common shares held of record by Xing Wei Institute Inc. Cheng-Yaw Sun, as sole director and shareholder of Twittering World Limited and sole director of Xing Wei Institute Inc. may be deemed to have sole voting and dispositive power over the Shares held of record by Twittering World Limited and Xing Wei Institute Inc.
None of our shareholders have different voting rights from other shareholders. We are not aware of any arrangement that may, at a subsequent date, result in a change of control of our company. See Item 6.B. Directors, Senior Management and Employees Compensation Share Incentives for information on options granted to our current directors and executive officers. To our knowledge, as of June 22, 2017, none of our common shares were held by holders of record in the United States. However, 25,503,526 common shares were registered in the name of a nominee of Citibank, N.A., the depositary of our ADSs. It is likely that a large number of beneficial owners of our ADSs reside in the United Sates.
ITEM 7. MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
A. Major Shareholders
Please refer to Item 6.E. Directors, Senior Management and Employees Share Ownership.
B. Related Party Transactions
Receivable due from shareholder
In May 2015, we terminated the VIE agreements with the nominee shareholders. The entire equity interests of ATA Online were transferred from the nominee shareholders to ATA Learning and Zhongxiao Zhixing for a consideration of RMB 10.0 million, equaling to the amount of the registered capital of ATA Online. As a result, ATA Online became a wholly owned subsidiary of our company. The consideration was paid to the nominee shareholders. Mr. Haichang Xiong, transferred his consideration of RMB 1.0 million to Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma on March 29, 2016 and we received RMB 10.0 million in cash from Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma on June 7, 2017.
Sublease of Jianwai SOHO office to Master Mind
ATA Testing subleased its Jianwai SOHO office to Master Mind, an equity method accounted investee, for a monthly rent of RMB 54,678, from May 17, 2015 to May 16, 2020. ATA Testing recognized the sublease income of RMB 0.6 million and RMB 0.7 million for the year ended March 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively. ATA Testing received advanced rental fee of RMB nil and RMB 0.1 million as of March 31, 2016 and 2017 respectively, and recorded the amount in deferred revenues.
ATA Testing received a rent deposit of RMB 0.1 million from Master Mind for the sublease and recorded the amount in accrued expenses and other payables as of March 31, 2016 and 2017.
USD 1.5 million Convertible Notes
On March 30, 2016 and April 28, 2016, ATA purchased the convertible promissory notes of USD 0.3 million and USD 1.2 million issued by Brilent, respectively.
Additional Investment in Satech
In April 2016, ATA Learning made an additional strategic investment of RMB 8.5 million ($1.2 million) in Satech, an equity method accounted investee, subsequent to its initial strategic investment in Satech in early 2015. Upon completion of the additional strategic investment, ATA Learning held 30.78% equity interest in Satech.
Acquisition of Puhua Technology
On August 31, 2016, ATA Online entered into an investment agreement to make a 60% equity investment in Puhua Technology with injection of RMB 2.0 million ($0.3 million) in cash. The director of Puhua Technology was a former director of ATA Learning, who resigned from ATA Learning in July 2016.
Agreements among ATA BVI, ATA Learning and ATA Online
We previously operated most of our business in China through ATA Online, a PRC company that was previously held by PRC citizens and then became a wholly-owned subsidiary of our company in May 2015. We did not own any equity interest in ATA Online before it became our subsidiary in May 2015. Through ATA Learning, our wholly-owned subsidiary in the PRC, we had entered into a series of contractual arrangements with ATA Online and its shareholders, including loan agreements, a call option and cooperation agreement, an equity pledge agreement, a technical support agreement, a strategic consulting service agreement and powers of attorney.
The following is a summary of certain provisions of these prior agreements. All of these agreements were terminated with effect from May 20, 2015. For more complete information you should read them in their entirety.
Technical support agreement, dated October 27, 2006. Under this prior agreement, ATA Learning provided ATA Online with exclusive technical support services for the maintenance of ATA Onlines servers, networks and other equipment, software and systems. In return, ATA Online paid a quarterly service fee to ATA Learning. The service fee was mutually agreed by both parties, and was determined based on certain objective criteria such as the actual services required by ATA Online and the actual labor costs, as determined by the number of days and personnel involved, incurred by ATA Learning for providing the services during the relevant period. In addition, ATA Online reimbursed ATA Learning for out of pocket costs ATA Learning incurred in connection with providing the services.
Strategic consulting service agreement, dated October 27, 2006. Under this prior agreement, ATA Learning provided ATA Online with strategic consulting and related services for ATA Onlines business, including (1) valuation of new products; (2) industry investigation and survey; (3) marketing and promotion strategies; and (4) other services related to ATA Onlines online test preparation services business. The fees for these services were confirmed by ATA Learning and calculated monthly but paid quarterly based on actual time spent providing the services. In addition, ATA Learning had the right to adjust the fees payable by ATA Online in accordance with its performance.
Equity pledge agreement, dated October 27, 2006, as amended and restated on February 12, 2007, as amended on July 7, 2009 and as amended on April 13, 2015. To secure the payment obligations of ATA Online under the exclusive technical support agreement and the strategic consulting service agreement described above and provide additional covenants, ATA Onlines shareholders had pledged to ATA Learning their entire equity ownership interests in ATA Online. Upon the occurrence of certain events of default specified in this agreement, ATA Learning could bring a suit against ATA Online in a local PRC court to confirm the debt amount and enforce the pledge by foreclosing on the pledged equity interest. Upon foreclosure, the pledged assets would be sold off by the court in a public auction and the proceeds used to satisfy ATA Onlines outstanding liabilities under the equity pledge agreement. ATA Learning or its designee could also take part in the auction to bid for the pledged assets itself. The purpose of the equity pledges was to act as collateral for ATA Onlines performance under those agreements.
Loans to the Shareholders of ATA Online, dated October 27, 2006, as amended on February 12, 2007, on July 7, 2009 and on April 13, 2015. ATA BVI entered into loan agreements with each of Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, Haichang Xiong, Walter Lin Wang and Jianguo Wang, the shareholders of ATA Online to extend each of Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, Haichang Xiong, Walter Lin Wang and Jianguo Wang an interest free loan in the amount of RMB 9.0 million, RMB 1.0 million, RMB 1.0 million and RMB 0.1 million, respectively, for the sole purpose of investing in ATA Online as ATA Onlines registered capital. The initial term of these loans in each case was ten years, which could be extended upon the parties agreement. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, Haichang Xiong, Walter Lin Wang and Jianguo Wang could only repay the loans by transferring all of their interest in ATA Online to ATA BVI or to a third party designated by ATA BVI.
Call option and cooperation agreement, dated October 27, 2006, as amended and restated on February 12, 2007, as amended on July 7, 2009 and April 13, 2015. Through the prior call option and cooperation agreement entered into between ATA BVI and ATA Online and its shareholders, ATA BVI or any third party designated by ATA BVI had the right to acquire, in whole or in part, the respective equity interests in ATA Online of its shareholders or ATA Onlines assets when permitted by applicable PRC laws and regulations. The proceeds from the exercise of the call option would be applied to repay the loans under the loan agreement described above. Further, without ATA BVIs prior written consent, ATA Online and its shareholders were prohibited from selling, assigning, mortgaging or otherwise disposing, or creating any encumbrance on, any of ATA Onlines assets or operation or any legal or beneficial interests with respect to its revenues, entering into any transaction which may materially affect ATA Onlines assets, liability, operations, equity or other legal rights, or distributing any dividend to its shareholders.
Power of Attorney, dated March 27, 2013, April 3, 2013 and April 13, 2015. Under these prior agreements, Haichang Xiong and Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, each irrevocably and exclusively appointed and constituted ATA Learning or its designee as his attorney-in-fact to exercise on his behalf any and all rights that he had as the shareholder of ATA Online.
C. Interests of Experts and Counsel
Not applicable.
A. Consolidated statements and other financial information.
Our consolidated financial statements are included at the end of this annual report.
Legal Proceedings
We are not currently involved in any litigation, arbitration or administrative proceedings that could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations. From time to time, we may be subject to various claims and legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business.
Dividend Policy
On June 1, 2017, we have declared a cash dividend of $0.205 per common share, or $0.41 per ADS. The total amount of cash dividend distributed is expected to be approximately $10.0 million, which will be paid from the cash held by ATA Inc. to all shareholders of record as of the close of business on June 12, 2017.
Any future determination to pay dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors and will be based upon our future operations and earnings, capital requirements and surplus, general financial condition, shareholders interests, contractual restrictions and other factors our board of directors may deem relevant.
Holders of our ADSs will be entitled to receive dividends, if any, subject to the terms of the deposit agreement, to the same extent as the holders of our common shares. Cash dividends will be paid to the depositary in U.S. dollars, which will distribute them to the holders of ADSs according to the terms of the deposit agreement. Other distributions, if any, will be paid by the depositary to the holders of ADSs in any means it deems legal, fair and practical.
Under Chinas EIT Law and its Implementation Rules, both of which became effective on January 1, 2008, dividends from our PRC subsidiaries to us may be subject to a 10% withholding tax if such dividends are derived from profits generated after January 1, 2008. If we are deemed to be a PRC resident enterprise, the withholding tax may be exempted, but we will be subject to a 25% tax on our worldwide income, and our non-PRC enterprise investors may be subject to PRC income tax withholding at a rate of 10%. See Item 3. Key Information D. Risk Factors Risks Relating to Regulation of Our Business Under the EIT Law, we may be classified as a resident enterprise of China. Such classification will likely result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and U.S. holders of our ADSs or common shares, and Item 10. Additional Information E. Taxation Peoples Republic of China Taxation.
B. Significant Changes
Except as disclosed elsewhere in this annual report, we have not experienced any significant changes since the date of our audited financial statements included in this report.
A. Offering and Listing Details.
Price Range of Our ADSs
Our ADSs are listed for trading on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol ATAI. The following table sets forth the monthly high and low trading prices of our ADSs on the Nasdaq Global Market for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
High |
|
Low |
| ||
|
Yearly Highs and Lows: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
7.45 |
|
$ |
3.09 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
6.41 |
|
$ |
3.78 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
5.53 |
|
$ |
2.50 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
7.35 |
|
$ |
2.03 |
|
|
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 |
|
$ |
6.91 |
|
$ |
2.96 |
|
|
Quarterly Highs and Lows: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Quarter ended June 30, 2014 |
|
$ |
5.53 |
|
$ |
3.88 |
|
|
Quarter ended September 30, 2014 |
|
$ |
5.22 |
|
$ |
3.79 |
|
|
Quarter ended December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
4.80 |
|
$ |
2.50 |
|
|
Quarter ended March 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
5.00 |
|
$ |
3.50 |
|
|
Quarter ended June 30, 2015 |
|
$ |
7.35 |
|
$ |
3.89 |
|
|
Quarter ended September 30, 2015 |
|
$ |
5.89 |
|
$ |
2.03 |
|
|
Quarter ended December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
6.80 |
|
$ |
2.55 |
|
|
Quarter ended March 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
7.32 |
|
$ |
3.97 |
|
|
Quarter ended June 30, 2016 |
|
$ |
6.91 |
|
$ |
4.41 |
|
|
Quarter ended September 30, 2016 |
|
$ |
4.90 |
|
$ |
3.33 |
|
|
Quarter ended December 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
4.58 |
|
$ |
3.30 |
|
|
Quarter ended March 31, 2017 |
|
$ |
4.10 |
|
$ |
2.96 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Monthly Highs and Lows: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
December 2016 |
|
$ |
4.20 |
|
$ |
3.43 |
|
|
January 2017 |
|
$ |
3.99 |
|
$ |
2.96 |
|
|
February 2017 |
|
$ |
4.10 |
|
$ |
2.97 |
|
|
March 2017 |
|
$ |
4.08 |
|
$ |
3.42 |
|
|
April 2017 |
|
$ |
4.16 |
|
$ |
3.62 |
|
|
May 2017 |
|
$ |
3.92 |
|
$ |
3.40 |
|
|
June 2017 (through June 22, 2017) |
|
$ |
5.00 |
|
$ |
3.54 |
|
On June 22, 2017, the closing sale price of our ADSs as reported on the Nasdaq Global Market was US$4.84 per ADS.
B. Plan of Distribution
Not applicable.
C. Markets
See Item 9.A. above.
D. Selling Shareholders
Not applicable.
E. Dilution
Not applicable.
F. Expenses of the Issue
Not applicable.
ITEM 10. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
A. Share capital
Not applicable.
B. Memorandum and Articles of Association
We incorporate by reference into this annual report the description of our third amended and restated memorandum and articles of association contained in Description of Share Capital of our F-1 registration statement (File No. 333-148512) originally filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on January 8, 2008, as amended.
C. Material Contracts
We have not entered into any material contracts other than in the ordinary course of business and other than those described in Item 4. Information on the Company, Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects, Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions or elsewhere in this annual report on Form 20-F.
D. Exchange Controls
Regulation of Foreign Exchange
Chinas government imposes restrictions on the convertibility of the Renminbi and on the collection and use of foreign currency by Chinese entities. Under current regulations, the Renminbi is convertible for current account transactions, which include dividend distributions, interest payments, and the import and export of goods and services. Conversion of Renminbi into foreign currency and foreign currency into Renminbi for capital account transactions, such as direct investment, portfolio investment and loans, however, is still generally subject to the prior approval of the PRC State Administration of Foreign Exchange, or SAFE.
Under current Chinese regulations, Foreign-Invested Enterprises such as our Chinese subsidiaries are required to apply to SAFE for a Foreign Exchange Registration Certificate for Foreign-Invested Enterprise. With such a foreign exchange registration certificate (which is subject to review and renewal by SAFE on an annual basis), a foreign-invested enterprise may open foreign exchange bank accounts at banks authorized to conduct foreign exchange business by SAFE and may buy, sell and remit foreign exchange through such banks, subject to documentation and approval requirements. Foreign-invested enterprises are required to open and maintain separate foreign exchange accounts for capital account transactions and current account transactions. In addition, there are restrictions on the amount of foreign currency that foreign-invested enterprises may retain in such accounts.
The value of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar and other currencies is affected by, among other things, changes in Chinas political and economic conditions and Chinas foreign exchange policies. The Peoples Bank of China regularly intervenes in the foreign exchange market to limit fluctuations in Renminbi exchange rates and achieve policy goals.
Dividend Distributions
We have adopted a holding company structure, and our holding companies may rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our current and future Chinese subsidiaries for their cash requirements, including the funds necessary to service any debt we may incur or financing we may need for operations other than through our Chinese subsidiaries. Chinese legal restrictions permit payments of dividends by our Chinese subsidiaries only out of their accumulated after-tax profits, if any, determined in accordance with Chinese accounting standards and regulations. Our Chinese subsidiaries are also required under Chinese laws and regulations to allocate at least 10% of their after-tax profits determined in accordance with PRC GAAP to statutory reserves until such reserves reach 50% of the companys registered capital. Allocations to these statutory reserves and funds can only be used for specific purposes and are not transferable to us in the form of loans, advances or cash dividends. As of March 31, 2017, our Chinese subsidiaries allocated RMB 55.2 million ($8.0 million) to the general reserve fund, which is restricted for distribution to the Company. Any limitations on the ability of our Chinese subsidiaries to transfer funds to us could materially and adversely limit our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could be beneficial to our business, pay dividends and otherwise fund and conduct our business.
E. Taxation
The following is a general summary of the material Cayman Islands, U.S. federal and Peoples Republic of China income tax consequences relevant to an investment in our ADSs and common shares. The discussion is not intended to be, nor should it be construed as, legal or tax advice to any particular prospective purchaser or current holders of our ADSs. The discussion is based on laws and relevant interpretations thereof in effect as of the date of this annual report, all of which are subject to change or different interpretations, possibly with retroactive effect. The discussion does not address United States state or local tax laws, or tax laws of jurisdictions other than the Cayman Islands and the United States. You should consult your own tax advisors with respect to the consequences of acquisition, ownership and disposition of our ADSs and common shares.
Cayman Islands Taxation
The Cayman Islands currently levies no taxes on individuals or corporations based upon profits, income, gains or appreciations and there is no taxation in the nature of inheritance tax or estate duty or withholding tax applicable to us or to any holder of ADSs or common shares. There are no other taxes likely to be material to us levied by the Government of the Cayman Islands except for stamp duties which may be applicable on instruments executed in, or after execution brought within the jurisdiction of the Cayman Islands. No stamp duty is payable in the Cayman Islands on transfers of shares of Cayman Islands companies except those which hold interests in land in the Cayman Islands. The Cayman Islands is a party to a double tax treaty entered into with the United Kingdom in 2010 but is otherwise not party to any double tax treaties. There are no exchange control regulations or currency restrictions in the Cayman Islands.
Pursuant to Section 6 of the Tax Concessions Law (1999 Revision) of the Cayman Islands, we have obtained an undertaking from the Governor-in-Cabinet:
· that no law which is enacted in the Cayman Islands imposing any tax to be levied on profits or income or gains or appreciations shall apply to the Company or its operations; and
· that the aforesaid tax or any tax in the nature of estate duty or inheritance tax shall not be payable on the shares, debentures or other obligations of the Company.
The undertaking for us is for a period of twenty years from October 3, 2006.
Peoples Republic of China Taxation
In 2007 China passed a new Enterprise Income Tax Law, or the EIT Law, and its Implementing Rules, both of which became effective on January 1, 2008. The EIT Law created a new resident enterprise classification, which, if applied to us, would impose a 10% withholding tax on our non-PRC enterprise shareholders and potentially 20% to our non-PRC individual shareholders on dividends we pay to them if such dividends are derived from profits generated after January 1, 2008 and with respect to gains derived by our non-PRC shareholders from disposition of our shares or ADSs, if such dividends or gains are determined to have been derived from sources within China. See Item 3. Key Information D. Risk Factors Risks Relating to Regulation of Our Business Under the EIT Law, we may be classified as a resident enterprise of China. Such classification will likely result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and U.S. holders of our ADSs or common shares.
If we are not deemed as a resident enterprise, then dividends payable to our non-PRC shareholders and gains from disposition of our shares of ADSs by our non-PRC shareholders will not be subject to PRC withholding income tax.
United States Federal Income Taxation
This discussion describes the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. Holders (as defined below) of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our ADSs or common shares. This discussion does not address any aspect of U.S. federal gift or estate tax, the Medicare tax, or the state, local or non-U.S. tax consequences of an investment in our ADSs and common shares. This discussion applies to you only if you beneficially own our ADSs or common shares as capital assets for U.S. federal income tax purposes. This discussion does not apply to U.S. Holders who are members of a class of holders subject to special rules, such as:
· dealers in securities or currencies;
· traders in securities that elect to use a mark-to-market method of accounting for securities holdings;
· banks or certain financial institutions;
· insurance companies;
· tax-exempt organizations;
· partnerships or other entities treated as partnerships or other pass-through entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes or persons holding ADSs or common shares through any such entities;
· regulated investments companies or real estate investment trusts;
· persons that hold ADSs or common shares as part of a hedge, straddle, constructive sale, conversion transaction or other integrated investment;
· persons whose functional currency for tax purposes is not the U.S. dollar;
· persons liable for alternative minimum tax; or
· persons who actually or constructively own 10% or more of the total combined voting power of all classes of our shares (including ADSs and common shares) entitled to vote.
This discussion is based on the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, which we refer to in this discussion as the Code, its legislative history, existing and proposed regulations promulgated thereunder, published rulings and court decisions, all as of the date hereof. These laws are subject to change, possibly on a retroactive basis. In addition, this discussion relies on our assumptions regarding the value of our ADSs and common shares and the nature of our business over time. Finally, this discussion is based in part upon the representation of the depositary and the assumption that each obligation in the deposit agreement and any related agreement will be performed in accordance with its terms.
Prospective purchasers are urged to consult their own tax advisor concerning the particular U.S. federal income tax consequences to them of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our ADSs and common shares, as well as the consequences to them arising under the laws of any other taxing jurisdiction.
For purposes of the U.S. federal income tax discussion below, you are a U.S. Holder if you beneficially own ADSs or common shares as capital assets within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code and are:
· an individual citizen or resident of the United States for U.S. federal income tax purposes;
· a corporation, or other entity taxable as a corporation, that was created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or any state thereof or the District of Columbia;
· an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or
· a trust if (a) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over its administration and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust, or (b) the trust has a valid election in effect to be treated as a U.S. person.
For U.S. federal income tax purposes, income earned through a U.S. or non-U.S. partnership or other flow-through entity is attributed to its owners. Accordingly, if a partnership or other flow-through entity holds ADSs or common shares, the tax treatment of the holder will depend on the status of the partner or other owner and the activities of the partnership or other flow-through entity.
The U.S. Treasury has expressed concerns that intermediaries in the chain of ownership between the holder of an ADS and the issuer of the security underlying the ADS may be taking actions that are inconsistent with the claiming of foreign tax credits for U.S. holders of ADSs. Such actions would also be inconsistent with the claiming of the reduced rate of tax, as described below, applicable to dividends received by certain non-corporate holders. Accordingly, the availability of the reduced tax rate for dividends received by certain non-corporate holders could be affected by actions taken by intermediaries in the chain of ownership between the holder of an ADS and our company.
Dividends on ADSs or Common Shares
Subject to the Passive Foreign Investment Company discussion below, if we make distributions and you are a U.S. Holder, the gross amount of any distributions with respect to your ADSs or common shares (including the amount of any taxes withheld therefrom) will be includible in your gross income on the day you actually or constructively receive such income as dividend income if the distributions are made from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, calculated according to U.S. federal income tax principles. With respect to non-corporate U.S. holders, certain dividends received from a qualified foreign corporation may be subject to a reduced capital gains rate of taxation. A non-U.S. corporation (other than passive foreign investment corporation) is treated as a qualified foreign corporation with respect to dividends from that corporation on shares (or ADSs backed by such shares) that are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States. U.S. Treasury Department guidance indicates that our ADSs, which are listed on the Nasdaq Global Market, but not our common shares, will be readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States. You should consult your own tax advisor as to the rate of tax that will apply to you with respect to dividend distributions, if any, that you receive from us.
Subject to the Passive Foreign Investment Company discussion below, to the extent, if any, that the amount of any distribution by us on ADSs or common shares exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles, it will be treated first as a tax-free return of the U.S. Holders adjusted tax basis in the ADSs or common shares and thereafter as capital gain. However, we do not intend to calculate our earnings and profits according to U.S. federal income tax principles. Accordingly, distributions on our ADSs or common shares, if any, will generally be reported to you as dividend distributions for U.S. tax purposes. Corporations will not be entitled to claim a dividends-received deduction with respect to distributions made by us. Dividends may constitute foreign source passive income for purposes of the U.S. foreign tax credit rules. You should consult your own tax advisors as to your ability, and the various limitations on your ability, to claim foreign tax credits in connection with the receipt of dividends.
Sales and Other Dispositions of ADSs or Common Shares
Subject to the Passive Foreign Investment Company discussion below, when you sell or otherwise dispose of ADSs or common shares, you will recognize capital gain or loss in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the sale or other disposition and your adjusted tax basis in the ADSs or common shares. Any such gain or losses that you recognize will be treated as U.S. source income for foreign tax credit purposes. Your adjusted tax basis will equal the amount you paid for the ADSs or common shares. Any gain or loss you recognize will be long-term capital gain or loss if your holding period in our ADSs or common shares is more than one year at the time of disposition. If you are a non-corporate U.S. Holder, including an individual, any such long-term capital gain will be taxed at preferential rates. Your ability to deduct capital losses will be subject to various limitations.
Passive Foreign Investment Company
We believe that we were not a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes for our taxable year ended March 31, 2017, and we do not expect to be a PFIC in any future taxable year. However, PFIC status is tested each year and depends on the composition of our assets and income and the value of our assets from time to time. Since we currently hold, and expect to continue to hold, a substantial amount of cash and other passive assets and, since the value of our assets is to be determined in large part by reference to the market prices of our ADSs and common shares, which is likely to fluctuate over time, there can be no assurance that we will not be a PFIC for any taxable year.
We will be classified as a PFIC in any taxable year if either: (a) the average quarterly value of our gross assets that produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income is at least 50% of the average quarterly value of our total gross assets or (b) 75% or more of our gross income for the taxable year is passive income (such as certain dividends, interest or royalties). For purposes of the first test: (a) any cash and cash invested in short-term, interest bearing, debt instruments, or bank deposits that are readily convertible into cash will count as producing passive income or held for the production of passive income, and (b) the total value of our assets is calculated based on our market capitalization.
We will be treated as owning our proportionate share of the assets and earning our proportionate share of the income of any other corporation in which we own, directly or indirectly, at least 25% (by value) of the stock.
If we were a PFIC for any taxable year during which you held ADSs or common shares, certain adverse U.S. federal income tax rules would apply. You would be subject to additional taxes and interest charges on certain excess distributions we make and on any gain realized on the disposition or deemed disposition of your ADSs or common shares, regardless of whether we continue to be a PFIC in the year in which you receive an excess distribution or dispose of or are deemed to dispose of your ADSs or common shares. Distributions in respect of your ADSs or common shares during a taxable year would constitute excess distributions if, in the aggregate, they exceed 125% of the average amount of distributions with respect to your ADSs or common shares over the three preceding taxable years or, if shorter, the portion of your holding period before such taxable year.
To compute the tax on excess distributions or any gain, (a) the excess distribution or the gain would be allocated ratably to each day in your holding period, (b) the amount allocated to the current year and any tax year prior to the first taxable year in which we were a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income in the current year, (c) the amount allocated to other taxable years would be taxable at the highest applicable marginal rate in effect for that year, and the interest charge generally applicable to underpayments of tax will be imposed on the resulting tax attributable to each such year. In addition, if we were a PFIC, no distribution that you receive from us would qualify for taxation at the preferential rate discussed in the Item 10.E. Additional Information Taxation Dividends on ADSs or Common Shares section above.
Under certain attribution rules, if we are a PFIC, you will be deemed to own your proportionate share of lower-tier PFICs, and will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on (a) a distribution on the shares of a lower-tier PFIC and (b) a disposition of shares of a lower-tier PFIC, both as if you directly held the shares of such lower-tier PFIC.
Each U.S. Holder of a PFIC is required to file an annual report containing such information as the U.S. Treasury may require and may be required to file Internal Revenue Service Form 8621 regarding distributions received on the ADSs or common shares and any gain realized on the disposition of the ADSs or common shares. You should consult with your own tax advisor regarding reporting requirements with regard to your ADSs and common shares.
If we were a PFIC in any year, you would generally be able to avoid the excess distribution rules described above by making a timely so-called mark-to-market election with respect to your ADSs provided our ADSs are marketable. Our ADSs will be marketable as long as they remain regularly traded on a national securities exchange, such as the Nasdaq Global Market. If you made this election in a timely fashion, you would recognize as ordinary income or ordinary loss the difference between the fair market value of the ADSs as of the close of your taxable year over your adjusted basis in such ADSs. Any ordinary income resulting from this election would be taxed at ordinary income rates and would not be eligible for the reduced rate of tax applicable to qualified dividend income. Any ordinary losses would be limited to the extent of the net amount of previously included income as a result of the mark-to-market election, if any. Your basis in the ADSs would be adjusted to reflect any such income or loss. You should consult your own tax advisor regarding potential advantages and disadvantages to you of making a mark-to-market election with respect to your ADSs. The mark-to-market election will not be available for any lower tier PFIC that is deemed owned pursuant to the attribution rules discussed above. We do not intend to provide you with the information you would need to make or maintain a Qualified Electing Fund election and therefore, you will not be able to make or maintain such an election with respect to your ADSs or common shares.
U.S. Information Reporting and Backup Withholding Rules
Dividend payments with respect to the ADSs or common shares and the proceeds received on the sale or other disposition of ADSs or common shares may be subject to information reporting to the IRS and to backup. Backup withholding will not apply, however, if you (a) are a corporation or come within certain other exempt categories and, when required, can demonstrate that fact or (b) provide a taxpayer identification number, certify as to no loss of exemption from backup withholding and otherwise comply with the applicable backup withholding rules. To establish your status as an exempt person, you will be required to provide certification on IRS Form W-9. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. The amount of any backup withholding will generally be allowed as a refund or a credit against your U.S. federal income tax liability, provided that you furnish the required information to the IRS. Certain individuals holding the ADSs or common shares other than in an account at a U.S. financial institution may be subject to additional information reporting requirements.
PROSPECTIVE PURCHASERS OF OUR ADSS AND COMMON SHARES SHOULD CONSULT THEIR OWN TAX ADVISOR REGARDING THE APPLICATION OF THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO THEIR PARTICULAR SITUATIONS AS WELL AS ANY TAX CONSEQUENCES RESULTING FROM PURCHASING, HOLDING OR DISPOSING OF OUR ADSS AND COMMON SHARES, INCLUDING THE APPLICABILITY AND EFFECT OF THE TAX LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL OR NON-US JURISDICTION AND INCLUDING ESTATE, GIFT AND INHERITANCE LAWS.
F. Dividends and Paying Agents
Not applicable.
G. Statement by Experts.
Not applicable.
H. Documents on Display
We previously filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission our registration statement on Form F-1 as amended.
We have filed this annual report on Form 20-F with the Securities and Exchange Commission under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Statements made in this annual report as to the contents of any document referred to are not necessarily complete. With respect to each such document filed as an exhibit to this annual report, reference is made to the exhibit for a more complete description of the matter involved, and each such statement shall be deemed qualified in its entirety by such reference.
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Exchange Act and file reports and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Reports and other information which the Company filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including this annual report on Form 20-F, may be inspected and copied at the public reference room of the Securities and Exchange Commission at 100 F Street, N.E. Washington D.C. 20549.
You can also obtain copies of this annual report on Form 20-F by mail from the Public Reference Section of the Securities and Exchange Commission, 100 F Street, N.E., Washington D.C. 20549, at prescribed rates. Additionally, copies of this material may be obtained from the Securities and Exchange Commissions Internet site at http://www.sec.gov. The Commissions telephone number is 1-800-SEC-0330.
I. Subsidiaries Information
Not applicable.
ITEM 11. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Our exposure to interest rate risk primarily relates to interest income generated by excess cash, which is mostly held in interest-bearing bank deposits. We have not used derivative financial instruments in our investment portfolio. Interest-earning instruments carry a degree of interest rate risk. We have not been exposed, nor do we anticipate being exposed, to material risks due to changes in market interest rates. However, our future interest income may fall short of expectations due to changes in market interest rates.
Foreign Currency Risk
Because substantially all of our revenues and expenditures are denominated in Renminbi, fluctuations in the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and Renminbi will affect our balance sheet and earnings per share in U.S. dollars. In addition, appreciation or depreciation in the value of the Renminbi relative to the U.S. dollar would affect our financial results reported in U.S. dollar terms without giving effect to any underlying change in our business or results of operations. Fluctuations in the exchange rate will also affect the relative value of any dividend we issue that will be exchanged into U.S. dollars and earnings from and the value of any U.S. dollar-denominated investments we make in the future.
The value of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar and other currencies is affected by, among other things, changes in Chinas political and economic conditions and Chinas foreign exchange policies. On July 21, 2005, the PRC government changed its decade-old policy of pegging the value of the Renminbi to the U.S. dollar. However, the Peoples Bank of China regularly intervenes in the foreign exchange market to limit fluctuations in Renminbi exchange rates and achieve policy goals. Following the removal of the U.S. dollar peg, the Renminbi appreciated more than 25% against the U.S. dollar over the following eight years. Since reaching a high against the U.S. dollar in July 2008, however, the Renminbi has traded within a narrow range against the U.S. dollar. On June 19, 2010, the Peoples Bank of China announced the removal of the de facto peg. In April 2012, the trading band has been widened to 1%, and in March 2014 it was further widened to 2%, which allows the Renminbi to fluctuate against the U.S. dollar by up to 2% above or below the central parity rate published by the PBOC. In August 2015, the PBOC changed the way it calculates the mid-point price of Renminbi against U.S. dollar, requiring the market-makers who submit for the PBOCs reference rates to consider the previous days closing spot rate, foreign-exchange demand and supply as well as changes in major currency rates. This change, and other changes such as widening the trading band that may be implemented, may increase volatility in the value of the Renminbi against foreign currencies. Renminbi has appreciated modestly, from 6.7968 Renminbi per U.S. dollar on June 21, 2010 to 6.8275 Renminbi per U.S. dollar on June 22, 2017, though there also have been periods when the Renminbi has lost value against the U.S. dollar.
Very limited hedging transactions are available in China to reduce our exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. To date, we have not entered into any hedging transactions in an effort to reduce our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. While we may decide to enter into hedging transactions in the future, the availability and effectiveness of these hedging transactions may be limited and we may not be able to successfully hedge our exposure at all. In addition, our currency exchange losses may be magnified by Chinese exchange control regulations that restrict our ability to convert Renminbi into foreign currency.
ATA Inc., ATA BVI and Xing Weis functional currency is the U.S. dollar, which resulted in our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. Primarily as a result of the appreciation of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar, the translation of the net assets of ATA Inc. and ATA BVI to Renminbi during consolidation resulted in translation gain of RMB 658,228 ($95,628) which we recognized as a component of other comprehensive loss as of March 31, 2017. If the Renminbi against U.S. dollar as of March 31, 2017 had further appreciated by 10% from 6.8993 to 6.2721 as of March 31, 2017, the other comprehensive loss would have decreased by RMB 353,091 ($51,297). Further, we recognized a net foreign currency exchange loss of RMB 62,054 ($9,015) as a result of the re-measurement of the foreign currency denominated monetary assets and liabilities. If the Renminbi against U.S. dollar as of March 31, 2017 had further appreciated by 10% from 6.8993 to 6.2721 as of March 31, 2017, the foreign currency exchange loss would have decreased by RMB 23,813 ($3,460).
Inflation
China has generally not experienced significant inflation in recent years. According to Chinas National Bureau of Statistics, the change in Chinas consumer price index was 2.0%, 1.4% and 2.3% in the years 2014, 2015 and 2016, respectively. In April 2017, the year-over-year change in Chinas consumer price index was 1.2%. Neither inflation nor deflation has had a material impact on our results of operations to date, and we do not currently expect the recent inflation in China to have a significant effect on our operations.
ITEM 12. DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES
A. Debt Securities
Not applicable.
B. Warrants and Rights
Not applicable.
C. Other Securities
Not applicable.
D. American Depositary Shares
Fees Payable by ADS Holders
Citibank, N.A., the depositary of our ADR program, collects its fees for issuance and cancellation of ADSs directly from investors depositing shares or surrendering ADSs for the purpose of withdrawal or from intermediaries acting for them. Such fees are typically paid to the depositary by the brokers (on behalf of their clients) receiving the newly issued ADSs from the depositary and by the brokers (on behalf of their clients) delivering the ADSs to the depositary for cancellation. The brokers in turn charge these transaction fees to their clients. Depositary fees payable in connection with distributions of cash or securities to ADS holders and the depositary service fee are charged by the depositary to the holders of record of ADSs as of the applicable ADS record date. In the case of cash distributions, the depositary fees are generally deducted from the cash being distributed. In the case of distributions other than cash (e.g., stock dividends, rights, etc.), the depositary charges the applicable fee to the ADS record date holders concurrent with the distribution. In the case of ADSs registered in the name of the investor (whether certificated or in DRS), the depositary sends invoices to the applicable record date ADS holders. In the case of ADSs held in brokerage and custodian accounts (via DTC), the depositary generally collects its fees through the settlement systems provided by DTC (whose nominee is the registered holder of the ADSs held in DTC) from the brokers and custodians holding ADSs in their DTC accounts. The brokers and custodians who hold their clients ADSs in DTC accounts in turn charge their clients accounts the amount of the fees paid to the depositary.
In the event of refusal to pay the depositary fees the depositary may, under the terms of the deposit agreement, refuse the requested service until payment is received or may set off the amount of the depositary fees (subject payment of the applicable fees) from any distribution to be made to the ADS holder.
An ADS holder is required to pay the following service fees to the depositary:
|
Service |
|
Fees |
|
|
|
|
|
· Issuance of ADSs |
|
US$5.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) issued |
|
|
|
|
|
· Cancellation of ADSs |
|
US$5.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) issued |
|
|
|
|
|
· Distribution of cash dividends or other cash distributions |
|
US$2.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) issued |
|
|
|
|
|
· Distribution of ADSs pursuant to stock dividends, free stock distributions or exercise of rights |
|
US$5.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) issued |
|
|
|
|
|
· Distribution of securities other than ADSs or rights to purchase additional ADSs |
|
US$5.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) issued |
|
|
|
|
|
· Depositary services |
|
US$2.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) issued |
An ADS holder will also be responsible to pay certain fees and expenses incurred by the depositary bank and certain taxes and governmental charges such as:
· taxes (including applicable interest and penalties) and other governmental charges;
· such registration fees as may from time to time be in effect for the registration of shares or other deposited securities on the share register and applicable to transfers of shares or other deposited securities to or from the name of the custodian, the depositary or any nominees upon the making of deposits and withdrawals, respectively;
· such cable, telex and facsimile transmission and delivery expenses as are expressly provided in the deposit agreement to be at the expense of the person depositing or withdrawing shares or holders and beneficial owners of ADSs;
· the expenses and charges incurred by the depositary in the conversion of foreign currency;
· such fees and expenses as are incurred by the depositary in connection with compliance with exchange control regulations and other regulatory requirements applicable to shares, deposited Securities, ADSs and ADRs; and
· the fees and expenses incurred by the depositary, the custodian, or any nominee in connection with the servicing or delivery of deposited securities. The fees and charges an ADS holder may be required to pay may vary over time and may be changed by us and by the depositary bank. ADS holders will receive prior notice of such changes.
Fees and Other Payments Made by the Depositary to Us
We had received from our depositary a reimbursement of $0.1 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
ITEM 13. DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARAGES AND DELINQUENCIES
None.
ITEM 14. MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS
The rights of securities holders have not been materially modified.
ITEM 15. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this annual report, an evaluation has been carried out under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our chief executive officer and our chief financial officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as such term is defined under Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Based on that evaluation, our chief executive officer and chief financial officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective in ensuring that material information required to be disclosed in this annual report is recorded, processed, summarized and reported to them for assessment, and required disclosure is made within the time period specified in the rules and forms of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Managements Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, for our company. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of a companys assets, (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that a companys receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of a companys management and directors, and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of a companys assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, a system of internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to consolidated financial statement preparation and presentation and may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and related rules as promulgated by the Securities and Exchange Commission, management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2017 using criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
Based on this assessment, management concluded that the internal control over financial reporting was effective as of March 31, 2017 based on the criteria established in this Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013).
KPMG Huazhen LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2017, as stated in their report which is included below.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
ATA Inc.:
We have audited ATA Inc.s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). ATA Inc.s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Managements Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on ATA Inc.s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A companys internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A companys internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the companys assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, ATA Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of ATA Inc. and subsidiaries as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity, and cash flows for the years then ended, and our report dated June 29, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
|
/s/ KPMG Huazhen LLP |
|
|
|
|
|
Beijing, China |
|
|
|
|
|
June 29, 2017 |
|
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by this annual report that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 16A. AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT
Our audit committee consists of Hope Ni and Alec Tsui. Hope Ni is the chairman of our audit committee. Our board of directors has determined that Hope Ni and Alec Tsui are independent directors within the meaning of Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(a)(2) and meet the criteria for independence set forth in Rule 10A-3(b) of the Exchange Act. Hope Ni meets the criteria of an audit committee financial expert as set forth under the applicable rules of the SEC.
Our board of directors has adopted a code of ethics that is applicable to our senior executive and financial officers. In addition, our board of directors adopted a code of conduct that is applicable to all of our directors, officers and employees. Our code of ethics and our code of conduct are publicly available on our web site, http://www.atai.net.cn.
ITEM 16C. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEE AND SERVICES
The following table sets forth the aggregate fees by categories specified below in connection with certain professional services rendered by KPMG Huazhen LLP, our principal accountant, for the periods indicated.
|
|
|
For the fiscal year ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
Audit fees(1) |
|
6,718,279 |
|
6,444,720 |
|
936,297 |
|
|
Audit-related fees(2) |
|
1,601,528 |
|
1,601,528 |
|
232,672 |
|
|
Tax fees(3) |
|
321,646 |
|
333,118 |
|
48,396 |
|
(1) Audit fees means the aggregate fees billed or payable for professional services rendered by our principal accountant for the audits of our consolidated financial statements and our internal control over financial reporting of ATA Inc., and the audits of ATA Onlines New Third Board listing, its annual financial statements and special audit.
(2) Audit-related fees means the aggregate fees billed or payable for assurance and related services by our principal accountant that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our consolidated financial statements and are not reported under Audit fees. Services comprising the fees disclosed under the category of Audit-related fees in the fiscal years ended March 31, 2016 and 2017 include principally limited procedures in connection with our quarterly financial information.
(3) Tax fees means the aggregate fees billed or payable for services rendered by our principal accountant for tax advisory, tax retainer and compliance.
The audit committee or our board of directors is to pre-approve all auditing services and permitted non-audit services to be performed for us by our independent registered public accounting firm, including the fees and terms thereof (subject to the de minimums exceptions for non-audit services described in Section 10A(i)(l)(B) of the Exchange Act which are approved by the audit committee or our board of directors prior to the completion of the audit).
ITEM 16D. EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES
None.
ITEM 16E. PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(c) Total Number |
|
(d) Maximum |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of ADSs |
|
Approximate Dollar |
| ||
|
|
|
(a) Total |
|
|
|
Purchased as Part |
|
Value of ADSs that May |
| ||
|
|
|
Number |
|
(b) Average |
|
of |
|
Yet |
| ||
|
|
|
of ADSs |
|
Price |
|
Publicly |
|
Be Purchased Under the |
| ||
|
Period |
|
Purchased |
|
Paid per ADS(1) |
|
Announced Plan |
|
Plan(1), (2) |
| ||
|
September 30, 2015 |
|
4,910 |
|
$ |
2.6873 |
|
4,910 |
|
$ |
2,986,805 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
(17.3277 |
) |
|
|
RMB |
(19,258,919 |
) |
|
October 1 October 30, 2015 |
|
90,630 |
|
$ |
3.3611 |
|
90,630 |
|
$ |
2,682,189 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
(21.6724 |
) |
|
|
RMB |
(17,294,755 |
) |
|
November 2 November 20, 2015 |
|
103,046 |
|
$ |
4.4871 |
|
103,046 |
|
$ |
2,219,811 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
(28.9328 |
) |
|
|
RMB |
(14,313,341 |
) |
|
December 1 December 31, 2015 |
|
181,481 |
|
$ |
5.9861 |
|
181,481 |
|
$ |
1,133,447 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
(38.5984 |
) |
|
|
RMB |
(7,308,466 |
) |
|
January 4 January 26, 2016 |
|
187,065 |
|
$ |
6.0591 |
|
187,065 |
|
$ |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
(39.0691 |
) |
|
|
RMB |
(13 |
) |
(1) All translations from U.S. dollar to Renminbi were made at a rate of RMB 6.4480 to US$1.00, which was the noon buying rate in effect as of March 31, 2016.
(2) On November 1, 2012, we announced a share repurchase plan. Under the plan, we are approved to repurchase up to US$5.0 million worth of our outstanding ADSs from time to time through March 31, 2013. On January 31, 2013, our board of director reviewed and approved the continuation of the share repurchase program through May 31, 2013. In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2014, we repurchased a total of 5,339 ADSs from the open market at an average price of $3.9956 per ADS pursuant to this share repurchase program. On August 5, 2014, we announced a share repurchase plan. Under the Plan, we are approved to repurchase up to US$5.0 million worth of our outstanding ADSs from time to time through January 31, 2015. On September 24, 2015, we announced a share repurchase plan, under which we are authorized to repurchase up to US$3.0 million of our outstanding ADSs from time to time through March 31, 2016. As of January 26, 2016, we repurchased a total of 567,132 ADS from the open market at an average price of $5.2898 per ADS pursuant to this share repurchase program.
Other than shown in the table above, there were no other repurchases during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.
ITEM 16F. CHANGE IN REGISTRANTS CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT
Not applicable.
ITEM 16G. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
As a foreign private issuer with shares listed on the Nasdaq Global Market we are subject to corporate governance requirements imposed by Nasdaq. Under Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5615(a)(3), a foreign private issuer such as us may follow its home-country corporate governance practices in lieu of certain of the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules corporate governance requirements. We are committed to a high standard of corporate governance. As such, we strive to comply with most of the Nasdaq corporate governance practices. However, our current corporate governance practices differ from Nasdaq corporate governance requirements for U.S. companies in certain respects, as summarized below:
· Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(b)(1) requires a Nasdaq-listed company to have a board of directors composed of at least a majority of independent directors. In this regard we have elected to adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Islands, which does not require us to have a majority of the board of directors composed of independent directors at this time.
· Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(c)(2) requires a Nasdaq-listed company to have an audit committee composed of at least three independent members. In this regard we have elected to adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Islands, which does not require us to have a three member audit committee or to fill all three seats on the audit committee at this time.
· Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5605(e)(1) requires a Nasdaq-listed company to have a nominations committee composed solely of independent directors to select or recommend for selection director nominees. In this regard we have elected to adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Islands, which does not require that any of the members of a companys nominations committee be independent directors.
· Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5635(a) requires a Nasdaq-listed company to obtain shareholder approval for issuance of securities in connection with acquisitions under certain circumstances. As a foreign private issuer, however, we may adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Island, which do not require shareholder approval for issuance of securities in connection with acquisitions.
· Nasdaq Stock Market Rule 5635(c) requires a Nasdaq-listed company to obtain shareholder approval for the establishment of or material amendments to equity compensation plans. As a foreign private issuer, however, we may adopt the practices of our home country, the Cayman Island, which do not require shareholder approval for establishment or material amendments to equity compensation plans. None of the 2005 Plan, the 2008 Plan and the Amended and Restated 2008 Plan requires shareholder approval for material amendments to the plan or awards granted under the plan, including without limitation increasing the number of share awards that may be issued under the plan or the repricing of outstanding options.
ITEM 16H. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
Not Applicable.
Our consolidated financial statements are included at the end of this annual report.
Index to Exhibits
|
Exhibit |
|
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
1.1 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association of the Registrant.* |
|
|
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
Form of Common Share Certificate.* |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
Form of Deposit Agreement between the Registrant and Citibank, N.A., as depositary.(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
2.3 |
|
Form of American depositary receipt evidencing American depositary shares (included in Exhibit 2.2).* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
2005 Share Incentive Plan of ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited.* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
|
2008 Employee Share Incentive Plan of the Registrant and form of ISO Option Agreement and NQSO Option Agreement.* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
|
Form of Indemnification Agreement between the Registrant and its directors.* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.4 |
|
Technical Support Agreement between ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd and ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., dated October 27, 2006.* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
Strategic Consulting Service Agreement between ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd and ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., dated October 27, 2006.* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
|
Loan Agreement between ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited and Xiaofeng Ma, dated October 27, 2006, which was amended on February 12, 2007.* |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6.1 |
|
Amendment to Loan Agreement between ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited and Xiaofeng Ma, dated July 7, 2009.** |
|
4.7 |
|
Loan Agreement between ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited and Lin Wang, dated October 27, 2006, which was amended on February 12, 2007.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.7.1 |
|
Amendment to Loan Agreement between ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited and Lin Wang, dated July 7, 2009.** | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.8 |
|
Call Option and Cooperation Agreement among ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited, Xiaofeng Ma, Lin Wang, Jianguo Wang and ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd, dated October 27, 2006.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.9 |
|
Framework Agreement for Option Right Exercise among ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited, Lin Wang, Jianguo Wang, ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd and ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., dated February 12, 2007.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.10 |
|
Option Exercise Notice between ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited and Jianguo Wang, dated February 12, 2007.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.11 |
|
Call Option and Cooperation Agreement among ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited, Xiaofeng Ma, Lin Wang and ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd, dated February 12, 2007.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.12 |
|
Equity Pledge Agreement among Xiaofeng Ma, Lin Wang and ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., dated February 12, 2007.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.13 |
|
Extended Control Agreement among Xiaofeng Ma, Lin Wang, ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd, ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., and ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited, amending the Technical Support Agreement (Exhibit 4.5), the Strategic Consulting Service Agreement (Exhibit 4.6), the Call Option and Cooperation Agreement (Exhibit 4.12), and the Equity Pledge Agreement (4.13), dated July 7, 2009. ** | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.14 |
|
Power of Attorney by Xiaofeng Ma in favor of ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., dated March 27, 2013.*** | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.15 |
|
Power of Attorney by Lin Wang in favor of ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc., dated April 3, 2013.*** | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
4.16 |
|
Framework Agreement on Restructuring, May 20, 2015.**** | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
8.1 |
|
List of Subsidiaries. | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
11.1 |
|
Code of Conduct.* | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
12.1 |
|
CEO Certification Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
12.2 |
|
CFO Certification Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
13.1 |
|
CEO Certification Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
13.2 |
|
CFO Certification Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
23.1 |
|
Consent of KPMG Huazhen LLP | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
23.2 |
|
Consent of KPMG | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
23.3 |
|
Consent of Jincheng Tongda & Neal Law Firm | ||
|
101.INS |
|
XBRL Instance Document |
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
* Previously filed with the Registrants registration statement on Form F-1 (File No. 333-148512), as amended.
** Previously filed with the Registrants annual report on Form 20-F, filed with the SEC on September 15, 2009.
*** Previously filed with the Registrants annual report on Form 20-F, filed with the SEC on June 26, 2013.
**** Previously filed with the Registrants annual report on Form 20-F, filed with the SEC on June 24, 2015.
(1) Incorporated by reference to the Registration Statement on Form F-6 (File No. 333-148641) filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission with respect to American depositary shares representing our common shares.
The registrant hereby certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this annual report on its behalf.
|
|
ATA INC. | |
|
|
| |
|
|
/s/ Amy Tung | |
|
|
Name: |
Amy Tung |
|
|
Title: |
Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: June 29, 2017 |
|
|
ATA Inc.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
|
F-2 - F-3 | |
|
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
|
|
|
|
|
F-4 | |
|
F-5 | |
|
F-6 | |
|
F-7 - F-8 | |
|
F-9 - F-43 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
ATA Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of ATA Inc. and subsidiaries as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity, and cash flows for the years then ended. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Companys management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of ATA Inc. and subsidiaries as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended March 31, 2017 have been translated into United States dollars solely for the convenience of the reader. We have audited the translation and, in our opinion, the consolidated financial statements expressed in Renminbi have been translated into United States dollars on the basis set forth in Note 2(d) of the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), ATA Inc.s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated June 29, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Companys internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG Huazhen LLP
Beijing, China
June 29, 2017
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
ATA Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity, and cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2015. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Companys management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the results of ATA Inc. and subsidiaries operations and their cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2015, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
|
/s/ KPMG |
|
|
|
|
|
Hong Kong, China |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 24, 2015 |
|
ATA INC.
|
|
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
Note |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
247,667,737 |
|
222,448,413 |
|
32,317,587 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
(3) |
|
50,552,034 |
|
56,161,255 |
|
8,159,178 |
|
|
Receivable due from shareholder |
|
(17) |
|
10,000,000 |
|
10,000,000 |
|
1,452,813 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
(4) |
|
8,268,380 |
|
7,335,824 |
|
1,065,757 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
|
316,488,151 |
|
295,945,492 |
|
42,995,335 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term investments |
|
(5) |
|
50,685,846 |
|
88,891,687 |
|
12,914,297 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
(7) |
|
57,229,727 |
|
51,868,914 |
|
7,535,581 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
(8) |
|
31,011,902 |
|
32,523,983 |
|
4,725,125 |
|
|
Intangible assets, net |
|
(8) |
|
750,895 |
|
11,326,513 |
|
1,645,530 |
|
|
Restricted cash |
|
(2)(m) |
|
|
|
30,000,000 |
|
4,358,438 |
|
|
Deferred income tax assets |
|
(12) |
|
3,687,804 |
|
3,388,760 |
|
492,323 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
|
10,606,805 |
|
5,894,767 |
|
856,400 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
|
470,461,130 |
|
519,840,116 |
|
75,523,029 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short term loan |
|
(2)(m) |
|
|
|
3,449,650 |
|
501,170 |
|
|
Accrued expenses and other payables |
|
(9) |
|
57,739,627 |
|
89,358,847 |
|
12,982,166 |
|
|
Deferred revenues |
|
(10) |
|
16,612,164 |
|
10,221,897 |
|
1,485,050 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
74,351,791 |
|
103,030,394 |
|
14,968,386 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred revenues |
|
(10) |
|
1,878,751 |
|
1,731,622 |
|
251,572 |
|
|
Deferred income tax liabilities |
|
(12) |
|
|
|
22,620,872 |
|
3,286,389 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
76,230,542 |
|
127,382,888 |
|
18,506,347 |
|
|
Shareholders equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common shares: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Par value USD 0.01, authorized: 500,000,000 shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issued: 46,439,706 and 49,068,082 shares as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding: 45,734,348 and 45,782,724 shares as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively |
|
|
|
3,530,704 |
|
3,533,912 |
|
513,411 |
|
|
Treasury shares585,358 common shares as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, at cost |
|
(14) |
|
(27,737,073 |
) |
(27,737,073 |
) |
(4,029,677 |
) |
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
|
395,876,282 |
|
402,631,430 |
|
58,494,803 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
(25,174,129 |
) |
(25,069,771 |
) |
(3,642,168 |
) |
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
|
47,734,804 |
|
38,018,802 |
|
5,523,420 |
|
|
Total shareholders equity attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
|
|
394,230,588 |
|
391,377,300 |
|
56,859,789 |
|
|
Non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
1,079,928 |
|
156,893 |
|
|
Total shareholders equity |
|
|
|
394,230,588 |
|
392,457,228 |
|
57,016,682 |
|
|
Commitments and contingencies |
|
(18) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and shareholders equity |
|
|
|
470,461,130 |
|
519,840,116 |
|
75,523,029 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
ATA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
Note |
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
Net revenues |
|
(11) |
|
350,157,824 |
|
417,139,969 |
|
472,385,716 |
|
68,628,794 |
|
|
Cost of revenues |
|
|
|
172,539,260 |
|
208,017,208 |
|
239,852,504 |
|
34,846,075 |
|
|
Gross profit |
|
|
|
177,618,564 |
|
209,122,761 |
|
232,533,212 |
|
33,782,719 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
|
36,836,338 |
|
36,529,145 |
|
43,430,385 |
|
6,309,622 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
|
45,186,175 |
|
42,645,682 |
|
47,823,235 |
|
6,947,820 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
|
64,759,122 |
|
78,341,173 |
|
69,078,028 |
|
10,035,743 |
|
|
Impairment of intangible assets |
|
|
|
310,153 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for (reversal of) doubtful accounts |
|
|
|
845,965 |
|
(127,852 |
) |
694,460 |
|
100,892 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
|
147,937,753 |
|
157,388,148 |
|
161,026,108 |
|
23,394,077 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other operating income |
|
|
|
2,077,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from operations |
|
|
|
31,758,311 |
|
51,734,613 |
|
71,507,104 |
|
10,388,642 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other income (loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share of losses of equity method investments |
|
|
|
(2,196,750 |
) |
(8,829,140 |
) |
(16,121,334 |
) |
(2,342,128 |
) |
|
Impairment loss of long-term investments |
|
(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
(32,199,372 |
) |
(4,677,965 |
) |
|
Gain from disposal of long-term investment |
|
(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
1,600,000 |
|
232,450 |
|
|
Interest income, net of interest expenses |
|
|
|
4,136,454 |
|
3,572,711 |
|
3,913,950 |
|
568,624 |
|
|
Foreign currency exchange losses, net |
|
|
|
(1,067,149 |
) |
(1,505,518 |
) |
(72,769 |
) |
(10,572 |
) |
|
Total other income (loss), net |
|
|
|
872,555 |
|
(6,761,947 |
) |
(42,879,525 |
) |
(6,229,591 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings before income taxes |
|
|
|
32,630,866 |
|
44,972,666 |
|
28,627,579 |
|
4,159,051 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income tax expense |
|
(12) |
|
9,575,146 |
|
18,921,479 |
|
38,596,986 |
|
5,607,419 |
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,969,407 |
) |
(1,448,368 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(253,405 |
) |
(36,815 |
) |
|
Net income (loss) attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
|
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,716,002 |
) |
(1,411,553 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,969,407 |
) |
(1,448,368 |
) |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of nil income tax |
|
|
|
(30,753 |
) |
2,002,553 |
|
658,228 |
|
95,628 |
|
|
Unrealized loss on available-for-sale investment, net of nil income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(553,870 |
) |
(80,467 |
) |
|
Total other comprehensive income(loss) |
|
|
|
(30,753 |
) |
2,002,553 |
|
104,358 |
|
15,161 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
|
23,024,967 |
|
28,053,740 |
|
(9,865,049 |
) |
(1,433,207 |
) |
|
Comprehensive loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(253,405 |
) |
(36,815 |
) |
|
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
|
|
23,024,967 |
|
28,053,740 |
|
(9,611,644 |
) |
(1,396,392 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) per common share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
(20) |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
(0.03 |
) |
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
attributable to ATA Inc. |
|
(20) |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
(0.03 |
) |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
ATA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
|
|
|
Common shares |
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
Retained |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
Number |
|
Amount |
|
Treasury |
|
Additional |
|
other |
|
Non- |
|
earnings |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of March 31, 2014 |
|
45,281,518 |
|
3,474,894 |
|
(1,029,766 |
) |
437,964,776 |
|
(27,145,929 |
) |
|
|
(1,372,103 |
) |
411,891,872 |
|
|
Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23,055,720 |
|
23,055,720 |
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of nil income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(30,753 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(30,753 |
) |
|
Share-based compensation (Note 13) |
|
214,314 |
|
|
|
2,983,072 |
|
4,128,244 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,111,316 |
|
|
Issuance of common shares with net-settlement of employee individual income tax |
|
577,064 |
|
38,824 |
|
(1,792,215 |
) |
3,814,809 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,061,418 |
|
|
Repurchase of common shares (Note 14) |
|
(612,314 |
) |
|
|
(8,362,136 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(8,362,136 |
) |
|
Special cash dividend (Note 15) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(58,405,029 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(58,405,029 |
) |
|
Balance as of March 31, 2015 |
|
45,460,582 |
|
3,513,718 |
|
(8,201,045 |
) |
387,502,800 |
|
(27,176,682 |
) |
|
|
21,683,617 |
|
377,322,408 |
|
|
Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26,051,187 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of nil income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,002,553 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,002,553 |
|
|
Share-based compensation (Note 13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,164,822 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,164,822 |
|
|
Issuance of common shares with net-settlement of employee individual income tax |
|
273,766 |
|
16,986 |
|
|
|
(791,340 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(774,354 |
) |
|
Repurchase of common shares (Note 14) |
|
|
|
|
|
(19,536,028 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(19,536,028 |
) |
|
Balance as of March 31, 2016 |
|
45,734,348 |
|
3,530,704 |
|
(27,737,073 |
) |
395,876,282 |
|
(25,174,129 |
) |
|
|
47,734,804 |
|
394,230,588 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(253,405 |
) |
(9,716,002 |
) |
(9,969,407 |
) |
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of nil income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
658,228 |
|
|
|
|
|
658,228 |
|
|
Unrealized loss on available-for-sale investment, net of nil income tax (Note 5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(553,870 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(553,870 |
) |
|
Share-based compensation (Note 13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,958,403 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,958,403 |
|
|
Issuance of common shares with net-settlement of employee individual income tax |
|
48,376 |
|
3,208 |
|
|
|
(203,255 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(200,047 |
) |
|
Acquisition of non-controlling interests (Note 21) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,333,333 |
|
|
|
1,333,333 |
|
|
Balance as of March 31, 2017 |
|
45,782,724 |
|
3,533,912 |
|
(27,737,073 |
) |
402,631,430 |
|
(25,069,771 |
) |
1,079,928 |
|
38,018,802 |
|
392,457,228 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of March 31, 2017-USD |
|
|
|
513,411 |
|
(4,029,677 |
) |
58,494,803 |
|
(3,642,168 |
) |
156,893 |
|
5,523,420 |
|
57,016,682 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
ATA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,969,407 |
) |
(1,448,368 |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest on restricted cash for financial standby letter of credit |
|
|
|
|
|
(495,247 |
) |
(71,950 |
) |
|
Gain from disposal of long-term investment (Note 5) |
|
|
|
|
|
(1,600,000 |
) |
(232,450 |
) |
|
Provision for (reversal of) doubtful accounts |
|
845,965 |
|
(127,852 |
) |
694,460 |
|
100,892 |
|
|
Impairment of intangible assets |
|
310,153 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
7,583,790 |
|
8,611,508 |
|
10,293,833 |
|
1,495,501 |
|
|
Loss (gain) from disposal of property and equipment |
|
734 |
|
(54,955 |
) |
(14,186 |
) |
(2,061 |
) |
|
Share-based compensation |
|
7,111,316 |
|
9,164,822 |
|
6,958,403 |
|
1,010,926 |
|
|
Deferred income tax expense (benefit) (Note 12) |
|
(849,689 |
) |
7,053,724 |
|
22,919,916 |
|
3,329,834 |
|
|
Share of losses of equity method investments |
|
2,196,750 |
|
8,829,140 |
|
16,121,334 |
|
2,342,128 |
|
|
Impairment loss of long-term investments |
|
|
|
|
|
32,199,372 |
|
4,677,965 |
|
|
Interest on convertible note (Note 5) |
|
|
|
|
|
(568,320 |
) |
(82,566 |
) |
|
Foreign currency exchange loss |
|
997,149 |
|
2,023,109 |
|
253,986 |
|
36,899 |
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of acquisition: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restricted cash |
|
2,700,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
19,357,064 |
|
(2,274,136 |
) |
(6,133,681 |
) |
(891,109 |
) |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
(893,856 |
) |
(1,129,761 |
) |
1,508,565 |
|
219,166 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
(7,574,162 |
) |
29,514 |
|
(245,162 |
) |
(35,617 |
) |
|
Income tax payable |
|
(11,258,806 |
) |
7,244,175 |
|
(3,044,352 |
) |
(442,287 |
) |
|
Accrued expenses and other payables |
|
(10,657,651 |
) |
4,099,848 |
|
(797,392 |
) |
(115,846 |
) |
|
Deferred revenues |
|
12,927,758 |
|
(5,015,552 |
) |
(6,537,396 |
) |
(949,761 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
45,852,235 |
|
64,504,771 |
|
61,544,726 |
|
8,941,296 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for property and equipment |
|
(14,836,069 |
) |
(3,086,987 |
) |
(3,210,222 |
) |
(466,385 |
) |
|
Cash paid for education assessment test caseware |
|
|
|
|
|
(6,721,698 |
) |
(976,536 |
) |
|
Cash receipt from property and equipment disposal |
|
30,490 |
|
67,830 |
|
14,536 |
|
2,112 |
|
|
Proceeds from disposal of affiliates |
|
|
|
|
|
5,500,000 |
|
799,047 |
|
|
Proceeds from acquisition of a subsidiary, less cash paid |
|
|
|
|
|
411,583 |
|
59,795 |
|
|
Cash paid for long-term investments |
|
(37,953,864 |
) |
(23,782,307 |
) |
(89,945,800 |
) |
(13,067,440 |
) |
|
Cash paid to shareholder (Note 17) |
|
|
|
(10,000,000 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
(52,759,443 |
) |
(36,801,464 |
) |
(93,951,601 |
) |
(13,649,407 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for employee individual income tax for net-settlement of vested shares |
|
(853,404 |
) |
(774,354 |
) |
(200,047 |
) |
(29,063 |
) |
|
Cash paid for repurchase of common shares |
|
(8,362,136 |
) |
(19,536,028 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from exercise of share options |
|
3,903,952 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash received from short-term loan |
|
|
|
|
|
3,449,650 |
|
501,170 |
|
|
Cash received from third party investors (Note 9) |
|
|
|
|
|
34,000,000 |
|
4,939,563 |
|
|
Restricted cash for financial standby letter of credit |
|
|
|
|
|
(30,000,000 |
) |
(4,358,439 |
) |
|
Special cash dividend |
|
(58,349,122 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash (used in)/received from financing activities |
|
(63,660,710 |
) |
(20,310,382 |
) |
7,249,603 |
|
1,053,231 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
ATA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (Continued)
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash |
|
(1,083,809 |
) |
(20,559 |
) |
(62,052 |
) |
(9,015 |
) |
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash |
|
(71,651,727 |
) |
7,372,366 |
|
(25,219,324 |
) |
(3,663,895 |
) |
|
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
|
311,947,098 |
|
240,295,371 |
|
247,667,737 |
|
35,981,482 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
|
240,295,371 |
|
247,667,737 |
|
222,448,413 |
|
32,317,587 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for income tax |
|
23,104,750 |
|
14,308,992 |
|
19,756,064 |
|
2,870,186 |
|
|
Cash refunded for income tax |
|
(1,421,109 |
) |
(9,685,409 |
) |
(1,034,642 |
) |
(150,314 |
) |
|
Cash paid for interest expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
57,572 |
|
8,364 |
|
|
Non-cash investing and financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of property and equipment included in accrued expenses and other payables |
|
146,126 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(1) DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS, ORGANIZATION AND SIGNIFICANT CONCENTRATIONS AND RISKS
Description of Business and Organization
ATA Inc. (the Company), through its subsidiaries, ATA Testing Authority (Holdings) Limited (ATA BVI), Xing Wei Institute (Hong Kong) Limited (Xing Wei), ATA Testing Authority (Beijing) Limited (ATA Testing), ATA Learning Data & Technology (Beijing) Limited (ATA Data) (formerly known as Beijing JinDiXin Software Technology Limited (Beijing JDX)), ATA Learning (Beijing) Inc. (ATA Learning), Zhong Xiao Zhi Xing Education Technology (Beijing) Limited (Zhongxiao Zhixing), and ATA Online (Beijing) Education Technology Co., Ltd. (ATA Online) and Beijing Puhua Huitong Education Technology Co., Limited (Puhua Technology) (collectively, referred to as the Group), primarily provides computer-based testing services, online education services and other related services in the Peoples Republic of China (the PRC). Prior to May 20, 2015, the Group had no legal ownership interest in ATA Online but had control over ATA Online through a series of contractual agreements as further described in Note (2)(w) below. In September 2016, the Company acquired 60% equity interest in Puhua Technology by injection of RMB 2.0 million in cash, as further described in Note (21).
Significant Concentrations and Risks
The Group is subject to the following significant concentration and risks:
Country risk
The Group is subject to special risks associated with the PRC. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic, legal and social environment in the PRC, including the relative difficulty of protecting and enforcing intellectual property rights in the PRC. The interpretation and application of current or proposed requirements and regulations may have an adverse effect on the Groups business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, the ability to negotiate and implement specific business development projects in a timely and favorable manner may be impacted by political considerations unrelated to or beyond the control of the Group. Although the PRC government has been pursuing economic reform policies for over three decades, no assurance can be given that the PRC government will continue to pursue such policies or that such policies may not be significantly altered. Any change in PRC government policies and regulations affecting the education and testing service industry may have a negative impact on the Groups operating results and financial condition.
Revenue concentration
For the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, RMB 246.2 million, RMB 301.5 million and RMB 329.6 million, representing 70.3%, 72.3% and 69.8% of the Groups net revenues, respectively, were generated from service fees from Chinese government controlled entities including governmental agencies, educational institutions and industry associations controlled by the PRC government. The demand for the Groups products and services by these agencies, institutions and associations is affected by government budgetary cycles, funding availability and government policies. Funding reductions, reallocations or delays could adversely impact demand for the Groups products and services or reduce the fees these customers are willing to pay for the Groups products and services.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Net revenues from customers that individually exceeded 10% of the Groups net revenues are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||||||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Chinese Institute of Certified Public Accountants |
|
64,944,327 |
|
18.5 |
% |
76,485,306 |
|
18.3 |
% |
90,455,936 |
|
19.1 |
% |
|
Asset Management Association of China |
|
|
|
|
|
23,183,787 |
|
5.6 |
% |
87,661,832 |
|
18.6 |
% |
|
China Banking Association |
|
64,169,577 |
|
18.3 |
% |
61,190,087 |
|
14.7 |
% |
55,521,062 |
|
11.8 |
% |
|
Securities Association of China |
|
66,847,350 |
|
19.1 |
% |
67,045,689 |
|
16.1 |
% |
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable, net from customers, that individually exceeded 10% of the Groups accounts receivable, net are as follows:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
| ||||
|
|
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
RMB |
|
% |
|
|
Asset Management Association of China |
|
13,243,230 |
|
26.2 |
% |
10,836,559 |
|
19.3 |
% |
|
The Chinese Institute of Certified Public Accountants |
|
6,069,096 |
|
12.0 |
% |
450,712 |
|
0.8 |
% |
Concentration of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash balances held at financial institutions
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash balances include deposits in:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Financial institutions in the mainland of the PRC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Denominated in Renminbi (RMB) |
|
236,843,121 |
|
251,487,461 |
|
|
Denominated in U.S. Dollar (USD) |
|
723 |
|
723 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash balances held at mainland PRC financial institutions |
|
236,843,844 |
|
251,488,184 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financial institutions in Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) of the PRC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Denominated in RMB |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
Denominated in Hong Kong Dollar |
|
20,873 |
|
263,216 |
|
|
Denominated in USD |
|
10,502,056 |
|
697,012 |
|
|
Denominated in Great Britain Pound |
|
300,964 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total cash balances held at HKSAR financial institutions |
|
10,823,893 |
|
960,229 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash balances held at financial institutions |
|
247,667,737 |
|
252,448,413 |
|
The bank deposits with financial institutions in the PRC are insured by the government authority up to RMB 500,000. The bank deposits with financial institutions in the HKSAR are insured by the government authority up to HK$ 500,000. To limit exposure to credit risk, the Company primarily places bank deposits with large financial institutions in the PRC and HKSAR with acceptable credit rating.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(2) SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
(a) Principles of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of the Company, its subsidiaries and, prior to May 20, 2015, its variable interest entity, or VIE for which the Company is the primary beneficiary. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated upon consolidation.
Non-controlling interests are separately presented as a component of equity in the consolidated financial statements.
(b) Basis of presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (U.S. GAAP).
(c) Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management of the Group to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Such estimates include the fair values of share-based payments and available-for-sale investment, the collectability of accounts receivable, the realizability of deferred income tax assets, the estimate for useful lives and residual values of long-lived assets, the recoverability of the carrying values of long-lived assets, goodwill and long-term investments, and the expected licensing period for perpetual licenses with respect to revenue recognition. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
(d) Foreign currency translation and risks
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been expressed in RMB, the Companys reporting currency.
The Company, ATA BVI and Xing Weis functional currency is the USD. The functional currency of the Companys PRC subsidiaries is the RMB.
Transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transaction. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency using the applicable exchange rates at the balance sheet dates. The resulting foreign exchange gains and losses are included in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income in the line item Foreign currency exchange losses, net.
Assets and liabilities of the Company, ATA BVI and Xing Wei are translated into RMB using the applicable exchange rate at each balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated into RMB at average rates prevailing during the year. The resulting foreign currency translation adjustments are recognized as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive loss within equity. Since the RMB is not a fully convertible currency, all foreign exchange transactions involving RMB must take place either through the Peoples Bank of China (the PBOC) or other institutions authorized to buy and sell foreign exchange. The exchange rates adopted for the foreign exchange transactions are the rates of exchange quoted by the PBOC.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
For the convenience of the readers, the 2017 RMB amounts included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been translated into USD at the rate of USD 1.00 = RMB 6.8832, the noon buying rate in New York cable transfers of RMB per USD as set forth in the H.10 weekly statistical release of Federal Reserve Board, as of March 31, 2017. No representation is made that the RMB amounts could have been, or could be, converted into USD at that rate or at any other rate on March 31, 2017.
(e) Commitments and contingencies
In the normal course of business, the Group is subject to contingencies, such as legal proceedings and claims that cover a wide range of matters. Liabilities for such contingencies are recorded when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the assessment can be reasonably estimated. If a potential material loss contingency is not probable but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, together with an estimate of the range of possible loss if determinable and material, is disclosed.
(f) Fair value measurements
The Group utilizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs to the extent possible. The Group determines fair value based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability in an orderly transaction and principal or most advantageous market. When considering market participant assumptions in fair value measurements, the following fair value hierarchy distinguishes between observable and unobservable inputs, which are categorized in one of the following levels:
· Level 1 Inputs: Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities accessible to the reporting entity at the measurement date.
· Level 2 Inputs: Other than quoted prices included in Level 1 inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the asset or liability.
· Level 3 Inputs: Unobservable inputs for the asset or liability used to measure fair value to the extent that observable inputs are not available, thereby allowing for situations in which there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability at measurement date.
The level in the fair value hierarchy within which a fair value measurement in its entirety falls is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. In situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability at the measurement date, the fair value measurement reflects managements own judgments about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. Those judgments are developed by management based on the best information available in the circumstances.
(g) Revenue recognition
The Groups revenues are principally derived from the provision of testing services and online education services. The Group recognizes revenues when all of the following have occurred:
· persuasive evidence of an agreement with the customer exists;
· services have been performed and/or delivery of goods has occurred;
· the fees for services performed and/or price of goods sold are fixed or determinable; and
· collectability of the fees and/or sales proceeds is reasonably assured.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The application of the above criteria for revenue recognition for each type of service or product is as follows:
i) Testing services
Fees for testing services are recognized upon the completion of the exam by the test taker since the Group has no significant future involvement after the completion of the examination. Fees received in advance of test delivery are recorded as deferred revenue.
ii) Online education services
The Group derives online education revenues from online education services.
The online training entitles end users to access online education services during a specified service period, which normally ranges between 90 to 360 days from activation.
Online training revenue is recognized over the service period commencing at the point of time the users access to the online training is activated and ending at the point of time the user complete training hours. If the online training sold to end users is not activated before the expiration date, related online service revenue is recognized on the expiration date.
The Group is not contractually obligated to accept, nor has the Group historically accepted, returns from end users.
iii) Other revenue
a) Licensing fees from authorized test centers
The Group receives a fixed fee for a perpetual license that provide authorized test centers the right to use the Groups brand name and e-testing platform.
The Group is obligated to provide ongoing technical support and unspecific system upgrades; and to provide training to authorized test centers staff. Fixed fees for perpetual licenses are recognized on a straight-line basis over the expected licensing period of 10 years, which is the period the Group is expected to have continuing involvement with the authorized test centers. Management estimates the expected licensing period based on its historical retention experience, factoring in the expected level of future competition, the risk of technological obsolescence, technological innovation, and the expected changes in the education training environment.
b) Test development services
Test development service fees are recognized upon the acceptance of the developed tests by the customer. The period to develop the tests is short, generally within two to six months from commencement of development.
c) Test administration software products
Test administration software products sales are recognized upon delivery and when collectability is reasonably assured.
d) Operating leases
The Group recognized the revenue from operating lease on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
iv) Business tax and value added tax (VAT)
Revenue is recognized net of business tax at the rate of 5% of gross revenues or VAT at the rate of 3% or 6% of gross revenues. Business tax and VAT collected from customers, net of VAT paid for purchases, is recorded as a liability in the consolidated balance sheets until paid to the tax authorities.
(h) Cost of revenues
Cost of revenues consists primarily of cost of test monitoring, royalty fees for IT vendors and test sponsor licensing arrangements, payroll compensation, and other related costs, which are directly attributable to the rendering of services and delivery of goods.
The test monitoring costs are recognized upon completion of examinations based on actual number of test takers. Royalty fees are recognized as cost of revenues based on actual usage according to contract provisions.
The test monitoring costs and royalty fees for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Test monitoring costs |
|
113,042,449 |
|
142,116,286 |
|
163,061,810 |
|
|
Royalty fees |
|
4,991,524 |
|
4,823,101 |
|
7,423,118 |
|
(i) Research and development costs
Research and development costs primarily consist of software developed for internal use and software developed for sale.
i) Software developed for internal use
The Group expenses all costs that are incurred in connection with the planning and implementation phases of the development of software. Costs incurred in the development phase are capitalized and amortized over the estimated product life. No costs were capitalized for any of the periods presented.
ii) Software developed for sale
Costs incurred internally in researching and developing a computer software product are charged to expense as research and development costs prior to technological feasibility being established for the product. Once technological feasibility is established, all computer software costs are capitalized until the product is available for general release to customers. Technological feasibility is established upon completion of all the activities that are necessary to substantiate that the computer software product can be produced in accordance with its design specifications, including functions, features, and technical performance requirements.
(j) Operating lease
The Group leases offices under non-cancellable operating leases. Leases with escalated rent provisions are recognized on a straight-line basis commencing with the beginning of the lease term. There are no contingent rent in the lease agreements. The lease terms range between 12 and 58 months. The Company has no legal or contractual asset retirement obligations at the end of the lease term.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(k) Income taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Under this method, deferred income tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and tax loss carryforwards. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred income tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates or tax status is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date or the date of change in tax status. A valuation allowance is provided to reduce the amount of deferred income tax assets if it is considered more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax assets will not be realized.
A deferred tax liability is not recognized for the excess of the Companys financial statement carrying amount over the tax basis of its investment in a foreign subsidiary, if there exists specific plans for reinvestment of undistributed earnings of a subsidiary which demonstrate that remittance of the earnings will be postponed indefinitely.
The Group recognizes in the consolidated financial statements the impact of a tax position, if that position is more likely than not of being sustained upon examination, based on the technical merits of the position. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. The Groups accounting policy is to accrue interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits, if and when required, as interest expense and a component of general and administrative expenses, respectively in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income.
(l) Share-based payment
The Group measures the cost of employee share options and non-vested shares based on the grant date fair value of the award and recognizes that cost over the period during which an employee is required to provide services in exchange for the award, which generally is the vesting period. For the graded vesting share options and non-vested shares, the Company recognizes the compensation cost over the requisite service period for each separately vesting portion of the award as if the award is, in substance, multiple awards. When no future services are required to be performed by the employee in exchange for an award of equity instruments, and if such award does not contain a performance or market condition, the cost of the award is expensed on the grant date. When there is a modification of the terms and conditions of an award of equity instruments, the Group calculates the incremental compensation cost of a modification as the excess of the fair value of the modified award over the fair value of the original award immediately before its terms are modified, measured based on the share price and other pertinent factors at the modification date. For vested options, the Group recognizes incremental compensation cost in the period the modification occurred. For unvested options, the Group recognizes, over the remaining requisite service period, the sum of the incremental compensation cost and the remaining unrecognized compensation cost for the original award on the modification date.
When there is a change in the grantee status from an employee to a non-employee, if grantee retains the awards on a change in status and continues to provide substantive services to the Group, the change in status results in a new measurement date for the unvested awards with compensation costs measured as if the awards were newly issued to the grantee on the date of the change in status. If grantee retains the awards on a change in status and is not required to provide substantive services to the grantor subsequent to that change in status, the change in status is, in substance, an acceleration of the vesting of the arrangement.
(m) Cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and short term loan
Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash in banks and highly liquid investments with original maturity less than three months. Restricted cash as of March 31, 2017 represents cash restricted as collateral for a short-term loan that ATA BVI has borrowed to support its business operations.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
On May 19, 2016, ATA BVI entered into a two-year Commercial Loan Facility (the Facility) with Industrial Bank Co., Ltd. Hong Kong Branch to borrow up to USD 4,000,000. ATA BVI shall pay interest at 2.5% per annum plus 3-month London Interbank Offer Rate (the LIBOR) on the commencement date for each drawdown. The Facility is fully secured by Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) for an amount at RMB 30,000,000, which was recorded as restricted cash.
The maturity date of each drawdown shall be twelve months after the first drawdown date but in any event no later than 5 business days prior to the expiration date of the corresponding SBLC unless otherwise extended by the bank in writing. In July 2016, ATA BVI borrowed RMB 3,449,650. In June 2017, the Group has fully repaid the drawdown and the interest thereon, and the SBLC was released in full.
(n) Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable are recognized at invoiced amounts, less an allowance for uncollectible accounts, if any.
The allowance for doubtful accounts is the managements best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses resulting from the inability of the Groups customers to make required payments. The allowance for doubtful accounts is based on a review of specifically identified accounts, aging data and historical collection pattern. Account balances are charged off against the allowance after all means of collection have been exhausted and the potential for recovery is considered remote. The Group does not have any off-balance-sheet credit exposure related to its customers.
(o) Long-term investments
Equity method investments
The Group applies the equity method to account for an equity interest in an investee over which the Group has significant influence but does not own a majority equity interest or otherwise control.
Under the equity method of accounting, the Groups share of the investees results of operations is reported as share of income (losses) of equity method investments in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss).
The Group recognizes an impairment loss when there is a decline in value below the carrying value of the equity method investment that is considered to be other-than-temporary. The process of assessing and determining whether impairment on an investment is other-than-temporary requires a significant amount of judgment. To determine whether an impairment is other-than-temporary, management considers whether it has the ability and intent to hold the investment until recovery and whether evidence indicating the carrying value of the investment is recoverable outweighs evidence to the contrary. Evidence considered in this assessment includes the reasons for the impairment, the severity and duration of the decline in value, any change in value subsequent to the period end, and forecasted performance of the investee.
Cost method investments
For equity investments in an investee that are not considered debt securities or equity securities that have readily determinable fair values and over which the Group neither has significant influence nor control, the Group carries the investment at cost and recognizes income as any dividends declared from distribution of investees earnings. The Group reviews the cost method investments for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may no longer be recoverable. An impairment loss is recognized in earnings equal to the difference between the investments cost and its fair value at the balance sheet date of the reporting period for which the assessment is made. The fair value of the investment would then become the new cost basis of the investment.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The fair value of a cost method investment is not estimated if there are no identified events or changes in circumstances that may have a significant adverse effect on the fair value of the investment. No events or circumstances indicating a potential impairment were identified as of or for the year ended March 31, 2017. The Company determines that it is not practicable to estimate fair value of cost method investments as of March 31, 2017, because the sales prices or bid-and-asked quotations of the equity interests of these entities are not currently available and the cost of obtaining an independent valuation appears excessive considering the materiality of the investments to the Company.
Available-for-sale investment
The Groups investment in convertible notes are classified as available-for-sale investments which are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income. An impairment loss on the available-for-sale investment is recognized in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) when the decline in value is determined to be other-than-temporary.
(p) Property and equipment, net
Property and equipment is stated at historical cost.
Depreciation is recognized over the following useful lives on the straight-line method, taking into consideration the assets estimated salvage value:
|
Building |
|
30 years |
|
Computer equipment |
|
3 to 5 years |
|
Furniture, fixtures and office equipment |
|
5 years |
|
Software |
|
3 to 5 years |
|
Motor vehicles |
|
5 years |
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
The shorter of lease terms and estimated useful lives |
Ordinary maintenance and repairs are charged to expenses as incurred, while replacements and betterments are capitalized. When items are retired or otherwise disposed of, income is charged or credited for the difference between net book value of the item disposed and proceeds realized thereon.
(q) Intangible assets
Intangible assets acquired are initially recognized and measured at fair value. Intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over their respective estimated useful lives, which range from 5 to 12 years.
The Group has no intangible assets with indefinite useful lives.
(r) Impairment of long-lived assets, excluding goodwill
Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment, and purchased intangible assets subject to amortization, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. If circumstances require a long-lived asset or asset group be tested for possible impairment, the Group first compares undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by that asset or asset group to its carrying value. If the carrying value of the long-lived asset or asset group is not recoverable on an undiscounted cash flow basis, an impairment is recognized to the extent that the carrying value exceeds its fair value. Fair value is determined through various valuation techniques including discounted cash flow models, quoted market values and third-party independent appraisals, as considered necessary. The Group recognized an impairment loss of intangible assets of RMB 310,153, RMB nil and RMB nil for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(s) Goodwill
Goodwill is an asset representing the future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. Goodwill is reviewed for impairment at least annually based on its identified reporting units, which are defined as reportable segments or groupings of businesses one level below the reportable segment level. The Group performs a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more-likely-than-not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount prior to performing the two-step goodwill impairment test. If this is the case, the two-step goodwill impairment test is required. If it is more-likely-than-not that the fair value of a reporting unit is greater than its carrying amount, the two-step goodwill impairment test is not required.
If the two-step goodwill impairment test is required, first, the fair value of the reporting unit is compared with its carrying amount (including goodwill). If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, an indication of goodwill impairment exists for the reporting unit and the entity must perform step two of the impairment test (measurement). Under step two, an impairment loss is recognized for any excess of the carrying amount of the reporting units goodwill over the implied fair value of that goodwill. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined by allocating the fair value of the reporting unit in a manner similar to a purchase price allocation and the residual fair value after this allocation is the implied fair value of the reporting units goodwill. Fair value of the reporting unit is determined using a discounted cash flow analysis. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, step two does not need to be performed.
Annual impairment review at March 31, and when a triggering event occurs between annual impairment tests was conducted over goodwill. No impairment loss of goodwill was recorded for any of the periods presented.
(t) Employee benefit plans
As stipulated by the regulations of the PRC, the Companys PRC subsidiaries are required to contribute to various defined contribution plans, organized by municipal and provincial governments on behalf of their employees. The contributions to these plans are based on certain percentages of the employees standard salary base as determined by the local Social Security Bureau. The Group has no other obligation for the payment of employee benefits associated with these plans beyond the annual contributions described above.
Employee benefit expenses recognized under these plans for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 are allocated to the following expense items:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Cost of revenues |
|
5,597,846 |
|
6,334,414 |
|
6,841,587 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
5,563,607 |
|
5,810,237 |
|
6,435,010 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
4,045,878 |
|
4,169,401 |
|
4,463,283 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
2,870,561 |
|
2,583,837 |
|
3,110,561 |
|
|
Total expense due to employee benefit plans |
|
18,077,892 |
|
18,897,889 |
|
20,850,441 |
|
(u) Earnings per share
Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net earnings by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year using the two-class method. Under the two-class method, net income is allocated between common shares and other participating securities based on their participating rights in undistributed earnings. The Companys non-vested shares relating to the share-based awards under the share incentive plan were considered participating securities since the holders of these securities have non-forfeitable rights to dividends or dividend equivalents (whether paid or unpaid).
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Diluted earnings per share is calculated by dividing net earnings adjusted for the effect of dilutive common equivalent shares, if any, by the weighted average number of common and dilutive common equivalent shares outstanding during the year. Common equivalent shares consist of common shares issuable upon the exercise of outstanding share options (using the treasury stock method). Common equivalent shares in the diluted earnings per share computation are excluded to the effect that they would be anti-dilutive. In calculating the diluted earnings per share, the undistributed earnings are not reallocated to the participating securities and the common and dilutive common equivalent shares.
(v) Segment reporting
The Group has one operating segment, testing and training services. Substantially all of the Groups operations and customers are located in the PRC. Consequently, no geographic information is presented.
(w) Variable interest entity (VIE)
PRC regulations prohibit direct foreign ownership of business entities that engage in internet content provision (ICP) services in the PRC. The Company and its foreign subsidiaries are prohibited from providing ICP services in the PRC, including having ownership of entities engaged in providing such services. Prior to July 2015, ATA Online had an ICP license for the provision of ICP services in the PRC. However, no ICP services were provided by ATA Online for all periods presented.
Prior to May 20, 2015, the Group had no legal ownership interest in ATA Online but had control over ATA Online through a series of contractual agreements as further described below. Prior to April 2015, the legal ownership interests of ATA Online were held by Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, the Companys co-founder and chairman and Mr. Walter Lin Wang, the Companys co-founder and director. In April 2015, Mr. Walter Lin Wang transferred all of his equity in ATA Online to Mr. Haichang Xiong, the Companys general counsel.
In May 2015, the Company decided to list ATA Online on the National Equities Exchange and Quotations System in the PRC. In preparation for the listing of ATA Online in the PRC, the contractual arrangements were terminated and the entire equity interests of ATA Online were transferred from Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Mr. Haichang Xiong (the nominee shareholders) to ATA Learning and Zhongxiao Zhixing on May 20, 2015 at the consideration of RMB 10.0 million determined based on the registered capital of ATA Online. As a result, ATA Online became a wholly equity-owned subsidiary of the Company. The consideration was paid to the nominee shareholders. Mr. Haichang Xiong transferred his consideration of RMB 1.0 million to Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma on March 29, 2016. The Group received RMB 10.0 million in cash from Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng on June 7, 2017. Further, ATA Online has de-registered its ICP license in July 2015 to be in compliance with PRC regulations.
VIE contractual agreements
A series of contractual agreements, including loan agreements, a call option and cooperation agreement, an equity pledge agreement, a technical support agreement, a strategic consulting service agreement and a power of attorney (collectively, the VIE Agreements) were entered among ATA BVI, ATA Learning, ATA Online, Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Mr. Walter Lin Wang. These contractual agreements were terminated in May 2015 as aforementioned.
The following is a description of the impact of the VIE Agreements on the Groups consolidated financial statements for reporting periods prior to May 2015.
ATA Online was determined to be a VIE because although Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Mr. Walter Lin Wang were the equity holders of ATA Online, (i) their equity investment of RMB 10.0 million in ATA Online was financed by the Group and (ii) they did not participate in any profit or loss of ATA Online.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Although the Company did not have an equity investment in ATA Online, the Company had other variable interests in ATA Online through, among others, (i) the Companys subordinated loans to Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Mr. Walter Lin Wang (used by them to finance their equity investment in ATA Online) and other subordinated loans to ATA Online, (ii) the Companys right, under the loan agreement, to receive all the dividends declared by ATA Online through its equity holders and (iii) the Companys exclusive purchase option to acquire (or to have the Groups designee acquire) 100% of the equity interest or assets in ATA Online for a consideration equal to the loans provided by the Group to Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Mr. Walter Lin Wang, to the extent permitted under PRC law. As a result of these variable interests, the Company had the obligation to absorb the expected losses and the right to receive expected residual returns of ATA Online.
Through the VIE Agreements, the Company had a controlling financial interest in ATA Online because the Company had (i) the power to direct activities of ATA Online that most significantly impact the economic performance of ATA Online ( refer to the Power of attorney agreement); and (ii) the obligation to absorb the expected losses and the right to receive expected residual return of ATA Online that could potentially be significant to ATA Online(refer to the Call option and cooperation agreement).
The termination of the VIE Agreements and the transfer of equity interests of ATA Online from the nominee shareholders to the Group had no impact on the Groups controlling financial interest in ATA Online. Accordingly, the financial statements of ATA Online are consolidated in the Companys consolidated financial statements for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017. All of the equity (net assets) and net incomes or losses of ATA Online are attributed to the Company; therefore, no non-controlling interest in ATA Online is presented in the Companys consolidated financial statements.
The key terms of these VIE Agreements were as follows:
Loan agreements: ATA BVI lent to ATA Onlines equity holders, Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma, and Mr. Walter Lin Wang, interest free loans in the amount of RMB10 million for the sole purpose of investing in ATA Online as ATA Onlines registered capital. The equity holders of ATA Online could only repay the loans by transferring all of their legal ownership interest in ATA Online to ATA BVI or to a third party designated by ATA BVI. The equity holders of ATA Online were required to pay to ATA BVI all dividend received from ATA Online.
Upon termination of the VIE Agreement in May 2015, the nominee shareholders received RMB 10.0 million from the transfer of the legal ownership interests in ATA Online to ATA Learning and Zhongxiao Zhixing in November 2015. Such proceeds have been repaid to ATA BVI.
Technical support agreement: ATA Learning had the exclusive right to provide technical support services to ATA Online. The service fees were mutually agreed by both parties, and were determined based on certain objective criteria such as the actual services required by ATA Online and the actual labor costs, as determined by the number of days and personnel involved, incurred by ATA Learning for providing the services during the relevant period.
Strategic consulting service agreement: ATA Learning provided ATA Online with strategic consulting and related services to ATA Online. The fees for these services were determined by ATA Learning and calculated monthly based on actual time spent providing the services. ATA Learning had the right to adjust the fees payable by ATA Online in accordance with its performance.
For the years ended March 31, 2015 and 2016, ATA Learning billed RMB 18.0 million and RMB nil to ATA Online based on the technical support agreement and strategic consulting service agreement.
Call option and cooperation agreement: Through the call option and cooperation agreement entered into among ATA BVI, ATA Online and its equity holders, ATA BVI or any party designated by ATA BVI, had an exclusive purchase option to acquire the equity interest in ATA Online from its equity holders or acquire ATA Onlines assets at any time when permitted by applicable Chinese laws and regulations. The proceeds from the exercise of the call option would be applied to repay the loans under the loan agreements described above.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Equity pledge agreement: To secure the payment obligations of ATA Online under the technical support agreement and the strategic consulting service agreement described above, ATA Onlines equity holders had pledged to ATA Learning their entire equity ownership interests in ATA Online. Under this agreement, equity holders of ATA Online may not transfer the pledged equity interest without ATA Learnings prior written consent. .
Power of attorney: Each of Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma and Mr. Walter Lin Wang signed a power of attorney, on March 27, 2013 and April 3, 2013 respectively, with ATA Learning to exclusively assign their rights as an shareholder of ATA Online to ATA Learning, including but not limited to voting right and right to appoint director and executive management of ATA Online. The assignment of the shareholders rights was legally binding, irrevocable.
The VIE Agreements were terminated in May 2015. The Companys involvement with the VIE under the VIE Agreements affected the Companys consolidated results of operations and cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2015 as indicated below.
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Net revenue |
|
154,454,044 |
|
|
Net income |
|
21,951,065 |
|
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
22,655,696 |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
(37,956,001 |
) |
|
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
|
|
(x) Business Combination
Business combinations are recorded using the purchase method of accounting in accordance with ASC topic 805 (ASC 805): Business Combinations. The purchase method of accounting requires that the consideration transferred to be allocated to the assets, including separately identifiable assets and liabilities acquired, based on their estimated fair values. The consideration transferred of an acquisition is measured as the aggregate of the fair values at the date of exchange of the assets given, liabilities incurred, and equity instruments issued as well as the contingent considerations and all contractual contingencies as of the acquisition date. The costs directly attributable to the acquisition are expensed as incurred. Identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities acquired or assumed are measured separately at their fair value as of the acquisition date, irrespective of the extent of any non-controlling interests. The excess of (i) the total of cost of acquisition, fair value of the non-controlling interests and acquisition date fair value of any previously held equity interest in the acquiree over (ii) the fair value of the identifiable net assets of the acquiree, is recorded as goodwill. If the cost of acquisition is less than the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary acquired, the difference is recognized directly in earnings.
Where the consideration in an acquisition includes contingent consideration the payment of which depends on the achievement of certain specified conditions post-acquisition, the contingent consideration is recognized and measured at its fair value at the acquisition date and if recorded as a liability it is subsequently carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in earnings.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(y) Recently issued accounting standards
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standard Update (ASU) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This ASU requires an entity to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. An entity should also disclose sufficient quantitative and qualitative information to enable users of financial statements to understand the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers. In December 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which deferred the effective date of ASU No. 2014-09. In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-08, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net) which clarifies the implementation guidance on principal versus agent considerations. The guidance includes indicators to assist an entity in determining whether it controls a specified good or service before it is transferred to the customers. The new standard is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The new standard may be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect recognized as of the date of adoption. The Group plans to complete its evaluation in next fiscal year, including an assessment of the new expanded disclosure requirements and a final determination of the transition method the Group will use to adopt the new standard.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASC Topic 842, Leases through ASU No. 2016-02. ASC Topic 842 requires a lessee to recognize all leases, including operating leases, on balance sheet via a right-of-use asset and lease liability, unless the lease is a short-term lease. All (or a portion of) fixed payments by the lessee to cover lessor costs related to ownership of the underlying assets, or executory costs, that do not represent payments for a good or service will be considered lease payments and reflected in the measurement of lease assets and lease liabilities by lessees. The new standard does not substantially change lessor accounting from current U.S. GAAP. The new standard also requires lessees and lessors to disclose more qualitative and quantitative information about their leases than current U.S. GAAP does. The standard is applied retrospectively, with elective reliefs. The new standard is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018 for a public business entity. Early adoption is permitted. The Group is currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2016-02 will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, Compensation-Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. ASU No. 2016-09 was issued as part of the FASBs simplification initiative aimed at reducing costs and complexity while maintaining or improving the usefulness of financial information. This update involves several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, forfeitures, statutory tax withholding requirements, and classification in the statement of cash flows. This ASU is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted for any interim or annual period. If an entity early adopts the amendments in an interim period, any adjustments should be reflected as of the beginning of the fiscal year that includes that interim period, and the entity must adopt all of the amendments in the same period. The Group does not expect the adoption of ASU No. 2016-09 will have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, which clarifies the presentation and classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Group is currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2016-15 will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows - Restricted cash. This ASU requires companies to include cash and cash equivalents that have restrictions on withdrawal or use in total cash and cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows. This ASU is effective for public business entities for annual and interim periods in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. If an entity early adopts the amendments in an interim period, adjustments should be reflected at the beginning of the fiscal year that includes that interim period. The amendments in this ASU should be applied using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. The Group is currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2016-18 will have on its consolidated financial statements.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(z) Recently adopted accounting standards
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes, which requires all deferred tax assets and liabilities, and related valuation allowances, to be classified as noncurrent on the Companys consolidated balance sheets. ASU No. 2015-17 is effective for the Company for annual periods in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and requires either prospective or retrospective adoption. The Company elected to early adopt the new standard retrospectively in the year ended March 31, 2017, which resulted in the reclassifications of RMB 3,663,864 from current to noncurrent deferred income tax assets in the consolidated balance sheet as of March 31, 2016.
(3) ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE, NET
Accounts receivable, net is summarized as follows:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
55,427,300 |
|
61,560,981 |
|
|
Less: allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
(4,875,266 |
) |
(5,399,726 |
) |
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
50,552,034 |
|
56,161,255 |
|
Management performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers financial condition and generally does not require collateral on accounts receivable.The activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts for accounts receivable for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 is as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Beginning allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
4,688,433 |
|
5,003,118 |
|
4,875,266 |
|
|
Additions charged to (reversal of) provision for doubtful accounts |
|
845,965 |
|
(127,852 |
) |
524,460 |
|
|
Write-off of accounts receivable |
|
(531,280 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Ending allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
5,003,118 |
|
4,875,266 |
|
5,399,726 |
|
(4) PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consist of the following:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Advances to employees |
|
982,530 |
|
373,071 |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
7,285,850 |
|
6,962,753 |
|
|
Total prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
8,268,380 |
|
7,335,824 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(5) LONG-TERM INVESTMENTS
Long-term investments consist of the following:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Equity method investments |
|
48,747,486 |
|
8,893,440 |
|
|
Cost method investments |
|
|
|
69,621,700 |
|
|
Available-for-sale investment |
|
1,938,360 |
|
10,376,547 |
|
|
Total long-term investments |
|
50,685,846 |
|
88,891,687 |
|
Equity method investments
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Beijing Zhishang Education Technology Ltd. |
|
7,701,753 |
|
2,740,234 |
|
|
Master Mind Education Company |
|
27,534,547 |
|
|
|
|
Beijing Satech Internet Educational Technology Ltd. |
|
4,520,146 |
|
|
|
|
Brilent Inc. |
|
8,991,040 |
|
6,153,206 |
|
|
Total equity method investments |
|
48,747,486 |
|
8,893,440 |
|
In August 2014, ATA Online made a 45% equity interest investment to establish Beijing Zhishang Education Technology Ltd. (Zhishang), an online professional training provider based in PRC, by paying cash of RMB 13,500,000. The other shareholder of Zhishang is New Oriental Education & Technology Group. ATA online accounted for the investment under equity method. ATA online recognized its share of loss from this equity investment of RMB 1,103,275, RMB 4,694,972 and RMB 4,961,519 for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
In December 2014, the Group made a 33% equity interest investment in Master Mind Education Company (Master Mind), a digital service provider for K-12 after-school tutoring institute based in the PRC, by paying cash of RMB 18,453,864 in December 2014, and RMB 12,302,000 in June 2015. The Company accounted for its 33% equity interest in Master Mind under the equity method. The Company recognized its share of loss from this equity investment of RMB 882,809, RMB 2,314,074 and RMB 5,230,027 for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
In January 2015, the Group made a 20% equity interest investment in Beijing Satech Internet Educational Technology Ltd. (Satech), an online SAT learning platform provider based in the PRC, by paying cash of RMB 6,000,000. In April, 2016, the Company acquired additional 10.78% equity interest of Satech at cash consideration of RMB 8,466,660. After the additional investment, the company has invested a total of RMB 14,466,660 in Satech and accounted for its 30.78% equity interest under equity method. The Company recognized its share of loss from this equity investment of RMB 210,666, RMB 1,269,187 and RMB 3,091,954 for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
In September 2015, ATA BVI entered into an agreement to purchase 2,156,721 Series AA Preferred Shares issued by Brilent Inc. (Brilent) at a price of $0.6955 per Series AA Preferred Shares with a total consideration of USD1.5 million. Brilent is a service provider with an easy to use SaaS (Software as a Service) based in the United States. ATA BVI held 15.47% equity interest of Brilent and one board seat out of six as of March 31, 2016. The investment is accounted for under the equity method as ATA BVI is able to exercise significant influence through its board seat. The Company recognized its share of loss from this equity investment of RMB 550,907 and RMB 2,837,834 for the years ended March 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Management evaluated whether there was an other than temporary impairment based on the facts, including recent financing activities, projected and historical financial performance, and considered there was no other than temporary impairment on equity method investments except for Master Mind and Satech.
Master Mind and Satech failed to meet the expected milestones and operation forecasts and encountered shortage of working capital resulted from continuous negative operating cash flows. Therefore, management considered that there were other than temporary impairments of the two investments and recorded impairment losses of RMB 22,304,520 and RMB 9,894,852 respectively at March 31, 2017.
The summarized financial information of the equity method investments were as follows:
|
|
|
Zhishang |
| ||
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Current assets |
|
16,915,455 |
|
7,193,920 |
|
|
Non-current assets |
|
1,519,523 |
|
1,107,731 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
1,319,972 |
|
1,513,637 |
|
|
Non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
698,605 |
|
|
Net assets attributable to Zhishangs shareholders |
|
17,115,006 |
|
6,089,409 |
|
|
|
|
Master Mind |
|
Satech |
| ||||
|
|
|
March 31, |
|
March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Current assets |
|
17,275,584 |
|
2,818,796 |
|
896,029 |
|
1,091,944 |
|
|
Non-current assets |
|
421,415 |
|
342,833 |
|
166,704 |
|
142,408 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
1,848,431 |
|
3,161,629 |
|
1,543,959 |
|
2,037,788 |
|
|
Equity |
|
15,848,568 |
|
|
|
(481,226 |
) |
(803,436 |
) |
|
|
|
Zhishang |
| ||||
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Net revenue |
|
|
|
5,910 |
|
486,711 |
|
|
Cost and operating expenses |
|
2,577,214 |
|
11,813,664 |
|
12,442,948 |
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
(2,451,723 |
) |
(10,433,271 |
) |
(11,160,739 |
) |
|
Net loss |
|
(2,451,723 |
) |
(10,433,271 |
) |
(11,160,739 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to Zhishangs shareholders |
|
(2,451,723 |
) |
(10,433,271 |
) |
(11,025,597 |
) |
|
|
|
Master Mind |
|
Satech |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, |
|
Year ended March 31, |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Net revenue |
|
143,100 |
|
592,961 |
|
609,837 |
|
|
|
9,674 |
|
326,188 |
|
|
Cost and operating expenses |
|
2,824,687 |
|
13,662,672 |
|
17,350,165 |
|
1,056,987 |
|
8,367,416 |
|
10,716,073 |
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
(2,675,180 |
) |
(13,012,346 |
) |
(15,848,568 |
) |
(1,053,332 |
) |
(8,345,933 |
) |
(10,380,733 |
) |
|
Net loss |
|
(2,675,180 |
) |
(13,012,346 |
) |
(15,848,568 |
) |
(1,053,332 |
) |
(8,345,933 |
) |
(10,380,733 |
) |
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Cost method investments
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Beijing Empower Education Online Co., Ltd. |
|
|
|
32,500,000 |
|
|
Medicine (Beijing) Education Technology Ltd. |
|
|
|
5,100,000 |
|
|
ApplySquare Education & Technology Co., Ltd. |
|
|
|
19,721,700 |
|
|
Beijing GlobalWisdom Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
|
|
|
12,300,000 |
|
|
Total cost method investments |
|
|
|
69,621,700 |
|
During the year ended March 31, 2017, the Group entered into shares purchase agreements to acquire 8.33% equity interest of Beijing Empower Education Online Co., Ltd. (EEO), 15% equity interest of Medicine (Beijing) Education Technology Ltd. (MDS), 9% equity interest of ApplySquare Education & Technology Co., Ltd (ApplySquare), and 8.2% equity interest of Beijing GlobalWisdom Information Technology Co., Ltd. (GlobalWisdom), by paying cash consideration of RMB 32,500,000, RMB 9,000,000, USD 3,000,000 (equivalent to RMB 19,721,700), and RMB 12,300,000 respectively. As of March 31, 2017, the Group has paid all the cash considerations. Because these investment terms contain substantive liquidation preference over common stock that are not available to common shareholders, these investments are not substantially similar to common stock. In addition, the Group determined that it was not practicable to estimate fair value of cost method investments as of March 31, 2017, because the sales prices or bid-and-asked quotations of the equity interests of these entities are not currently available and the cost of obtaining an independent valuation appears excessive considering the materiality of the investments to the Group. The Group recognized the cost of these investments at cash consideration and accounts for the investment by the cost method in accordance with ASC 325: Investments-Other.
In December 2016, the Company sold 6.5% of the equity interest in MDS for RMB 5,500,000 in cash, and recognized gain from disposal of long-term investment of RMB 1,600,000.
Available-for-sale investment
On March 24, 2016, ATA BVI entered into a convertible promissory note (the Notes) purchase agreement with Brilent pursuant to which Brilent will issue up to USD 2,500,000 of the Notes to certain investors including ATA BVI. On March 30, 2016 and April 28, 2016, Brilent issued the Notes to ATA BVI in the principal amount of USD 300,000 and USD 1,200,000 at a 6% interest rate per annum, in exchange for cash of USD 1,500,000. The Notes are due and redeemable 24 months from issuance. If a qualified financing occurs on or prior to the maturity date of the Notes, the Notes and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon shall convert, at ATA BVIs option, into qualified financing securities at 75% of the qualified financing security purchase price subject to certain adjustment. The Company determined the fair value of the Notes as of March 31, 2017 to be USD 1,504,000 (RMB 10,376,547).
For the year ended March 31, 2017, RMB 568,320 was recognized as interest income in consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss). The investment is classified as available-for-sale investment and is measured at fair value as of the balance sheet date. Unrealized holding loss of RMB 553,870 was reported in other comprehensive income (loss) for the year ended March 31, 2017.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aggregate |
|
|
|
Unrealized |
|
currency |
|
Aggregate |
|
|
|
|
cost |
|
Interest |
|
holding |
|
translation |
|
fair |
|
|
|
|
basis |
|
income |
|
loss |
|
adjustment |
|
value |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Convertible note |
|
9,895,800 |
|
568,320 |
|
(553,870 |
) |
466,297 |
|
10,376,547 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(6) FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT
The following tables present the placement in the fair value hierarchy of assets that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis at March 31, 2017:
|
|
|
|
|
Fair value disclosure or measurement at |
| ||||
|
|
|
March 31, 2017 |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
Level 3 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Available-for-sale investment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Convertible note |
|
10,376,547 |
|
|
|
|
|
10,376,547 |
|
To estimate the fair value of the Notes, the Group used the Cox, Ross and Rubinstein Binomial Model (Binomial-Model), which is based on the fair value of the entire invested capital of Brilent evaluated by an income approach. The significant inputs for the valuation model included the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, 2017 |
| ||
|
Total fair value of underlying asset as at valuation date |
|
|
|
USD 12,000,000 |
|
|
Risk free rate of interest |
|
For the March 30, 2016 Note |
|
1.02% |
|
|
|
|
For the April 28, 2016 Note |
|
1.04% |
|
|
Maturity Date |
|
For the March 30, 2016 Note |
|
2018/3/30 |
|
|
|
|
For the April 28, 2016 Note |
|
2018/4/28 |
|
|
Volatility |
|
For the March 30, 2016 Note |
|
35.22% |
|
|
|
|
For the April 28, 2016 Note |
|
36.10% |
|
The fair value of the underlying asset has been determined using income approach including discounted cash flow model and unobservable inputs including assumptions of projected revenue, expenses, capital spending, other costs and a discount rate of 26% by using the weighted average cost of capital method.
Risk free rate of interest adopted for the valuation were estimated based on the U.S. daily treasury yield as at valuation date with term similar to the expected term of the Notes.
Maturity date is the time to maturity of the Notes according to the investment agreement.
The expected equity volatility were estimated based on the annualized standard deviation of the daily return embedded in the historical stock price of comparable companies with a time horizon close to the expected term determined based on the maturity date.
The following table presents a roll-forward of the fair value of Level 3 (significant unobservable inputs) asset for the year ended March 31, 2017, which only contains available-for-sale investment:
|
|
|
Convertible note |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Beginning balance as of April 1, 2016 |
|
1,938,360 |
|
|
Purchase |
|
7,957,440 |
|
|
Total gain or losses: |
|
|
|
|
Included in net income (loss) |
|
568,320 |
|
|
Included in other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
(553,870 |
) |
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment |
|
466,297 |
|
|
Ending balance as of March 31, 2017 |
|
10,376,547 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The Group did not have any nonfinancial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as of March 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
The Groups financial instruments consist of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, advances to third parties, employees and suppliers, which are included in the prepaid expenses and other current assets, restricted cash, short-term loan and accrued expenses and other payables, all of which have a carrying amount that approximate fair value because of the short maturity of these instruments.
(7) PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment, net consist of the following:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Building |
|
53,049,213 |
|
53,049,213 |
|
|
Computer equipment |
|
27,972,606 |
|
28,964,985 |
|
|
Furniture, fixtures and office equipment |
|
2,358,500 |
|
2,471,985 |
|
|
Software |
|
15,833,639 |
|
15,994,016 |
|
|
Motor vehicles |
|
2,401,570 |
|
2,767,358 |
|
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
16,118,799 |
|
16,412,286 |
|
|
|
|
117,734,327 |
|
119,659,843 |
|
|
Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
|
(60,504,600 |
) |
(67,790,929 |
) |
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
57,229,727 |
|
51,868,914 |
|
Total depreciation expense recognized for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 is allocated to the following expense items:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenues |
|
2,218,458 |
|
2,923,170 |
|
3,283,130 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
199,886 |
|
879,228 |
|
1,064,370 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
464,404 |
|
514,458 |
|
601,509 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
4,162,029 |
|
4,101,778 |
|
3,743,084 |
|
|
Total depreciation expense |
|
7,044,777 |
|
8,418,634 |
|
8,692,093 |
|
(8) GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS, NET
(a) Goodwill
The change in the carrying amount of goodwill is as follows:
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of April 1, 2015 and 2016 |
|
31,011,902 |
|
|
Acquisition of Puhua Technology (Note 21) |
|
1,512,081 |
|
|
Balance as of March 31, 2017 |
|
32,523,983 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(b) Intangible assets
The following table summarizes the Companys intangible assets, as of March 31, 2016 and 2017.
|
|
|
March 31, 2016 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
Net |
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
carrying |
|
amortization |
|
|
|
carrying |
|
Amortization |
|
|
|
|
amount |
|
/deduction |
|
Impairment |
|
amount |
|
Period |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
Years |
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
1,300,000 |
|
(767,500 |
) |
|
|
532,500 |
|
12 |
|
|
Training platform |
|
422,700 |
|
(204,305 |
) |
|
|
218,395 |
|
5 |
|
|
Total intangible assets |
|
1,722,700 |
|
(971,805 |
) |
|
|
750,895 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
March 31, 2017 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
Net |
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
carrying |
|
amortization |
|
|
|
carrying |
|
Amortization |
|
|
|
|
amount |
|
/deduction |
|
Impairment |
|
amount |
|
Period |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
Years |
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
1,300,000 |
|
(875,832 |
) |
|
|
424,168 |
|
12 |
|
|
Training platform |
|
422,700 |
|
(288,845 |
) |
|
|
133,855 |
|
5 |
|
|
Royalty arrangement (i) |
|
8,000,000 |
|
(1,200,000 |
) |
|
|
6,800,000 |
|
5 |
|
|
Education assessment test caseware (ii) |
|
4,177,358 |
|
(208,868 |
) |
|
|
3,968,490 |
|
5 |
|
|
Total intangible assets |
|
13,900,058 |
|
(2,573,545 |
) |
|
|
11,326,513 |
|
|
|
Amortization expenses for intangible assets recognized as cost of revenues were RMB 192,873, RMB 192,874 and RMB 1,601,740 for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
(i) Royalty arrangement represents the exclusive right the Group authorized to launch the online education services for banks registered under and supervised by China Banking Association for five years.
(ii) Education assessment test caseware is the test content purchased for the Companys strategic K-12 academic assessment business, which includes three subjects of Literature, Mathematics and English over six grades of junior and senior high school.
As of March 31, 2017, the estimated amortization expense for the next five years is as follows:
|
|
|
March 31 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
2018 |
|
2,628,345 |
|
|
2019 |
|
2,593,120 |
|
|
2020 |
|
2,543,805 |
|
|
2021 |
|
2,534,639 |
|
|
2022 |
|
1,026,604 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(9) ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER PAYABLES
Accrued expenses and other payables consist of the following:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Value-added tax and other taxes payable |
|
3,851,923 |
|
2,407,530 |
|
|
Accrued payroll and welfare |
|
14,524,290 |
|
17,042,283 |
|
|
Accrued test monitoring fees |
|
14,702,303 |
|
17,141,791 |
|
|
Royalty fees payable |
|
532,185 |
|
734,571 |
|
|
Income taxes payable |
|
3,044,352 |
|
|
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
21,084,574 |
|
52,032,672 |
|
|
Total accrued expenses and other payables |
|
57,739,627 |
|
89,358,847 |
|
Other current liabilities as of March 31, 2016 and 2017 mainly include accrued traveling expenses, rental expenses, meeting expense and other operating expenses. The balance as of March 31, 2017 also includes an investment prepayment of RMB 34,000,000 made to ATA Data by two third party investors, for the acquisition of 20% equity shares of ATA Data pursuant to the investment agreement signed on February 23, 2017. As of March 31, 2017, the closing terms have not been completed in accordance with relevant legal rules in PRC. Therefore, the amount was recognized as a liability as of March 31, 2017.
(10) DEFERRED REVENUES
Deferred revenues consist of the following:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Testing service |
|
14,611,826 |
|
8,047,140 |
|
|
Online education services |
|
223,821 |
|
297,602 |
|
|
Other revenue licensing fees from authorized test centers |
|
2,451,093 |
|
2,333,983 |
|
|
Other revenue others |
|
1,204,175 |
|
1,274,794 |
|
|
Total deferred revenues |
|
18,490,915 |
|
11,953,519 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Representing: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current deferred revenues |
|
16,612,164 |
|
10,221,897 |
|
|
Non-current deferred revenues |
|
1,878,751 |
|
1,731,622 |
|
(11) NET REVENUES
The components of net revenues for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Testing services |
|
319,055,019 |
|
384,799,721 |
|
430,056,696 |
|
|
Online education services |
|
5,710,827 |
|
4,896,879 |
|
7,462,036 |
|
|
Other revenue |
|
25,391,978 |
|
27,443,369 |
|
34,866,984 |
|
|
Net revenues |
|
350,157,824 |
|
417,139,969 |
|
472,385,716 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Other revenue primarily includes licensing fees from authorized test centers, test development services, test certificate services, test administration software product sales and operating lease income. The net revenues from product sales are RMB 1,252,673, RMB 490,152 and RMB 570,576 for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
(12) INCOME TAXES
Cayman Islands and British Virgin Islands
Under the current laws of the Cayman Islands and the British Virgin Islands, the Group is not subject to any income tax in these jurisdictions.
Hong Kong
Xing Wei did not derive any income that is subject to Hong Kong profits tax for the taxable years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017. Accordingly, no provision for Hong Kong profits tax was required. The payment of dividends by Hong Kong companies is not subject to any Hong Kong withholding tax.
Peoples Republic of China
The Companys consolidated PRC entities file separate income tax returns.
Under the Enterprise Income Tax Law (EIT Law), the statutory income tax rate is 25% effective from January 1, 2008. Entities that qualify as high-and-new technology enterprises eligible for key support from the State (HNTE) are entitled to a preferential income tax rate of 15%.
The Companys PRC entities are subject to income tax at 25%, unless otherwise specified.
In December 2008, ATA Testing received approval from the tax authority that it qualified as an HNTE. The certificate entitled ATA Testing to the preferential income tax rate of 15% effective retroactively from January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2010. In October 2011, ATA Testing received approval from the tax authority on its renewal as an HNTE which entitled it to the preferential income tax rate of 15% effective retroactively from January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2013. In October 2014, ATA Testing received approval from the tax authority on its renewal as an HNTE which entitled it to the preferential income tax rate of 15% effective retroactively from January 1, 2014 to December 31, 2016. ATA Testing is currently in the process of renewing its HNTE certificate for another three years. Upon successful renewal, ATA Testing would be entitled to a preferential tax rate of 15% retroactively from January 1, 2017.
In December 2009, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data received approvals from the tax authorities that they qualified as HNTEs. The certificates entitled them to the preferential income tax rate of 15% effectively retroactively from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2011. In May and July 2012, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data received approvals from the tax authorities on its renewals as HNTEs which entitled them to the preferential income tax rate of 15% effective retroactively from January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2014. In November 2015, ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data received approvals from the tax authorities on its renewals as HNTEs which entitled them to the preferential income tax rate of 15% effective retroactively from January 1, 2015 to December 31, 2017. The applicable income tax rate for ATA Learning, ATA Online and ATA Data from January 1, 2018 onward will be 25% unless they can re-qualify as HNTE.
Zhongxiao Zhixing, a PRC subsidiary of Xing Wei, is subject to an income tax rate of 25%.
Puhua Technology, a PRC subsidiary of ATA Online, is subject to an income tax rate of 25%
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The EIT Law and its relevant regulations impose a withholding tax at 10%, unless reduced by a tax treaty or agreement, for dividends distributed by a PRC-resident enterprise to its immediate holding company outside the PRC for earnings generated beginning on January 1, 2008. Undistributed earnings generated prior to January 1, 2008 are exempt from withholding tax. As of March 31, 2017, the Company has accrued withholding tax of RMB 22,620,872 on undistributed earnings of RMB 226,208,715 generated by its PRC consolidated entities since January 1, 2008 as the Company has changed its plan with respect to distribution of earnings from its PRC subsidiaries and does not believe the indefinite reinvestment exception for not recognizing deferred tax liability is met. The deferred income tax liability recognized related to these earnings was RMB 22,620,872 as of March 31, 2017. The unrecognized defferred income tax liability as of March 31, 2016 was RMB 17,856,205.
The earnings before income taxes were generated in the following jurisdictions:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Cayman Islands and British Virgin Islands |
|
(15,524,612 |
) |
(23,126,473 |
) |
(7,439,119 |
) |
|
PRC |
|
48,142,932 |
|
68,147,366 |
|
36,100,641 |
|
|
Hong Kong |
|
12,546 |
|
(48,227 |
) |
(33,943 |
) |
|
Earnings before income taxes |
|
32,630,866 |
|
44,972,666 |
|
28,627,579 |
|
Income tax expense (benefit) recognized in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income consists of the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
PRC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current expense |
|
10,424,835 |
|
11,867,755 |
|
15,677,070 |
|
|
Deferred expense (benefit) |
|
(849,689 |
) |
7,053,724 |
|
22,919,916 |
|
|
Total income tax expense |
|
9,575,146 |
|
18,921,479 |
|
38,596,986 |
|
The actual income tax expense reported in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income differs from the respective amount computed by applying the PRC statutory income tax rate of 25% for each of the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 to earnings before income taxes due to the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Computed expected income tax expense |
|
8,157,716 |
|
11,243,167 |
|
7,156,895 |
|
|
Increase in valuation allowance |
|
1,307,368 |
|
16,146,033 |
|
21,150,760 |
|
|
Preferential income tax rate |
|
(4,922,088 |
) |
(7,911,837 |
) |
(12,853,725 |
) |
|
Entities not subject to income tax |
|
2,100,188 |
|
3,502,469 |
|
1,868,266 |
|
|
Non-deductible expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entertainment |
|
1,225,250 |
|
792,099 |
|
662,669 |
|
|
Share-based compensation |
|
1,777,829 |
|
2,291,206 |
|
1,739,601 |
|
|
Bad debt loss |
|
1,383,597 |
|
(31,963 |
) |
173,615 |
|
|
Tax rate differential |
|
5,629,196 |
|
(3,974,403 |
) |
|
|
|
Additional deduction of research and development costs |
|
(8,489,742 |
) |
(4,900,698 |
) |
(4,856,620 |
) |
|
Withholding tax related to undistributed earnings |
|
|
|
|
|
22,620,872 |
|
|
Other |
|
1,405,832 |
|
1,765,406 |
|
934,653 |
|
|
Actual income tax expense |
|
9,575,146 |
|
18,921,479 |
|
38,596,986 |
|
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The applicable PRC statutory tax rate is used since the Groups taxable income is generated in the PRC.
The tax effects of the Groups temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred income tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Deferred income tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tax loss carryforwards |
|
20,326,608 |
|
28,887,161 |
|
|
Share of losses of equity method investments |
|
1,112,843 |
|
3,193,339 |
|
|
Impairment loss of long-term investments |
|
|
|
8,049,843 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
70,475 |
|
276,921 |
|
|
Accrued expenses and other payables |
|
2,375,267 |
|
4,292,260 |
|
|
Total gross deferred income tax assets |
|
23,885,193 |
|
44,699,524 |
|
|
Less: valuation allowance |
|
(20,028,588 |
) |
(41,179,348 |
) |
|
Total deferred income tax assets, net |
|
3,856,605 |
|
3,520,176 |
|
|
Deferred income tax liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
114,202 |
|
97,952 |
|
|
Training platform |
|
54,599 |
|
33,464 |
|
|
Withholding tax related to distributable earnings |
|
|
|
22,620,872 |
|
|
Total gross deferred income tax liabilities |
|
168,801 |
|
22,752,288 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net deferred income tax assets |
|
3,687,804 |
|
3,388,760 |
|
|
Net deferred income tax liabilities |
|
|
|
22,620,872 |
|
The movements of the valuation allowance are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at the beginning of the year |
|
2,575,187 |
|
3,882,555 |
|
20,028,588 |
|
|
Additions |
|
1,307,368 |
|
16,146,033 |
|
21,150,760 |
|
|
Balance at the end of the year |
|
3,882,555 |
|
20,028,588 |
|
41,179,348 |
|
As of March 31, 2017, the valuation allowance of RMB 41,179,348 was related to the deferred income tax assets of PRC entities which were in loss position. As of March 31, 2017, management believes it is more likely than not that the Group will realize the deferred income tax assets, net of the valuation allowance. The amount of the deferred income tax assets, however, considered realizable as of March 31, 2017 could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future taxable income are reduced.
As of March 31, 2017, the Group had tax loss carry forwards for PRC income tax purpose of RMB 120,772,769 of which RMB 4,996,057, RMB 5,438,101, RMB 41,458,162, RMB 43,372,847 and RMB 25,507,602 will expire if unused by December 31, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021 and 2022, respectively.
For the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, the Group had no unrecognized tax benefits, and thus no related interest and penalties were recorded. Also, the Group does not expect that the amount of unrecognized tax benefits will significantly increase within the next twelve months.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
According to the PRC Tax Administration and Collection Law, the statute of limitation is three years if the underpayment of taxes is due to computational errors made by the taxpayer or the withholding agent. The statute of limitation is extended to five years under special circumstances where the underpayment of taxes is more than RMB 100,000. In the case of transfer pricing issues, the statute of limitation is ten years. There is no statute of limitation in the case of tax evasion. The income tax return of each of the Companys PRC consolidated entities is subject to examination by the relevant tax authorities for the calendar tax years beginning in 2012.
(13) SHARE BASED COMPENSATION
2005 Share incentive plan
In April 2005, the Company adopted a share incentive plan (the 2005 Plan), pursuant to which the Company is authorized to issue options to officers, employees, directors and consultants of the Group to purchase up to 2,894,000 of its common shares. In October 2007, the Companys board of directors approved an increase in the number of shares reserved for issuance under the 2005 Plan to 3,310,300 shares. The 2005 Plan expired in April 2015. Options awards provide for accelerated vesting if there is a change in control (as defined in the 2005 Plan).
2008 Share incentive plan
On January 7, 2008, the Company adopted a share incentive plan (the 2008 Plan), pursuant to which the Company is authorized to issue options and other share-based awards to officers, employees, directors and consultants of the Group to purchase up to 336,307 of its common shares, plus, unless the board of directors determines a lesser amount, an annual increase on January 1 of each calendar year beginning in 2009 equal to the lesser of 1) one percent of the number of shares issued and outstanding on December 31 of the immediately preceding calendar year, and 2) 336,307 shares (the replenish terms). The 2008 Plan expires in ten years. Options awards provide for accelerated vesting if there is a change in control (as defined in the 2008 Plan). On December 30, 2016, the Company amended the 2008 Plan to increase the number of Common Shares of the Company reserved for issuance to 5,726,763 shares and extend the plan together with the replenish terms for ten years from December 30, 2016. As of March 31, 2017, 6,063,070 shares were reserved for issuance under the 2008 Plan.
Under both the 2005 Plan and 2008 Plan, share options are generally granted with 25% vesting on the first anniversary of the grant date and the remaining 75% vesting ratably over the following 36 months, unless a shorter or longer duration is established at the time of the option grant. Share options are granted at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Companys share at the date of grant and expire 10 years from the grant date.
Under the 2008 Plan, non-vested shares are granted with a graded vesting as to 25% at the end of each year from the grant date over 4 years.
For the graded vesting share options and non-vested shares, the Company recognizes the compensation cost over the requisite service period for each separately vesting portion of the award as if the award is, in substance, multiple awards.
In October 2013, 1,469,460 share options were granted to an officer, 25% of the options vest on the first anniversary of the grant date with the remaining 75% vesting evenly over the following three years. The exercise price of these options is USD2.50 per common share. In October 2014, the remaining 75% share options were forfeited upon the officers resignation. The expense of RMB 4,014,513 related to the unvested share options recognized previously was reversed.
In February 2015, 1,469,460 share options were granted to an officer, 25% of the options vest on the first anniversary of the grant date with the remaining 75% vest evenly over the following three years. The exercise price of these options is USD2.24 per common share.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
In February 2015, 100,000 and 114,314 common shares of the Company were granted to two officers respectively, using the Companys treasury shares. These common shares were immediately vested on grant date. The fair value of the common shares on the grant date of RMB 2,831,396 was recognized as general and administrative expense for the year ended March 31, 2015. The difference between the cost of the treasury shares repurchased of RMB 2,983,072 and the fair value of the common shares on grant date of RMB 151,676 was recognized as a reduction of additional paid-in capital.
In April 2015, the Company extended the exercise period of vested share options of certain employees for an additional six months. The modification resulted in additional compensation expense of RMB 1,635,726 for the year ended March 31, 2016. All of these share options were expired without any exercise as of March 31, 2016.
In January 2017, 2,700,000 non-vested shares were granted to Companys employees and officers with a graded vesting as to 25% at the end of each year from the grant date over 4 years and 900,000 share options were granted to Companys employees and officers, 25% of the options vest on the first anniversary of the grant date with the remaining 75% vesting evenly over the following 36 months. The exercise price of these options is USD 1.705 per common share.
A summary of the shares options activities for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 is presented below:
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
Weighted |
|
Aggregate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
average |
|
remaining |
|
intrinsic |
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
exercise |
|
contractual |
|
value |
|
|
|
|
shares |
|
USD |
|
years |
|
USD |
|
|
Outstanding as of March 31, 2014 |
|
4,214,667 |
|
2.72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
1,469,460 |
|
2.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
(300,000 |
) |
2.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
(1,102,095 |
) |
2.50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expired |
|
(396,365 |
) |
2.58 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding as of March 31, 2015 |
|
3,885,667 |
|
2.66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expired |
|
(1,981,600 |
) |
2.72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding as of March 31, 2016 |
|
1,904,067 |
|
2.61 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
900,000 |
|
1.71 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
(100,000 |
) |
1.71 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expired |
|
(253,000 |
) |
3.60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding as of March 31, 2017 |
|
2,451,067 |
|
2.21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vested and expected to vest as of March 31, 2017 |
|
2,451,067 |
|
2.21 |
|
7.96 |
|
156,000 |
|
|
Exercisable as of March 31, 2017 |
|
916,337 |
|
2.63 |
|
6.45 |
|
|
|
The aggregate intrinsic value of options outstanding and exercisable at March 31, 2017, was determined based on the closing price of the Companys common shares on March 31, 2017.
The total intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended March 31, 2016 and 2017 was nil and nil respectively.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Information relating to options outstanding and exercisable as of March 31, 2017 is as follows:
|
Options outstanding as of March 31, 2017 |
|
Options exercisable as of March 31, 2017 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
Exercise |
|
Remaining |
|
|
|
Exercise |
|
Remaining |
|
|
Number of |
|
Price |
|
Contractual |
|
Number |
|
Price |
|
Contractual |
|
|
Shares |
|
per Share |
|
Life |
|
of Shares |
|
per Share |
|
Life |
|
|
|
|
USD |
|
Years |
|
|
|
USD |
|
Years |
|
|
74,000 |
|
3.60 |
|
0.50 |
|
74,000 |
|
3.60 |
|
0.50 |
|
|
100,000 |
|
4.75 |
|
0.83 |
|
100,000 |
|
4.75 |
|
0.83 |
|
|
7,607 |
|
2.69 |
|
1.91 |
|
7,607 |
|
2.69 |
|
1.91 |
|
|
1,469,460 |
|
2.24 |
|
7.86 |
|
734,730 |
|
2.24 |
|
7.86 |
|
|
800,000 |
|
1.71 |
|
9.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,451,067 |
|
2.21 |
|
7.96 |
|
916,337 |
|
2.63 |
|
6.45 |
|
The Company calculated the fair value of the share options on the grant or the modification date, for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, using the Black-Scholes-Merton pricing valuation model. The assumptions used in the valuation model are summarized as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
0% |
|
0% |
|
0% |
|
|
Expected volatility |
|
71% |
|
50% |
|
63% |
|
|
Expected term |
|
6.25 |
|
0.25 |
|
6.08 |
|
|
Risk-free interest rate (per annum) |
|
1.70% |
|
0.72% |
|
1.98% |
|
The expected volatility was based on the historical volatilities of the Company. The expected term was related to the period of time the options are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate for periods within the contractual life of the option is based on the United States treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant or modification.
Compensation expense for share options of RMB 984,595, RMB 8,040,512 and RMB 4,079,082 was recognized for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017.
As of March 31, 2017, RMB 7,429,354 of total unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested share options is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 3.1 years.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Non-vested shares
A summary of the non-vested shares activities for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 is presented below:
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
Number |
|
grant date |
|
|
|
|
of shares |
|
fair value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
USD |
|
|
Outstanding at March 31, 2014 |
|
810,000 |
|
3.989 |
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vested |
|
(335,000 |
) |
4.380 |
|
|
Forfeited |
|
(30,000 |
) |
2.145 |
|
|
Outstanding at March 31, 2015 |
|
445,000 |
|
3.819 |
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vested |
|
(325,000 |
) |
4.437 |
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at March 31, 2016 |
|
120,000 |
|
2.145 |
|
|
Granted |
|
2,700,000 |
|
1.650 |
|
|
Vested |
|
(60,000 |
) |
2.145 |
|
|
Forfeited |
|
(60,000 |
) |
1.650 |
|
|
Outstanding at March 31, 2017 |
|
2,700,000 |
|
1.661 |
|
The total fair value of shares vested during the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, was USD 821,250, USD 831,375 and USD 157,176 respectively.
Upon the vesting of the non-vested shares, the Company withholds the shares issued to the employees to meet the relevant minimum tax withholding requirements. For the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, the Company withheld 54,000, 51,234 and 11,624 vested shares upon the vesting of the non-vested shares to satisfactory the minimum tax withholding obligation compensation expense recognized for non-vested shares for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 is allocated to the following expense items:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Cost of revenues |
|
164,741 |
|
90,002 |
|
455,115 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
179,186 |
|
75,834 |
|
495,440 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
295,519 |
|
150,420 |
|
525,542 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
5,487,275 |
|
808,054 |
|
1,403,224 |
|
|
Total share based compensation expense |
|
6,126,721 |
|
1,124,310 |
|
2,879,321 |
|
As of March 31, 2017, RMB 27,417,420 of total unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested shares is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 3.8 years.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(14) COMMON SHARES
The Companys board of directors approved a share repurchase program on November 1, 2012 to repurchase up to USD 5.0 million worth of its issued and outstanding American Depository Shares (ADS) in both open-market and privately negotiated transactions. On January 31, 2013, the Companys board of director reviewed and approved the continuation of the share repurchase program through May 31, 2013. The Companys board of directors approved a share repurchase program on August 5, 2014 to repurchase up to USD 5.0 million worth of its issued and outstanding ADSs in open-market through January 31, 2015. The Companys board of directors approved a share repurchase program on September 24, 2015 to repurchase up to USD 3.0 million worth of its issued and outstanding ADSs in open-market through March 31, 2016. For the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, the Company repurchased 612,314, 1,134,264 and nil common shares at a repurchase price of RMB 8,362,136, RMB 19,536,028 and RMB nil, respectively.
(15) CASH DIVIDENDS
On May 30, 2014, the Companys board of directors declared a special cash dividend of USD 0.205 per common share, or USD 0.41 per ADS. The total amount of dividend was USD 9.5 million (RMB 58,349,122) and was paid in cash in July 2014.
(16) STATUTORY RESERVES
In accordance with the relevant laws and regulations of the PRC, the Companys PRC consolidated entities are required to transfer 10% of their respective after tax profit, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations to a general reserve fund until the balance of the fund reaches 50% of the registered capital of the respective entity. The transfer to this general reserve fund must be made before distribution of dividends can be made. As of March 31, 2016 and 2017, the PRC consolidated entities had appropriated RMB 36,431,792 and RMB 55,164,065, respectively, to the general reserve fund, which is restricted for distribution to the Company.
(17) RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
(a) Receivable due from shareholder
In May 2015, the Group terminated the VIE agreements with the nominee shareholders. The entire equity interests of ATA Online were transferred from the nominee shareholders to ATA Learning and Zhongxiao Zhixing for a consideration of RMB 10.0 million, equaling to the amount of the registered capital of ATA Online. As a result, ATA Online became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Group. The consideration was paid to the nominee shareholders. Mr. Haichang Xiong, has transferred his consideration of RMB 1.0 million to Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng Ma on March 29, 2016. The Group received RMB 10.0 million in cash from Mr. Kevin Xiaofeng on June 7, 2017.
(b) Sublease of Jianwai SOHO office to Master Mind
ATA Testing subleased its Jianwai SOHO office to Master Mind, an equity method accounted investee, for a monthly rent of RMB 54,678, from May 17, 2015 to May 16, 2020. The Group recognized the sublease income of RMB 575,483 and RMB 650,478 for the years ended March 31, 2016 and 2017. ATA Testing received advanced rental fee of RMB nil and RMB 103,655 as of March 31, 2016 and 2017 respectively, and recorded the amount in deferred revenues.
ATA Testing received a rent deposit of RMB 115,097 from Master Mind for the sublease and recorded the amount in accrued expenses and other payables as of March 31, 2016 and 2017.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(c) Acquisition of Puhua Technology
On August 31, 2016, ATA Online entered into an agreement to make a 60% equity investment in Puhua Technology with a total cash consideration of RMB 2.0 million. The director of Puhua Technology was a director of ATA learning, who resigned from ATA learning in July 2016. Please refer to Note (21).
(18) COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
(a) Lease commitments
The Group entered into non-cancelable operating leases, primarily for office space, for initial terms of 12 to 58 months.
Minimum rent payments under operating leases are recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease, including any periods of free rent.
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases (with initial or remaining lease terms in excess of one year) as of March 31, 2017 are:
|
|
|
Minimum |
|
|
|
|
Lease Payments |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Year ended March 31: |
|
|
|
|
2018 |
|
14,078,048 |
|
|
2019 |
|
11,194,606 |
|
|
2020 |
|
11,056,698 |
|
|
2021 |
|
1,409,891 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
37,739,243 |
|
Rental expense for operating leases (except leases with a term of one month or less that are not renewed) for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 were RMB 14,096,009, RMB 12,803,338 and RMB 13,206,748 respectively.
(b) Purchase commitments
On August, 11, 2011, the Group entered into an agreement with a vender granting the Group a license to distribute the vendors test related products in Mainland China for 10 years. Each party may terminate this agreement at any time for any reason by giving the other party not less than twelve months written notice subject only that the earliest termination date may not be before the fifth anniversary of this agreement unless either party is in breach of this agreement. The future minimum payments under the non-cancelable purchase agreement as of March 31, 2017 are:
|
|
|
Required Payments |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Year ended March 31: |
|
|
|
|
2018 |
|
4,838,400 |
|
|
2019 |
|
1,296,000 |
|
|
|
|
6,134,400 |
|
License fee for the non-cancelable purchase agreement for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017 were RMB 2,282,288, RMB 2,642,777 and RMB 3,485,967 respectively.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(19) OPERATING LEASES
Minimum rental income under operating lease is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease, including any periods of free rent.
Property on Operating Lease
|
|
|
March 31, 2016 |
|
March 31, 2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Building |
|
53,049,213 |
|
53,049,213 |
|
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation |
|
(12,030,383 |
) |
(13,812,837 |
) |
|
|
|
41,018,830 |
|
39,236,376 |
|
Rentals under Operating Lease
Future minimum rental income under non-cancelable operating lease as of March 31, 2017 are:
|
|
|
Minimum |
|
|
|
|
Rentals Amount |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Year ended March 31: |
|
|
|
|
2018 |
|
4,816,386 |
|
|
2019 |
|
4,170,397 |
|
|
2020 |
|
4,056,594 |
|
|
2021 |
|
95,821 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13,139,198 |
|
(20) EARNINGS (LOSS) PER COMMON SHARE
Basic and diluted earnings (loss) per common share are calculated as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
|
Numerator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net earnings (loss) |
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,716,002 |
) |
|
Less: Dividends paid to participating securities |
|
(693,728 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Net earnings (loss) attributable to participating securities |
|
|
|
(130,924 |
) |
|
|
|
Net earnings (loss) available to common shareholders |
|
22,361,992 |
|
25,920,263 |
|
(9,716,002 |
) |
|
Denominator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Denominator for basic earnings (loss) per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
45,597,580 |
|
45,635,186 |
|
45,772,916 |
|
|
Plus: Incremental shares issuable upon exercise of share options |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Denominator for diluted earnings (loss) per share |
|
45,597,580 |
|
45,635,186 |
|
45,772,916 |
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) per common share |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
|
0.49 |
|
0.57 |
|
(0.21 |
) |
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The following table summarizes potential common shares outstanding excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings (loss) per share for the years ended March 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, because their effect is anti-dilutive:
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
Shares issuable under share options |
|
3,885,667 |
|
1,904,067 |
|
2,451,067 |
|
(21) ACQUISITION
On September 12, 2016, the Group acquired 60% equity interest in Puhua Technology by injection of RMB 2.0 million in cash. Puhua Technology is primarily engaged in technology development and online education consulting business. As of March 31, 2017, RMB 2.0 million has been fully paid to Puhua Technology. This acquisition was accounted for under the acquisition method and resulted in Puhua Technology becoming a consolidated subsidiary of the Group.
The acquired business contributed net revenue of RMB 71,349 and net loss of RMB 633,513 to the Group for the period from September 12, 2016 to March 31, 2017.
The following table summarizes the consideration paid to acquire Puhua Technology and the amount of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the acquisition date:
|
|
|
As of September 12, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Fair value of consideration transferred: |
|
|
|
|
Cash paid |
|
2,000,000 |
|
|
Fair value of non-controlling interests |
|
1,333,333 |
|
|
Fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed: |
|
|
|
|
Cash |
|
2,411,583 |
|
|
Other receivables and prepayments |
|
746,009 |
|
|
Other non-current assets |
|
16,848 |
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
3,174,440 |
|
|
Other liabilities |
|
(1,353,188 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amount of identifiable net assets |
|
1,821,252 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
1,512,081 |
|
The goodwill represents the workforce of the acquired business and synergies expected to arise after the Groups acquisition of Puhua Technology and expanding the product offering of testing services. All of the goodwill was assigned to the enterprise level.
(22) SUBSEQUENT EVENT
On June 1, 2017, the Company declared a cash dividend of USD 0.205 per common share, or USD 0.41 per ADS. The total amount of cash distributed was approximately USD 10.0 million and will be paid to all shareholders of record as of the close of business on June 12, 2017.
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(23) ATA INC. (Parent Company)
The following presents condensed financial information of the Parent Company only.
Condensed Balance Sheets
|
|
|
March 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
Cash |
|
2,931,353 |
|
505,082 |
|
73,379 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
197,252 |
|
210,100 |
|
30,524 |
|
|
Investments in subsidiaries |
|
392,077,013 |
|
392,224,481 |
|
56,982,868 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
395,205,618 |
|
392,939,663 |
|
57,086,771 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
|
975,030 |
|
1,562,363 |
|
226,982 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
975,030 |
|
1,562,363 |
|
226,982 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common shares |
|
3,530,704 |
|
3,533,912 |
|
513,411 |
|
|
Treasury shares |
|
(27,737,073 |
) |
(27,737,073 |
) |
(4,029,677 |
) |
|
Additional paid in capital |
|
395,876,282 |
|
402,631,430 |
|
58,494,803 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
(25,174,129 |
) |
(25,069,771 |
) |
(3,642,168 |
) |
|
Retained earnings |
|
47,734,804 |
|
38,018,802 |
|
5,523,420 |
|
|
Total shareholders equity |
|
394,230,588 |
|
391,377,300 |
|
56,859,789 |
|
|
Total liabilities and shareholders equity |
|
395,205,618 |
|
392,939,663 |
|
57,086,771 |
|
Condensed Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses |
|
(4,612,306 |
) |
(4,292,082 |
) |
(3,818,608 |
) |
(554,773 |
) |
|
Investment income (loss) |
|
27,609,211 |
|
30,476,370 |
|
(6,587,058 |
) |
(956,976 |
) |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
|
|
|
(75,918 |
) |
(11,029 |
) |
|
Interest income |
|
144,869 |
|
79,847 |
|
568,503 |
|
82,593 |
|
|
Foreign currency exchange gains (losses), net |
|
(86,054 |
) |
(212,948 |
) |
197,079 |
|
28,632 |
|
|
Earnings before income taxes |
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,716,002 |
) |
(1,411,553 |
) |
|
Income tax expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
23,055,720 |
|
26,051,187 |
|
(9,716,002 |
) |
(1,411,553 |
) |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
(30,753 |
) |
2,002,553 |
|
104,358 |
|
15,161 |
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
23,024,967 |
|
28,053,740 |
|
(9,611,644 |
) |
(1,396,392 |
) |
ATA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
|
|
|
Year Ended March 31, |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
RMB |
|
USD |
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
(4,304,976 |
) |
(3,150,707 |
) |
(2,858,989 |
) |
(415,358 |
) |
|
Cash flows from investing activities : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Collection from subsidiaries: |
|
7,670,574 |
|
17,406,546 |
|
400,783 |
|
58,226 |
|
|
Net cash provided by investing activities |
|
7,670,574 |
|
17,406,546 |
|
400,783 |
|
58,226 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for repurchase of common shares |
|
(8,362,136 |
) |
(19,536,028 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from exercise of share options |
|
3,903,952 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
(4,458,184 |
) |
(19,536,028 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash |
|
(30,753 |
) |
7,443 |
|
31,935 |
|
4,640 |
|
|
Net decrease in cash |
|
(1,123,339 |
) |
(5,272,746 |
) |
(2,426,271 |
) |
(352,492 |
) |
|
Cash at beginning of year |
|
9,327,438 |
|
8,204,099 |
|
2,931,353 |
|
425,871 |
|
|
Cash at end of year |
|
8,204,099 |
|
2,931,353 |
|
505,082 |
|
73,379 |
|